This article is intended for finance, risk, and compliance professionals with business and system integration knowledge of SAP, but also includes contextual guidance for broader audiences.
1. Introduction
SAP Treasury and Risk Management (SAP TRM) provides a robust framework to meet the need for enhanced transparency, mitigate financial risks, and ensure regulatory compliance, but its effectiveness depends on the correct implementation of control mechanisms and automated checks.
In Japan, the approach to financial and treasury management is influenced by principles of Kaizen (continuous improvement) and high-quality process control. The core emphasis is on minimizing errors, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring the reliability of Treasury management systems.
The approach aligns with the necessity of seamless internal controls in SAP TRM, where even minor inconsistencies can lead to significant financial risks and losses.
This article outlines key controls within SAP TRM, provides practical implementation steps, and explores AI-driven enhancements that improve compliance, security, and operational efficiency.
2. SAP TRM: Key Areas Requiring Controls
SAP TRM covers a broad range of treasury functions, each requiring specific control mechanisms:
- Transaction Management: Handling financial instruments such as FX, money markets, securities, derivatives, etc.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating market and credit risks.
- Cash and Liquidity Management: Real-time cash positioning and cash flow forecasting, and optimization.
- Hedge Management and Accounting: Compliance with IFRS 9 and other standards.
3. How SAP TRM Supports Real-Time Risk Control
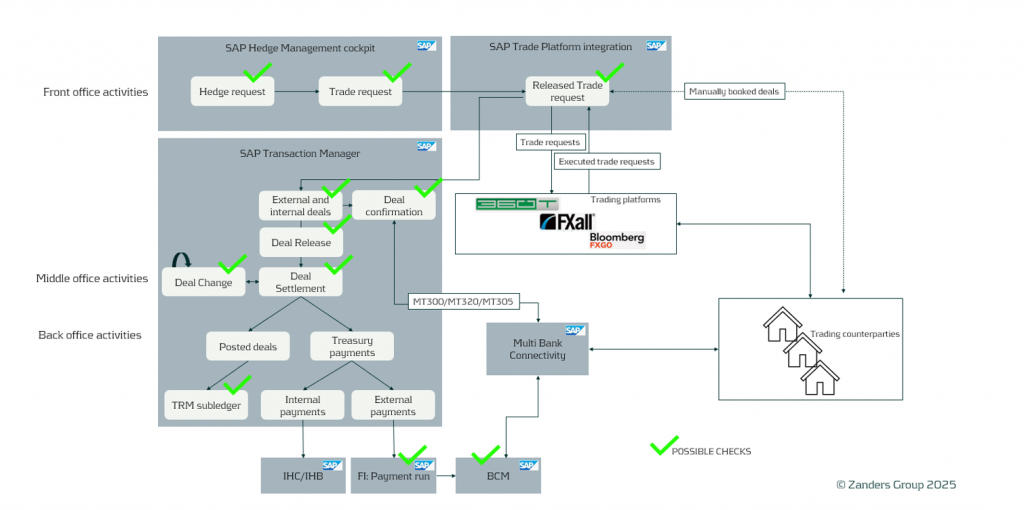
A solid control framework requires detailed analysis, alignment, and structured implementation. Below are some key controls that should be assessed and implemented within transaction management of SAP TRM. In the picture, the areas where possible checks can be applied are highlighted:
Deal Release (Approval) Control
Ensuring proper authorization and validation before a deal is released (approved internally) is essential to prevent unauthorized or erroneous transactions from being booked, modified, and processed in SAP.
Proposed configuration objects to consider:
- Business Rule Framework Plus (BRFplus): Define validation checks, such as ensuring that only authorized users can release deals above a certain value.
Deal Settlement Control
Settlement is SAP term for the deal confirmation with counterparties. The deal status is changed to "Settlement" immediately after confirmation.
Accurate deal confirmation is crucial to avoid financial mismatches or discrepancies in payment details. The settlement process is required for all external deals and may also be needed for intercompany deals. Settlement is required for every key lifecycle step of a deal: creation, NDF fixing, rollover, option exercise, etc. Settlement can be done manually or automatically upon counter-confirmation of the correspondence (MT300, MT320, MT305, or deal confirmation messages).
Proposed configuration objects to consider:
- Set up automated reports to track unsettled deals within a specific timeframe (as of today or as of the current week).
- SAP Fiori app “Display Treasury alerts” is an effective solution for this.
Ensuring Transaction Integrity: Key Checks in SAP
Automating the matching process minimizes manual errors and improves operational efficiency, reducing the time required for this process.
Proposed configuration objects to consider:
- Define a report to show all pending unmatched correspondences. This is often proposed as a control over the matching process. It can be implemented using the Correspondence Monitor or the Fiori app "Display Treasury Alerts."
Restricted Deal Modifications
To prevent unauthorized modifications of the treasury transactions that could lead to fraudulent or erroneous results, deal changes should be strictly controlled. We do not recommend allowing deals in status Settlement (after confirmation matching process) to be changed—especially key matching fields such as amounts, value dates, and currencies. However, modifications may be required from time to time. In such cases, they need to be controlled and may require another round of verification and counter-confirmation matching.
Proposed configuration objects to consider:
- Enable Change Log Activation: Use SAP Audit Information System (AIS) to track modifications and maintain audit trails for TRM.
- Implement SAP TRM Deal Approval Workflow: Require validation and approval for all deal amendments and reversals.
- Restrict critical field modifications: Configure SAP field selection variant to lock key fields of the deals from being altered after deal approval/settlement.
- Enforce Segregation of Duties (SoD): Ensure different users handle deal creation, approval, settlement processing, and modifications to prevent errors or fraud.
Deal Payment Controls Using BCM Approvers
Ensuring that deal payments go through the correct approval process reduces financial risk and enhances security. It is important to define unusual treasury payment scenarios, such as when cash flow processing occurs outside normal business hours.
Proposed configuration objects to consider:
- Implement a Payment Block Mechanism: Ensure that payments are blocked unless predefined criteria are met, or review and approval is done/granted.
- Automated Exception Handling: Configure Bank Communication Management (BCM) rules to flag transactions that deviate from standard payment behavior, requiring manual review before processing (e.g., payments to a new business partner or deals posted outside normal business hours).
4. AI-Driven Enhancements for Treasury Control
AI is transforming treasury processes by automating risk detection, optimizing forecasting, and enhancing decision-making. Key AI-powered enhancements in SAP TRM include:
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning models in SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) to detect suspicious transactions.
- SAP Business Integrity Screening: AI-driven software from SAP that improves anomaly detection, risk identification, and compliance checks.
- Automated Matching: AI-powered bots in SAP Intelligent RPA match transactions (especially when non-SWIFT correspondence is used), helping eliminate manual errors.
5. Best Practices for SAP TRM Control Optimization
The following best practices are recommended as part of the business-as-usual process:
- Conduct regular Role & Authorization reviews: Update SAP GRC, Governance, Risk, and Compliance, settings to align with changes in Treasury team structure.
- Leverage SAP Fiori apps for real-time analytics and visibility into treasury processes, ensuring that no payments are stuck and that all back-to-back and mirroring deals are in place and processed on time.
- Create and integrate AI-powered tools: Deploy SAP AI solutions to enhance risk analysis, compliance monitoring and decision-making.
- Adopt a Kaizen approach: Continuously monitor and refine TRM controls to improve efficiency and accuracy, as technology is rapidly evolving and controls must remain valid and preventive.
6. Conclusion
Implementing strong controls in SAP TRM is critical for maintaining compliance, minimizing financial risks, and improving operational efficiency.
By leveraging SAP’s built-in functionalities—along with AI-driven enhancements—corporate treasurers can create a secure, transparent, and highly automated treasury management process. By integrating Kaizen principles and AI-driven automation, companies can transform their treasury operations into a continuously improving and highly efficient Treasury Management System.
Zanders consultants are deeply involved in this crucial topic, which can be addressed as a standalone initiative to improve controls, as part of ongoing treasury support, or within an SAP TMS implementation project. We are ready and eager to help your company enhance system controls and checks in SAP TRM.
For more information, please contact Aleksei Abakumov.
Case Study: SAP TRM in Practice
A multinational, multibillion-dollar company operating across the globe, with its HQ in Tokyo, Japan, implemented SAP TRM. By using J-SOX controls (both business and system) in SAP TRM, the company managed to build world-class, secure control mechanisms that are used and applied throughout the entire organization, across all markets. The company regularly validates these controls and challenges them when they are obsolete or adds new controls if needed due to changing external conditions.