
As a worldwide supplier in the global vehicle industry, Kongsberg Automotive needed to transform its treasury function.

In a short period, the company took several steps in maturing its treasury, so successfully that it received an Adam Smith Award. How did Kongsberg Automotive manage to achieve this?
Since the late 1950’s, Kongsberg Automotive has developed from a Scandinavian automotive parts supplier to a global leader in one of the most competitive and complex industries in the world. With more than 11,000 employees in 19 countries worldwide (European countries, USA, Canada, Mexico, South Korea, India and China), the company provides high-quality products to the global vehicle industry, such as custom powertrain and chassis solutions, interior comfort systems, cables and actuators for passenger cars.
When Abraham Geldenhuys joined Kongsberg Automotive as Group Treasurer in October 2017, the company’s treasury function needed further development. “At that time our treasury department was very administrative of nature,” he says. “It is key for treasurers and CFOs to know their company’s cash balance. That was partly not at our disposal. There was a clear need for a treasury transformation, with better cash visibility, cash flow forecasting and control over payments and liquidity. Due to our global activities, these things were hard to combine and tough to control – they needed to be centralized.”
At that time our treasury department was very administrative of nature. It is key for treasurers and CFOs to know their company’s cash balance. That was partly not at our disposal.
Abraham Geldenhuys, Group Treasurer
Challenge
Road map
Kongsberg Automotive’s treasury therefore started a journey to become more mature. Geldenhuys: “During the 2017 EuroFinance Conference, I met some Zanders people. The conference was full of buzzwords like blockchain, machine learning and RPA. We were talking about all these new technologies but most of us still have a lot to innovate in that area. It was clear that, like many companies, we need to get rid of repetitive, Excel-based ways of doing treasury. It was time to clearly define and then centralize, standardize and automate treasury processes. Technology is evidently the enabler to bring all this together. You can’t be strategic when your house is not in order.”
Shortly after joining Kongsberg Automotive, Geldenhuys formulated a three-year strategic Treasury Transformation roadmap to determine where the treasury was today and where it wanted to be tomorrow. “In our roadmap I described the vision, function, building blocks of treasury, a road map time line and existing risks,” he explains. “In January 2018, I presented this roadmap to our CFO. We agreed that cash visibility was key and that we needed daily cash reports to be able to make the right decisions. The roadmap also included refinancing the group. We needed to ensure our capital structure and financing was in order and finally decided to refinance by issuing a corporate bond. The transaction was done in a very short space of time. Timing was critical and the transaction were concluded in July 2018. We then really started our journey, together with Zanders, to achieve centralization, standardization and optimization of our treasury activities.”
Solution
Pricing tool
Two main steps in the treasury transformation journey were a complete bank reorganization and the implementation of a new treasury management system (TMS). “In May 2018, we completed the solution design and a blueprint for our Treasury Transformation and after presenting our business case, I got final approval in early November 2018,” Geldenhuys says. “I was challenged to have the new structure up and running by June 2019. With this very short timeline the big challenge was without a doubt: will we be able to go live in June? We effectively officially kicked off in mid-November 2018 with our selected TMS partner and in January 2019 with our new selected corporate banking partners.”
Kongsberg Automotive’s treasury also needed a solution to leverage technology for arm’s length transfer pricing of financial transactions. Geldenhuys: “If you have a global zero balance cash pool and intercompany loans, the pricing needs to be in order and set. The focus on these intercompany transactions has increased in the past couple of years. With the current focus of tax authorities globally, we need to make sure that we are ahead of the curve. So, we shared our thoughts with Zanders and the idea was to have a full-proof, state-of-the-art pricing to meet all requirements. Their solution was a Transfer Pricing Solution. With a new Intercompany Rating & Pricing (ICRP) tool we were able to price our cash pool and our intercompany loans.”
Packaged and presented
Next to bank reorganization, the implementation of a new TMS and the ICRP tool, the company took it a step further to enhance and standardize cash application. Geldenhuys explains: “Redesigning this process, we went from having people manually print out all bank statements and manually booking all to pushing these statements to the ERP environment and achieving automated reconciliation to a larger extent. We’ve made great strides. Together with the cash pool and the TMS we also implemented an in-house bank. One of the big achievements of this project was that we – the central treasury team – are now releasing the majority of Kongsberg Automotive’s payment traffic after validating these payments against the global liquidity and currency positions and planning. Soon, in addition to this, we will further streamline our payment traffic by going live with Payments on behalf of (POBO).”
The next question was how to put these massive changes to the organization. “The biggest challenge is bringing the people with you on the journey,” says Geldenhuys. “The coaching, teaching and showing was a daily job. All of the new tools had to be packaged and presented within the organization – the users of these tools. And we managed to do so through new technologies – again the enabler.”
In terms of cash visibility and liquidity planning, the treasury organization is now able and equipped to effectively manage the cash needs of the group. “All these things were previously done in Excel, but now completely captured in the TMS,” Geldenhuys adds. “We make sure to utilize as much functionality in our new TMS as possible. We really have a one-stop solution for all treasury activities.”
We’ve made great strides. Together with the cash pool and the TMS we also implemented an in-house bank.
Abraham Geldenhuys, Group Treasurer
Performance
Extensive Journey
The new TMS went live in June 2019. “Keeping the timeline in mind this was an immensely intense period,” says Geldenhuys. “Two things were absolutely key. Support from our in-house project management function and the role of our consultants as a reliable, trusted partner. From the blue print stage to the system selection and bank reorganization, to a tool that can do the pricing of your cash pool and intercompany loans. That journey has been an extensive one; Accounting, Legal, Tax (Transfer pricing), Change Management, Implementation teams and Technical teams on banking and payments were involved – apart from the dreaded KYC procedures that accompany a bank reorganization. So, all in all implementing completely new features and solutions to treasury – all to be able to say that the foundation has been laid. It’s been an intense journey containing a lot of details, a journey that could not have been taken on by ourselves.”
One of the final steps to take, and quite a tedious one according to Geldenhuys, is the transition from the old to the new banking environment, so ensuring that customers pay to the new accounts. “But when you get to the point where we are now, focusing on closing legacy bank accounts, it’s rewarding to see that the entire picture and plan has come together and is starting to lean towards a real transformation.”
A good foundation
Doing a treasury transformation – implementing a new global cash pool, a new system and really centralizing payments – takes a lot of effort and commitment, Geldenhuys emphasizes. “But it’s worth it, absolutely! It’s been a tremendous journey, from the start to where we are right now. It is important that your C-suite believes in it and that it delivers its fruits – a project of this scale needs to be justified. Although technology is the key to standardize, centralize, automate and combine all treasury activities, processdesign and effectiveness still ranks at the top of my treasury foundation, and it’s exactly here where I believe in leveraging the technology to ensure that we have a real treasury function. It is process married with technology.”
Zanders was part of this project in six different areas, according to Geldenhuys: group advisory, system selection, bank reorganization and negotiation, change management and operational support. “Also, they did a lot of sound boarding. We went from nothing to today having daily bank statement reporting, full control over our payments and much more details around this. That is probably the most important part: if the foundation of your house is not solid, forget about the rest.”

Sulzer was looking for a cloud platform to collect its market data. The Swiss company decided to use Zanders’ market data platform to bridge the source systems and target systems.

The new data system now takes care of the storage, conversion and application of data needed for treasury, to determine the rates for its loans, forwards or swaps.
Sulzer is a Swiss industrial engineering and manufacturing firm that specializes in pumping solutions and offers services for rotating equipment and technology for separation, mixing and application. The company, established in 1834 as Sulzer Brothers, now has a network of over 180 production and service sites in around 50 countries around the world.
“As a company we have concentrated our activities and divided these into four divisions,” says Alexander Sika, senior treasury manager at Sulzer. “There are four of these divisions and they are quite diverse. One produces centrifugal pumps and mixers for a broad range of industries. The second one offers services and repair solutions for rotating equipment such as turbines, pumps, compressors, motors and generators. The third division is called Chemtech and offers components and services for separation columns and static mixing. And the fourth, a relatively new division, delivers mixing and dispensing systems for liquid applications, for healthcare markets, amongst others. So, it’s all very diverse from a treasury perspective.”
We wanted an automated, more secure and stable framework for our financial data.
Alexander Sika, Senior Treasury Manager
Challenge
The perfect edge
Sulzer aimed for a unified ERP to support all its data-driven processes. “It was required to have rate visibility and to automate our treasury,” explains Sika. “To improve the rate visibility and automate our treasury we started to look for partners. We have been teaming up with Zanders since 2008, so we knew what they could deliver. They could implement the middleware, bridging the operating system to the database and applications. First it was a manual process, so we wanted an automated, more secure and stable framework for our financial data – that was rather important for our treasury activities.”
Once the system was implemented, the organization needed to take the next step: a solution to collect market rate data. Within our network we heard about Brisken as an approved designer and developer of rate apps.
“We saw a demo from Brisken and they offered exactly what we wanted,” Sika says. “Flexible and web-based, without the requirement to code, independent maintenance and up- or download of rates without from internal or external help. Zanders wanted to team up with Brisken, so it came out that Zanders could offer us the software that we would have chosen anyways. It was the perfect edge for us.”
Solution
How to share the data
Market data often is retrieved from external sources, so an interface needs to be built and maintained. Then, these raw data cannot be used directly in applications and needs transformation into the right formats. Sika selected Bloomberg to provide all market data. “The data we need is interest rates, FX rates and VOLA rates,” he explains. “A data provider like Bloomberg can supply us with these data. We have been partners of Bloomberg since many years and as we are used to the terminals, we decided to go for the Data License as well. Best price, easiest logic and one partner for market data were the factors that made the decision.”
First, Sulzer checked with Bloomberg how to share the data and to discuss how it would be visualized. “That’s when we reached out to Zanders and Brisken to set up the strategy; this is what we want, and this is how we’ll set it up,” notes Sika. “We rolled out the project plan and coordinated between Bloomberg, Zanders and ourselves to set up the cloud and its users. It was a rather hands-on approach in which we designed our needs; what data do we need, when do we need it, how should it be checked and when should it be sent to whom? The timeline was pushed a little, but that was no problem. In October, we did the final tests to see whether all data was activated well and integrated with our treasury management system (TMS) IT2 and other system elements. These tests were all successful, so we then implemented the Zanders Market Data Platform, went live and completed our first month-end process in November.”
It was a rather hands-on approach in which we designed our needs.
Alexander Sika, Senior Treasury Manager
Performance
System independency
The data from Bloomberg can now be collected from the cloud platform that was designed and developed by Brisken. “As we were building our partnership with Zanders, it was a great opportunity to become part of this,” says Dirk Neumann, executive director at Brisken. “It’s good to hear that all features of the portal and the needs for the customer are identical. Zanders has shown to be very good at sourcing and managing data and to bring it into place with this system. They offered the flexibility; the market data pool is always well managed. There may be other parts in the organization that can benefit from this too. And with the system it can grow further into the future.”
On behalf of Zanders, Joanne Koopman joined the project in early 2019 to support on the system tests and choices. Then the set ups took place to give an impression of the data flows via the new platform.
“We needed specific data from Bloomberg, which formed a very technical part of the project,” says Sika. “Zanders arranged the data on the platform. In August, Zanders started training sessions to show us the new system and all possible data flows on the new platform.”
The aim of the training was to increase the system independency, Koopman explains: “When the company wants to make any changes, it should be able to deal with them itself. But advice is, of course, always available if needed.”
SAP integration
So, what are the next steps? “So far we have loaded the rates into the system, making them ready to be sent to target systems,” says Sika. “We receive all data daily via the cloud platform, which works on a very stable process. During the last six years, we have strengthened our treasury strategy and systems, working towards the basic goals of providing the service that we should provide as a treasury department. First, we didn’t have a real treasury roadmap, now we have one and we are thinking about making a new one. We now want to extend what we have been doing already, with a new system, new functions for a broader user base. We plan another update of our IT2 TMS – we expect to enhance our system in terms of function and user accessibility. As an organization, we were early in developing our treasury. But now, in terms of technical level and straight-through processing (STP), we have quite some more treasury ambitions.”

Over the past 15 years, the 240-year-old Japanese multinational pharmaceutical company Takeda has made a number of key acquisitions which have positioned them as a leader in the global patient-focused market.

To standardize banking connectivity worldwide, record all financial instruments and increase cash visibility, Takeda implemented Kyriba Treasury as its TMS back in 2019. Subsequent to this initial implementation, a second phase of the project – to implement the Payments module of the TMS – was embarked upon in 2022. For this, Takeda enlisted the help of Zanders.
Takeda has a long history, dating back to 1781 when its founder Chobei Takeda I began selling traditional Japanese and Chinese herbal medicines in Osaka’s medicine district, Doshomachi. He quickly gained a reputation for business integrity and quality products and services, values that have continued through the years and are now integral to Takeda’s corporate philosophy.
Today, Takeda is a patient-focused, values-driven biopharmaceutical company committed to improving the lives of patients worldwide. The company has six key product areas: Oncology, Rare diseases, Neuroscience, Gastroenterology, Plasma-derived therapies, and Vaccines. With approximately 48,000 employees across 80 different countries, Takeda operates in Japan, the USA, Europe & Canada (EUCAN), and Growth and Emerging Markets (GEM). These four regions are responsible for providing access to Takeda’s entire portfolio in the countries where it operates. In terms of revenue split, half of the revenue comes from the US market, 21% from EUCAN, 18% from Japan, and 12% from GEM.
“Our company is values-based,” explains Fiona Foley, VP and Assistant Treasurer, Treasury Operations at Takeda. “We are guided by the principles of what we call Takeda-ism, which incorporates four tenets: integrity, fairness, honesty, and perseverance. These values are brought to life through our actions which are based on patient, trust, reputation, and business – in that order.”
The project was a combination of various specialties, including treasury, IT, languages, and process and cultural alignment.
Fiona Foley, VP and Assistant Treasurer
Challenge
Integrating treasuries
In January 2019, Takeda acquired Shire PLC, a UK-founded and Irish-based pharmaceutical company specializing in rare diseases. With the earlier acquisition of Swiss pharmaceutical company Nycomed in 2011, Takeda now has three treasury centers located in Tokyo, Zurich, and Dublin.
Foley explains that they have a three-pillar treasury approach. “The first pillar is the Treasury Operations team which looks after all the day-to-day cash management, intercompany liquidity, pooling, cash centralization, and cash forecasting. The Financial Risk management pillar is responsible for all financial risks, such as FX, interest rate, credit and counterparty risks, and also manages trade finance and bank guarantees. Finally, the Capital Markets pillar is responsible for new sources of funding and managing the company’s significant debt portfolio.”
Before the merger, Takeda and Shire were very different companies in terms of operational culture and functional structures. Foley notes that both companies had different degrees of centralization. “Shire was much more centralized in terms of its Treasury, while Takeda was more decentralized. As a combined company there were many fragmented and non-integrated data sources for treasury, particularly in the areas of bank accounts and cash visibility, leading to poor forecast accuracy. Furthermore, there were numerous banking connectivity routes, different electronic banking systems, and a large number of applications.”
Neither company used a TMS for day-to-day cash management, and the TMS systems that were in place hadn’t been updated in quite some time and were only used for recording a specific set of financial instruments. The newly formed treasury team recognized the need to address these issues and began preparing a request for proposal (RFP) for a new TMS. Foley: “We wanted to move away from an overreliance on Excel for cash positioning, forecasting and reporting which exposed us to the risk of input error and manipulation of data by different users.”
Given the company’s size and the complexity of the challenges they were facing, they needed a TMS that was adaptable, met their requirements, and future-proofed them for integrated activity. As a result, Takeda implemented Kyriba Treasury, including the Payments module, to standardize banking connectivity globally, increase cash visibility, and centralize its payments. Zanders was asked to help with the Payments implementation which followed after all other modules.
Solution
Creating visibility
Takeda’s implementation of Kyriba Treasury was done in a modular manner, with the first phase focusing on banking and cash management to create visibility. Kyriba was able to gather bank statements, enabling the company to manage their cash on a day-to-day basis. The subsequent modules involved integrating investments, risk management (FX, interest rate and counterparty risk), and managing debt portfolio and capital market activity. Payments settlement was not included in the initial implementation scope.
To address this as part of a second project phase, Takeda moved into the lifecycle of the Payments module, explains Meliosa O’Byrne, Associate Director Treasury Operations at Takeda. “We recognized the need to standardize and harmonize payments for all the banks. We faced challenges due to the lack of connectivity and the absence of a standard approval process in place. To address these issues, we decided to use Kyriba and organized a workshop with the Zanders team to gain better understanding. This was followed by a phased approach to implement the Payments module with seven key global core cash management banks.”
Specific challenges per phase
The first phase started with Deutsche Bank – the primary bank in Europe – as pilot. The focus was to understand the Payment module in Kyriba, processes, and flows. O’Byrne: “A key decision factor to start with Deutsche bank was that our hedging program was migrating to our Treasury entity in Zurich and the volume of payments to support this being the most significant Treasury flows each month.”
Phase two involved Citibank, which covered all Takeda regions (EUCAN, Japan, USA) and Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC) which was Japan-centric. During this phase, training sessions were provided by Zanders in local language for the Japanese users, which was key element to the success of the project. The EUCAN team was already trained during phase one.
O’Byrne explains: “We started from Europe and then engaged Japan team for phase two. They were working with our back office team to make sure we continued the standardization and harmonization approach identified for Deutsche Bank. SMBC is one of the main banks for Japan and Zanders’ Katsuo Sekikawa became part of the team that managed the implementation from Japan.”
Keisuke Suzuki, Lead Treasury Solutions of Takeda Japan: “With Katsuo Sekikawa, Zanders offered solid practical experience in the banking sector in Japan and knowledge of the Kyriba system – a great contribution with respect to the Japanese banks going live with Kyriba Payments.”
With the implementation of Kyriba, Takeda was able to fully automate the process of treasury payments, explains Suzuki: “This allowed us to have improved treasury payment automation. The centralized data provided by Kyriba enabled us to easily track our transactions, which was particularly important due to our significant amount of external debt, bonds, derivative and ICO contracts.”
We faced challenges due to the lack of connectivity and the absence of a standard approval process in place.
Meliosa O'Byrne, Associate Director Treasury Operations
Performance
Successfully live
During the user acceptance testing (UAT) and penny testing for Citi and SMBC, phase three was initiated in the background, specifically for the remaining four banks – Mizuho Bank and MUFG (both for Japan), Nordea (Europe) and JP Morgan (USA). Each bank encountered its own challenges in terms of time perspective, but all followed the agreed-upon eight-stage process with Kyriba and Zanders.
O’Byrne: “Upon completion of each phase, there was a hypercare period of five days after going live, which was supported by Zanders. By the end of September, all phases were successfully live, with a few minor bumps along the way. All stakeholders were extremely happy with the results.”
The comfortable and confident relationships built between Zanders and the various teams in Europe and Japan were an important foundation for the success of the project, according to Foley: “With three project phases focusing on different parts of the world, the project was a combination of various specialties, including treasury, IT, languages, and process and cultural alignment. Working with multiple internal and external stakeholders, and different banking partners, made the project complex. Despite the challenges posed by different time zones, the project was successfully completed in the timeframe agreed at the outset.”
Takeda now has a bank-agnostic approach to deliver the benefits of automated payments workflow while addressing local operating requirements. Foley: “The standardization and alignment of processes from all regions has been tremendous with respect to the overall Takeda approach. Kyriba allows for fully integrated payment systems, enabling Takeda to make large transactions with the security of robust system support. This allows us to turn all our attention to our day-to-day cash & liquidity planning to ensure that funds are in the right place at the right time and all risks are properly hedged.”

MODEC, the world’s largest independent operator of offshore floating production systems for the oil and gas industry, was managing its foreign exchange (FX) hedging process manually.

In 2020, the company decided to automate this process, successfully reducing the time spent on it from three days to within one day.
Headquartered in Tokyo, MODEC is a general contractor for the engineering, procurement, construction and installation (EPCI) of floating systems for deep-sea oil production. These systems include FPSO (floating production storage and offloading) units, FSO (floating storage and offloading) units, floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facilities, tension-leg platforms (TLPs), semi-submersible platforms, mooring systems and new technologies to meet the challenges of gas production floaters.
As largest independent operator of FPSO’s in the world, MODEC specializes in units for offshore deep sea oil production. “Then we either sell it to our clients or own and operate it on client’s behalf for 20 to 25 years,” says Qiurong Chong, Financial Planning & Treasury Manager at MODEC. Her business unit is located in Singapore and handles the conversion and EPCI of the FPSOs. From there, majority of the constructed FPSOs are handed over to MODEC’s business unit in Brazil responsible for the operations and maintenance of the vessels. “Our operations are therefore substantially in Brazil. But we do have presence in Australia, Ghana and Vietnam too.”
Since our functional currency is US dollars, we are exposed to a significant FX risk.
Qiurong Chong, Financial Planning & Treasury Manager
Challenge
Need for automation
As a global company, MODEC deals with a lot of vendors and major equipment suppliers. Chong: “Our vendors are located everywhere. Some are in China, where we usually do our transactions in US dollars. The major equipment vendors are located in Europe, such as Italy, Germany and The Netherlands. Therefore, the euro is one of the main foreign currencies. And since our functional currency is US dollars, we are exposed to a significant FX risk.”
MODEC’s finance department was managing the FX hedging process manually with the use of spreadsheets. By the end of 2019, there were approximately 350 outstanding FX forwards hedging the future cash flows of the purchase orders (POs) associated with MODEC’s projects. “The POs contain the information we need from the vendors for the FX process, including the cost in dollar value, the breakdown of the payment milestones and the expected payment date,” Chong explains.
The PO information was extracted from its system to be incorporated in an Excel overview driving their hedging activities. This was a labor-intensive process and since the expected number of FX transactions increased, MODEC decided to automate this process. Chong: “With Excel you have less control over the data integrity and only a few people had access to the account data. There were quite some governance concerns on this manual spreadsheet. We wanted to improve this process. And as our company grows, with an increasing number of projects running at the same time, the effort that we spend on updating and maintaining hundreds of transactions was too much.”
SAP TRM for straight-through-processing
Previously, all FX forwards were communicated via email, letter or phone and processed through a single cash centre between two banks. Bank accounts exist within each bank for all the currencies transacted, which total around eight for each bank. Monthly valuations are provided by the banks and upon settlement the bank automatically debits and credits MODEC’s bank accounts accordingly. GL journal entries were manually created in SAP. In the coming years, the number of FX forwards is expected to grow to 500 or more.
In the summer of 2020, MODEC Finance decided to implement SAP TRM for the straight-through-processing of FX forwards. Chong: “We asked around in the market about what system they used for their FX transactions. Our accounting migrated to SAP in 2017, which is quite recent. And since our information on vendors and POs are all in SAP, we thought: why not integrate everything together? That is why we decided to choose SAP TRM.”
Solution
Meeting the requirements
Thereafter, the new system needed to be integrated and automated. “We had been working with SAP successfully for some time and they recommended Zanders to support us. We reached out and asked Zanders for a demo. During that demo the team showed us the flow and functionalities that the TRM module in SAP could offer. It met our requirements, and we felt comfortable as Zanders could explain what we did not understand. It is important to be able to communicate with consultants in very simple terms and things that our department could understand. That is why we chose Zanders to support us in this project.”
Chong then asked Zanders to customize a program that could correctly capture the exposure positions and hedge relationships with the FX forward contracts. “Once a new PO is created, it can read that information and integrate it into the treasury module. We had quite some difficulties in trying to make the program to what it should be. The way we use SAP is not very standard, at some points, things got quite complex, but Zanders was able to resolve the complexities. Now the program is running very well. This process is expected to provide hedge accounting documentation under IFRS 9 and generate GL journal entries for monthly valuations and settlement.”
We thought: why not integrate everything together?
Qiurong Chong, Financial Planning & Treasury Manager
Performance
Connected
“We kicked off the project in August 2020 with a key user training, which was very useful – it prepared us well for the whole process. After that we had four weeks of requirements gathering, which was quite intensive but very productive. We had a few challenging areas that required additional effort by Zanders to do some research. Eventually all challenges were resolved, and we went live in February this year, so the project took about a half year.”
The systems are now connected. “So far, the systems are running well. There have been some small issues here and there – then we reached out to Zanders to resolve it. Zanders consultants Michiel and Mart were really very helpful throughout the whole process. Even our hedge accounting entries are done by the system. The automation reduces the processing time from an average of three days to within one day. The main beneficial part for us is that the business has the hedge documentation available from the system. In the past, we spent hours on computing effectiveness for the hundreds of transactions. When we were using Excel, we were only doing this on a quarterly basis. Now we can do it every month.”
Next steps
Are there still any challenges to be met for MODEC Finance? Chong: “We are still trying to stabilize the work process and get the hang of the new system. Once everything is more stable, there are some things we may explore. Automating this FX transaction was a first step for us in the treasury department. We are still doing many other reports manually for our headquarters in Japan. By bringing our HQ onboard this TRM module, we can have a seamless flow of information between us and them, which reduces any lag time and the need for us to extract the reports for them.”

Treasury transformation refers to the definition and implementation of the future state of a treasury department. This includes treasury organization & strategy, the banking landscape, system infrastructure and treasury workflows & processes.

Treasury transformation refers to the definition and implementation of the future state of a treasury department. This includes treasury organization & strategy, the banking landscape, system infrastructure and treasury workflows & processes.
Introduction
Zanders has witnessed first-hand a treasury transformation trend sweeping global corporate treasuries in recent years and has seen an elite group of multinationals pursue increased efficiency, enhanced visibility and reduced cost on a grand scale in their respective finance and treasury organizations.
Triggers for treasury transformations
Why does a treasury need to transform? There comes a point in an organization’s life when it is necessary to take stock of where it is coming from, how it has grown and especially where it wants to be in the future.
Corporates grow in various ways: through the launch of new products, by entering new markets, through acquisitions or by developing strong pipelines. However, to sustain further growth they need to reinforce their foundations and transform themselves into stronger, leaner, better organizations.
What triggers a treasury organization to transform? Before defining the treasury transformation process, it is interesting to look at the drivers behind a treasury transformation. Zanders has identified five main triggers:
1. Organic growth of the organization Growth can lead to new requirements.
As a result of successive growth the as-is treasury infrastructure might simply not suffice anymore, requiring changes in policies, systems and controls.
2. Desire to be innovative and best-in-class
A common driver behind treasury transformation projects is the basic human desire to be best-in-class and continuously improve treasury processes. This is especially the case with the development of new technology and/or treasury concepts.
3. Event-driven
Examples of corporate events triggering the need for a redesign of the treasury organization include mergers, acquisitions, spin-off s and restructurings. For example, in the case of a divestiture, a new treasury organization may need to be established. After a merger, two completely different treasury units, each with their own systems, processes and people, will need to find a new shape as a combined entity.
4. External factors
The changing regulatory environment and increased volatility in financial markets have been major drivers behind treasury transformation in recent years. Corporate treasurers need to have a tighter grasp on enterprise risks and quicker access to information.
5. The changing role of corporate treasury
Finally the changing role of corporate treasury itself is a driver of transformation projects. The scope of the treasury organization is expanding into the fi nancial supply chain and as a result the relationship between the CFO and the corporate treasurer is growing stronger. This raises new expectations and demands of treasury technology and organization.
Treasury transformation – strategic opportunities for simplification
A typical treasury transformation program focuses on treasury organization, the banking landscape, system infrastructure and treasury workflows & processes. The table below highlights typical trends seen by Zanders as our clients strive for simplified and effective treasury organizations. From these trends we can see many state of the art treasuries strive to:
- be centralized
- outsource routine tasks and activities to a financial shared service centre (FSSC)
- have a clear bank relationship management strategy and have a balanced banking wallet
- maintain simple and transparent bank account structures with automatic cash concentration mechanisms
- be bank agnostic as regards bank connectivity and formats
- operate a fully integrated system landscape
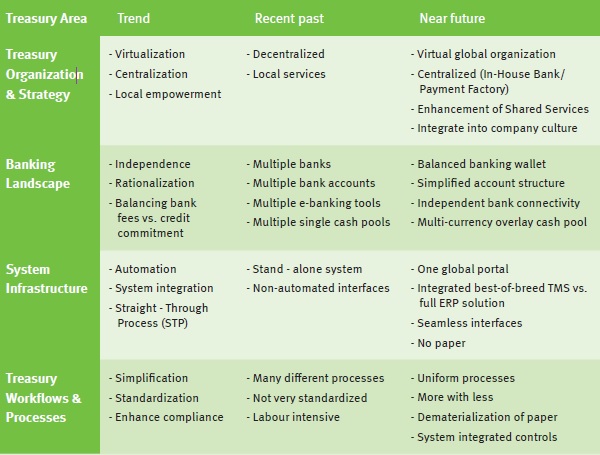
Figure 1: Strategic opportunities for simplification
The seven steps
Zanders has developed a structured seven-step approach towards treasury transformation programs. These seven steps are shown in Figure 2 below
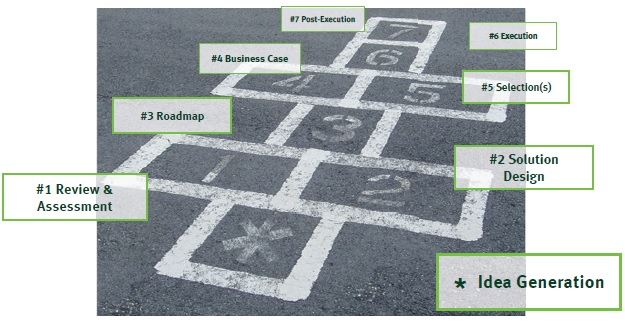
Figure 2: Zanders seven steps to treasury transformation projects
Step 1: Review & Assessment
Review & assessment, as in any business transformation exercise, provides an in-depth understanding of a treasury’s current state. It is important for the company to understand their existing processes, identify disconnects and potential process improvements.
The review & assessment phase focusses on the key treasury activities of treasury management, risk management and corporate finance. The first objective is to gain an in-depth understanding of the following areas:
- organizational structure
- governance and strategy policies
- banking infrastructure and cash management
- financial risk management
- treasury systems infrastructure
- treasury workflows and processes

Figure 3: Example of data collection checklist for review & assessment
Based on the review and assessment, existing short-falls can be identified as well as where the treasury organization wants to go in the future, both operationally and strategically.
Figure 4 shows Zanders’ approach towards the review and assessment step.
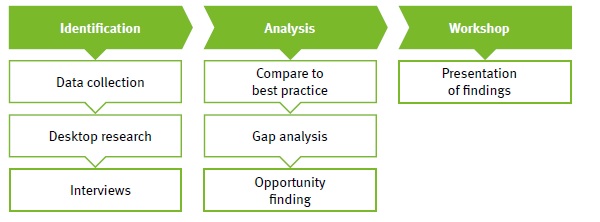
Figure 4: Review & assessment break-down
Typical findings
Based on Zanders’ experience, common findings of a review and assessment are listed below:
Treasury organization & strategy:
- Disjointed sets of policies and procedures
- Organizational structure not sufficiently aligned with required segregation of duties
- Activities being done locally which could be centralized (e.g. into a FSSC), thereby realizing economies of scale
- Treasury resources spending the majority of their time on operational tasks that don’t add value and that could be automated. This prevents treasury from being able to focus sufficiently on strategic tasks, projects and fulfilling its internal consulting role towards the business.
Banking landscape:
- Mismatch between wallet share of core banking partners and credit commitment provided
- No overview of all bank accounts of the company nor of the balances on these bank accounts
- While cash management and control of bank accounts is often highly centralized, local balances can be significant due to missing cash concentration structures
- Lack of standardization of payment types and payment processes and different payment fi le formats per bank
System infrastructure:
- Considerable amount of time spent on manual bank statement reconciliation and manual entry of payments
- The current treasury systems landscape is characterized by extensive use of MS Excel, manual interventions, low level of STP and many different electronic banking systems
- Difficulty in reporting on treasury data due to a scattered system landscape
- Manual up and downloads instead of automated interfaces
- Corporate-to-bank communication (payments and bank statements processes) shows significant weaknesses and risks with regard to security and efficiency
Treasury workflows & processes:
- Monitoring and controls framework (especially of funds/payments) are relatively light
- Paper-based account opening processes
- Lack of standardization and simplification in processes
The outcome of the review & assessment step will be the input for step two: Solution Design.
Step 2: Solution Design
The key objective of this step is to establish the high-level design of the future state of treasury organization. During the solution design phase, Zanders will clearly outline the strategic and operational options available, and will make recommendations on how to achieve optimal efficiency, effectiveness and control, in the areas of treasury organization & strategy, banking landscape, system infrastructure and treasury workflows & processes.
Using the review & assessment report and findings as a starting point, Zanders highlights why certain findings exist and outlines how improvements can be implemented, based on best market practices. The forum for these discussions is a set of workshops. The first workshop focuses on “brainstorming” the various options, while the second workshop is aimed at decision-making on choosing and defining the most suitable and appropriate alternatives and choices.
The outcome of these workshops is the solution design document, a blueprint document which will be the basis for any functional and/or technical requirements document required at a later stage of the project when implementing, for example, a new banking landscape or treasury management system.
Step 3: Roadmap
The solution design will include several sub-projects, each with a different priority, some more material than others and all with their own risk profile. It is important therefore for the overall success of the transformation that all sub-projects are logically sequenced, incorporating all inter-relationships, and are managed as one coherent program.
The treasury roadmap organizes the solution design into these sub-projects and prioritizes each area appropriately. The roadmap portrays the timeframe, which is typically two to five years, to fully complete the transformation, estimating individually the duration to fully complete each component of the treasury transformation program.
“A Program is a group of related projects managed in a coordinated manner to obtain benefits and control not available from managing them individually”.
Zanders
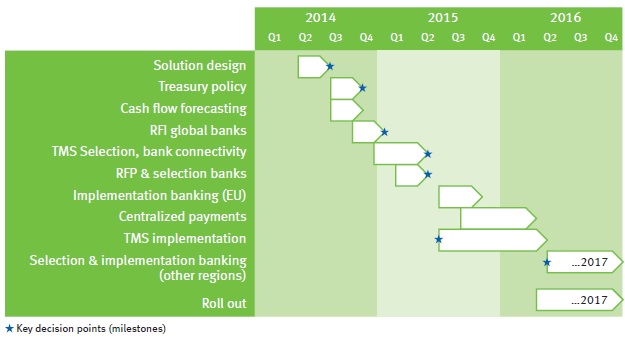
Figure 5: Sample treasury roadmap
Step 4: Business Case
The next step in the treasury transformation program is to establish a business case.
Depending on the individual organization, some transformation programs will require only a very high-level business case, while others require multiple business cases; a high level business case for the entire program and subsequent more detailed business cases for each of the sub-projects.
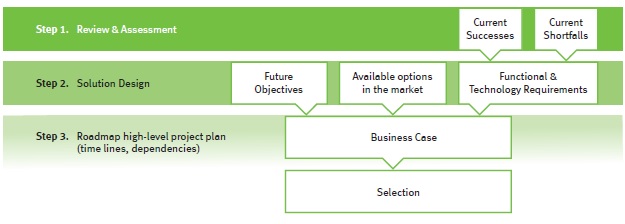
Figure 6: Building a business case
The business case for a treasury transformation program will include the following three parts:
- The strategic context identifies the business needs, scope and desired outcomes, resulting from the previous steps
- The analysis and recommendation section forms the significant part of the business case and concerns itself with understanding all of the options available, aligning them with the business requirements, weighing the costs against the benefits and providing a complete risk assessment of the project
- The management and controlling section includes the planning and project governance, interdependencies and overall project management elements
Notwithstanding the financial benefits, there are many common qualitative benefits in transforming the treasury. These intangibles are often more important to the CFO and group treasurer than the financial benefits. Tight control and full compliance are significant features of world-class treasuries and, to this end, they are typically top of the list of reasons for embarking on a treasury transformation program. As companies grow in size and complexity, efficiency is difficult to maintain. After a period of time there may need to be a total overhaul to streamline processes and decrease the level of manual effort throughout the treasury organization. One of the main costs in such multi-year, multi-discipline transformation programs is the change management required over extended periods.
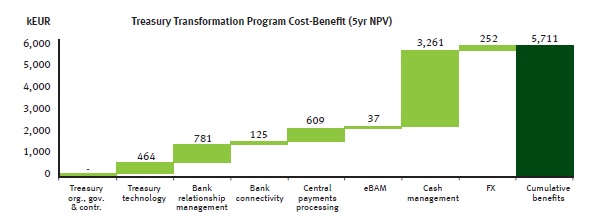
Figure 7: Sample cost-benefit
Figure 7 shows an example of how several sub-projects might contribute to the overall net present value of a treasury transformation program, providing senior management with a tool to assess the priority and resource allocation requirements of each sub-project.
Step 5: Selection(s)
Based on Zanders’ experience gained during previous treasury transformation programs, key evaluation & selection decisions are commonly required for choosing:
- bank partners
- bank connectivity channels
- treasury systems
- organizational structure
Zanders has assisted treasury departments with selection processes for all these components and has developed standardized selection processes and tools.
Selection process for bank partners
Common objectives for including the selection of banking partners in a treasury transformation program include the following:
- to align banks that provide cash and risk management solutions with credit providing banks
- to reduce the number of banks and bank accounts
- to create new banking architecture and cash pooling structures
- to reduce direct and indirect bank charges
- to streamline cash management systems and connectivity
- to meet the service requirements of the business; and
- to provide a robust, scalable electronic platform for future growth/expansion.
Zanders’ approach to bank partner selection is shown in Figure 8 below.

Figure 8: Bank partner selection process
Selection process for bank connectivity providers or treasury systems (treasury management systems, in-house banks, payment factories)
The selection of new treasury technology or a bank connectivity provider will follow the selection process depicted in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Treasury technology selection process
Organizational structure
If change in the organizational structure is part of the solution design, the need for an evaluation and selection of the optimal organizational structure becomes relevant. An example of this would be selecting a location for a FSSC or selecting an outsourcing partner. Based on the high-level direction defined in the solution design and based on Zanders’ extensive experience, we can advise on the best organization structure to be selected, on a functional, strategic and geographical level.
Step 6: Execution
The sixth step of treasury transformation is execution. In this step, the future-state treasury design will be realized. The execution typically consists of various sub-projects either being run in parallel or sequentially.
Zanders’ implementation approach follows the following steps during execution of the various treasury transformation sub-projects. Since treasury transformation entails various types of projects, in the areas of treasury organization, system infrastructure, treasury processes and banking landscape, not all of these steps apply to all projects to the same extent.
For several aspects of a treasury transformation program, such as the implementation of a payment factory, a common and tested approach is to go live with a number of pilot countries or companies first before rolling out the solution across the globe.

Figure 10: Zanders’ execution approach
Step 7: Post-Execution
The post-execution step of a treasury transformation is an important part of the program and includes the following activities:
6-12 months after the execution step:
– project review and lessons learned
– post implementation review focussing on actual benefits realized compared to the initial business case
On an ongoing basis:
– periodic benchmark and continuous improvement review
– ongoing systems maintenance and support
– periodic upgrade of systems
– periodic training of treasury resources
– periodic bank relationship reviews
Zanders offers a wide range of services covering the post-execution step.
Importance of a structured approach
There are many internal and external factors that require treasury organizations to increase efficiency, effectiveness and control. In order to achieve these goals for each of the treasury activities of treasury management, risk management and corporate finance, it is important to take a holistic approach, covering the organizational structure and strategy, the banking landscape, the systems infrastructure and the treasury workflows and processes. Zanders’ seven steps to treasury transformation provides such an approach, by working from a detailed as-is analysis to the implementation of the new treasury organization.
Why Zanders?
Zanders is a completely independent treasury consultancy f rm founded in 1994 by Mr. Chris J. Zanders. Our objective is to create added value for our clients by using our expertise in the areas of treasury management, risk management and corporate finance. Zanders employs over 130 specialist treasury consultants who are the key drivers of our success. At Zanders, our advisory team consists of professionals with different areas of expertise and professional experience in various treasury and finance roles.
Due to our successful growth, Zanders is a leading consulting firm and market leader in independent consulting services in the area of treasury and risk management. Our clients are multinationals, financial institutions and international organizations, all with a global footprint.
Independent advice
Zanders is an independent firm and has no shareholder or ownership relationships with any third party, for example banks, accountancy firms or system vendors. However, we do have good working relationships with the major treasury and risk management system vendors. Due to our strong knowledge of the treasury workstations we have been awarded implementation partnerships by several treasury management system vendors. Next to these partnerships, Zanders is very proud to have been the first consultancy firm to be a certified SWIFTNet management consultant globally.
Thought leader in treasury and finance
Tomorrow’s developments in the areas of treasury and risk management should also have attention focused on them today. Therefore Zanders aims to remain a leading consultant and market leader in this field. We continuously publish articles on topics related to development in treasury strategy and organization, treasury systems and processes, risk management and corporate finance. Furthermore, we organize workshops and seminars for our clients and our consultants speak regularly at treasury conferences organized by the Association of Financial Professionals (AFP), EuroFinance Conferences, International Payments Summit, Economist Intelligence Unit, Association of Corporate Treasurers (UK) and other national treasury associations.
From ideas to implementation
Zanders is supporting its clients in developing ‘best in class’ ideas and solutions on treasury and risk management, but is also committed to implement these solutions. Zanders always strives to deliver, within budget and on time. Our reputation is based on our commitment to the quality of work and client satisfaction. Our goal is to ensure that clients get the optimum benefit of our collective experience.

Compared with only a few years ago, today’s corporate treasurers are exposed to a much greater variety of counterparty risks within both their supply chains and financial institutions. This article provides guidance on how these counterparty risks can be effectively monitored and managed.

In recent years, the counterparty risks that corporates are exposed to have dramatically changed. Besides the traditional default risk that corporates hold on their customers, there has been an increase in counterparty risk regarding the exposures to financial institutions (FIs), the total supply chain, and also to sovereign risk. Market volatility remains high and counterparty risk is one of the top risks that need to be managed. Any failure in managing counterparty risk effectively can result in a direct adverse cash flow effect.
There are two important factors that have resulted in greater attention being paid to counterparty risk related to FIs in treasury. Firstly, FIs are no longer considered ‘immune’ to default. Secondly, the larger and better-rated corporates are now hoarding a day’s more cash compared to their pre-2008 crisis practice, due to restricted investment opportunities in the current economic environment, limited debt redemption and share buy-back possibilities and the desire to have financial flexibility.
Several trends can be identified regarding counterparty risk in the corporate landscape. In a corporate-to-bank relationship, counterparty risk is being increasingly assessed bilaterally. For example, the days are over when counterparty risk mitigating arrangements, such as the credit support annex (CSA) of an International Swaps and Derivative Association (ISDA) agreement, were only in favor of FIs. Nowadays, CSAs are more based on equivalence between the corporate and FI.
Measuring and Quantifying of Counterparty Risks
The magnitude of counterparty risk can be estimated according to the expected loss (EL), which is a combination of the following elements:
- Probability of default (PD): The probability that the counterparty will default.
- Exposure at default (EAD): The total amount of exposure on the counterparty at default. Besides the actual exposure the potential future exposure can also be taken into account. This is the maximum exposure expected to occur in the future at a certain confidence level, based on a credit-at-risk model.
- Loss given default (LGD): Magnitude of actual loss on the exposure at default.
This methodology is also typically applied by FIs to assess counterparty risk and associated EL. The probability of default is an indicator of the credit standing of the counterparty, whereas the latter two are an indicator of the actual size of the exposure. Maximum exposure limits on the combination of the two will have to be defined in a counterparty risk management policy.
Another form of counterparty risk is settlement risk, or the risk that one party of the agreement does not deliver a security, or its value in cash, as per the agreement after the other party has already delivered the security or cash value. Whereas EAD and LGD are calculated on a net market value for derivatives, settlement risk entails risk to the entire face value of the exposure. Settlement risk can be mitigated, for example by the joining multicurrency cash settlement system Continuous Link Settlement (CLS), which settles gross transactions of both legs of trades simultaneously with immediate finality.
Counterparty Exposures
In order to be able to manage and mitigate counterparty risk effectively, treasurers require visibility over the counterparty risk. They must ensure that they measure and manage the full counterparty exposure, which means not only managing the risk on cash balances and bank deposits but also the effect of lending (the failure to lend), actual market values on outstanding derivatives and also indirect exposures.
Any counterparty risk mitigation via collateralisation of exposures, such as that negotiated in a CSA as part of the ISDA agreement and also legally enforceable netting arrangements, also has to be taken into account. Such arrangements will not change the EAD, but can reduce the LGD (note that collateralisation can reduce credit risk, but it can also give rise to an increased exposure to liquidity risk).
Also, clearing of derivative transactions through a clearing house – as is imposed for certain counterparties by the European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) – will alter counterparty risk exposure. Those cleared transactions are also typically margined. Most corporates will be exempted from central clearing because they will stay below the EMIR-defined thresholds.
It will be important to take a holistic view on counterparty risk exposures and assess the exposures on an aggregated basis across a company’s subsidiaries and treasury activities.
Assessing Probability of Default
A good starting point for monitoring the financial stability of a counterparty has traditionally been to assess the credit rating of the institutions as published by ratings agencies. Recent history has proved however that such ratings lag somewhat behind other indicators and that they do not move quickly enough in periods of significant market volatility. Since the credit rating is perceived to be somewhat more reactive they will have to be treated carefully. Market driven indicators, such as credit default swap (CDS)* spreads, are more sensitive to changes in the markets. Any changes in the perceived credit worthiness are instantly reflected in the CDS pricing. Tracking CDS spreads on FIs can give a good proxy of their credit standing.
How to use CDS spreads effectively and incorporate them into a counterparty risk management policy is, however, sometimes still unclear. Setting fixed limits on CDS values is not flexible enough when the market changes as a whole. Instead, a more dynamic approach that is based on the relative standing of an FI in the form of a ranking compared to its peers will add more value, or the trend in the CDS of a FI compared against that of its peers can give a good indication.
A combination of the credit rating and ‘normalised’ CDS spreads will give a proxy of the FI’s financial stability and the probability of default.
Counterparty Risk Management Policy
It is important to implement a clear policy to manage and monitor counterparty risk and it should, at the very least, address the following items:
- Eligible counterparties for treasury transactions, plus acceptance criteria for new counterparties – for example, to ensure consistent ISDA and credit support agreements are in place. This will also be linked to the credit commitment. Banks which provide credit support to the company will probably also demand ancillary business, so there should be a balanced relationship. While the pre-crisis trend was to rationalise the number of bank relationships, since 2008 it has moved to one of diversification. This is a trade-off between cost optimisation and risk mitigation that corporates should make.
- Eligible instruments and transactions (which can be credit standing dependent).
- Term and duration of transactions (which can be credit standing dependent).
- Variable maximum credit exposure limits based on credit standing.
- Exposure measurement – how is counterparty risk identified and quantified?
- Responsibility and accountability – at what level/who should have ultimate responsibility for managing the counterparty risk.
- Decision making to provide an overall framework for decision making by staff, including treatment of breaches etc.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) – Selection of KPIs to measure and monitor performance.
- Reporting – Definition of reporting requirements and format.
- Continuous improvement – What procedures are required to keep the policy up to date?
Conclusion
To set up an effective counterparty risk management process, there are five steps to be taken as shown below; from identifying, quantifying, setting a policy to process and execute the set policy regarding counterparty risk.

Treasurers should avoid this becoming an administrative process; instead it should really be a risk management process. It will be important that counterparty risk can be monitored and reported on a continuous basis. Having real-time access to exposure and market data will be a prerequisite in order to be able to recalculate the exposures on a frequent basis. Market volatility can change exposure values rapidly.
* A credit default swap protects against default. In the event of a default the buyer will receive compensation. The spread (CDS spread) is the (insurance) premium paid for the swap.


