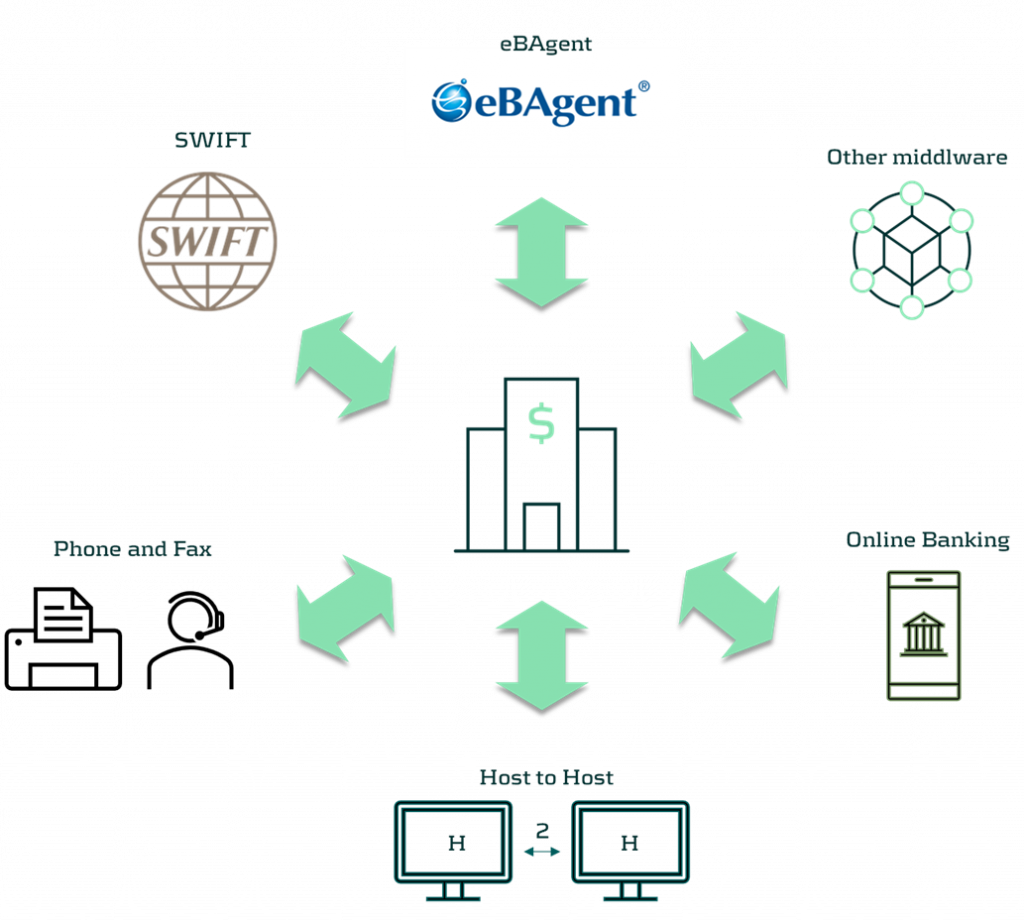
Treasurers dealing with multiple jurisdictions, scattered banking landscape, and local requirements face many challenges in this regard. Japan is one of the markets where bank connectivity is indeed a challenge, especially when it comes to connecting with local banks.
Traditional options
The initial reaction from treasurers not familiar with local market conventions might be to seek connection through the SWIFT network. However, in Japan only a handful of banks offer SWIFT connectivity. Second natural choice is the Host-to-Host connection (H2H). This is the classic File Transfer Protocol (FTP), or preferably the secured version (sFTP) setup. Some will say old fashioned, rather than classic, since it is as old as the internet. Nonetheless, it is still popular, and frankly quite often the best fit for the purpose. However, if there are dozens of local banks to connect to, it can be difficult to be expected to connect to each of them with a direct H2H. While this could be technically feasible, it would be nothing short of a nightmare to maintain, with the initial setup being time-consuming in the first place.
Other solutions
There is an answer, or should we rather say ANSER, to this question. ANSER, an abbreviation of ‘Automatic answer Network System for Electrical Request’, is a data transfer system provided by NTT Data Corporation since 1981, which links banks with firms.[1] ANSER then is a way to connect a corporate client to the bank. The system has been around for a while, and together with Cash Management Service (CMS) centers it is a part of the so-called Firm Banking solution in Japan. Since its inception, ANSER offered a wider range of services, through which corporates could access their banking information. Among the offered channels are telephone, fax, firm banking terminal, and personal computer. With the ever-increasing need for speedy and accurate information exchange, the more traditional ways, such as telephone and fax, gave way to the more sophisticated and automated solution, namely eBAgent.
eBAgent making use of API
The said eBAgent is a proprietary middleware platform offered by NTT Data. The solution establishes an automated connection with banks through the above-mentioned ANSER network. In short, eBAgent offers a gateway to multiple local banking partners in Japan utilizing the ANSER network. The remaining part for the corporate is then to establish a connection between the TMS and eBAgent, and secure appropriate contracts with the eBAgent provider, NTT Data, as well as the banks.
As for the connection protocol, the choice is between the classic sFTP, or Application Programming Interface (API). The latter has the real-time advantage, with less lag between the pick-and-drop sFTP connection. API seems to be a choice for an increasing number of corporates these days in this area. What is also interesting, apart from the API connection, are the supported formats for transfers and bank statements. In addition to the local Japanese ZENGIN, the protocol also offers data transmission in a proprietary XML format. This XML format is actually quite simple, with a very limited amount of tags. In addition to this, unlike the ISO 20022 standard, it contains only one level of tags, without the nesting function. Depending on the exact ERP/TMS infrastructure, eBAgent can also provide conversion services from and to the IS 20022 standard. As for the connection to eBAgent, the whole setup seems easier said than done. However, some TMS providers, in response to the demand from the market, started offering off-the-shelf solutions for a plug-and-play connection to eBAgent. Kyriba and Reval already offer it, with SAP set to roll out its solution on the S/4HANA and Multi Bank Connectivity (MBC) platform in early 2024.
Various ways to connect TMS / ERP with banks in Japan
How to connect with local banks in Japan?
It all depends on the exact landscape of banks and systems. It may just as well turn out that a hybrid solution would be best suited. There is no one-size fits all, as each corporate is unique, thus careful consideration and design will be paramount for a stable and reliable connection with banks. One thing is certain, solutions that involve obtaining bank statement information and enact payments by telephone or fax are simply no longer sufficient. In this day and age, when much sensitive information is exchanged between corporates and banks, having a reliable, automated solution is indispensable.
If you would like to know more, do not hesitate to get in touch with Michal Zelazko via [email protected] or via + 81 (0) 8 3255 9966
[1] https://www.boj.or.jp/en/paym/outline/pay_boj/pss0305a.pdf