Canada’s largest railway set out to simplify its payments and improve reconciliation with enhanced remittance data, while also reducing IT support costs. The project will run parallel with the Canadian Payments Association’s (CPA’s) initiative to modernize the system and introduce ISO 20022 formats. So, following a thorough request for information (RFI) and request for proposal (RFP) process with the banks, the Canadian National Railway Company (CN) now has its future vision for bank connectivity and global-standard payments, as well as a multi-year roadmap to establish best practices.
‘North America’s Railroad’
CN operates approximately 20,000 route miles of transcontinental railroad from Vancouver in the west to Halifax in the east, and all the way down to New Orleans on America’s southern coast. Its market cap of US$43bn (C$57bn), as of February 2016, makes ‘North America’s Railroad’, as it’s known, the biggest rail company in Canada in terms of both network and value. The majority of business, consisting of freight, takes place in North America, but CN’s reach extends much further, with operations and transport services in Asia and South America.
The group treasury, centralized in Montreal, takes care of cash management functions and does all FX hedging and cash pooling with the two main operating currencies, Canadian dollar and US dollar. This business model meant that CN needed a bank with a strong presence in the US and Canada, as well as an international footprint. In 2015, therefore, the company started to look into streamlining its banking relationships.
European perspective on Canada
Zanders was asked to provide guidance on both the RFI and RFP phases of the bank selection process. The aim was to choose one or two relationship banks for domestic and global operations. Due to the specifics of the Canadian market, the company chose one bank for its North American operations and one for the rest of the world. Zanders was an active ‘sparring’ partner in this process and supported CN throughout the RFP, during the evaluation of responses, decision-making, and selection phases.
The vision
Paul Tawel, who was senior manager of treasury operations at CN during the RFI and RFP process, explains how the project began: “Our main goal was to get a vision of best practices in different areas of treasury, so it originally started as a ‘quest for knowledge’. On our side, we had a lot of good processes in place but we wanted to learn more about protocols for bank communication.”
The project group at CN went through a questioning process, looking at all outsourced services and how it communicated with its banks. While they recognized that many of the protocols in place were already working well, there were areas that could be improved. Tawel, who has now retired from CN, adds: “We really wanted an internal vision and we now have that – we have put in place a cross-functional task force, including treasury, accounting, procurement, marketing, and IT to implement the vision and roadmap that we have developed. We have a timeline of three years to put these changes into practice. There are separate plans for AP, collections, and treasury. On the payables side, the vision can be implemented quite quickly.”
The job is ongoing, and CN is currently drawing up an action plan for three areas: payments and collections, payment format harmonization, and bank connectivity.
World-class payments and collections
During the research phase, which took place in mid-2015, running alongside the bank RFI and RFP, it became apparent that there were areas of payments and collections that could be optimized. Cheques are still a mainstay of CN’s collections in both Canada and the US, representing 43 per cent and 62 per cent of collections volume, respectively. Meanwhile, on the payments side, there was far less reliance on cheques (seven per cent of volume of payments in Canada, 10 per cent in the US), although there was still an opportunity to reduce volumes. Another factor on the collections side was the wide variability of remittance data sent by customers. “We want to eliminate cheques as much as possible. However, in North America, they are part of the culture, and suppliers demand them. The right communications strategy will be a key part of successfully encouraging suppliers and customers to accept another digital payment,” says Tawel.
Another important consideration was the unique payments environment in Canada, explains Mark van Ommen, associate director at Zanders: “We had to take the nature of the Canadian payments system into account. One of the challenges is that they are still very much cheque-driven, mainly on the receivables side, so that is a big difference in the Canadian environment.”
CN’s overall vision for payments and collections is to rationalize payment/collection methods and reduce cheques in receivables, while also increasing the level of pre-authorized debits. On the outbound payables side, as well as further reducing cheque usage, it was decided to leverage SAP technology.
Formats harmonization
CN also wished to simplify the way it communicates transaction data with its banks. The company currently uses a large number of formats, some of which were customized, and this increases payment and IT costs. Moreover, the Canadian clearing system doesn’t permit payment messages to contain all the data necessary, so that separate files are required for remittance.
However, the Canadian Payments Association (CPA) has now launched an initiative to modernize Canada’s core payments infrastructure, gradually replacing multiple formats – often based on Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) formats – with the international ISO 20022 standard payment formats. The design phase of the initiative is expected to be completed by the end of 2016, but implementation will take several years. The CPA will also adopt Extended Remittance Information (ERI), which will enable the reconciliation of payment remittances to be automated, saving companies such as CN significant resources.
Despite the CPA’s initiative to introduce standardized XML payment formats by 2020, CN had to consider the best option in the current environment. They chose to adopt CGI payment formats that provide combined payment and remittance info, enabling more efficient reconciliation and less complexity from an IT point of view. Van Ommen adds: “We were able to provide advice based on our experience of European XML standardized payment formats. Although the non-standard payments environment in Canada is a challenge, the CPA is intent on bringing this in line with global standards.”
Bank connectivity
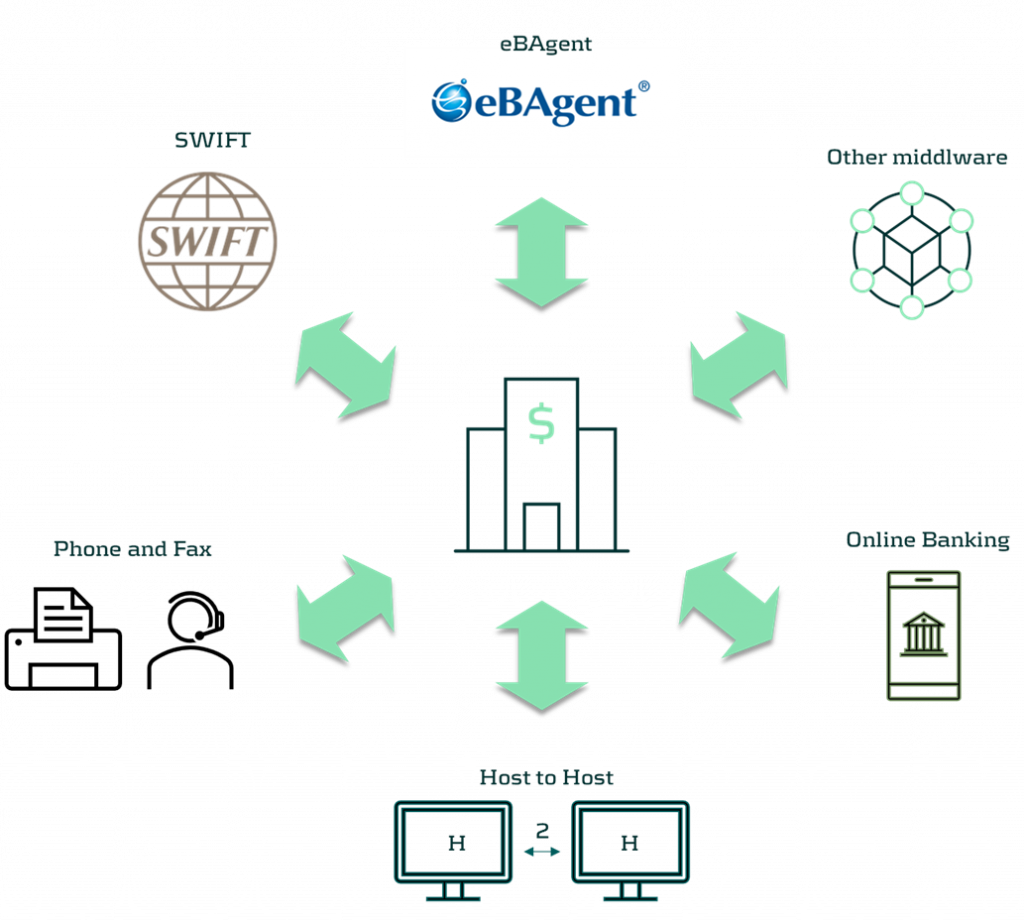
The multiple payment format types, along with the company’s multiple host-to-host interfaces with various e-banking systems, mean there is a raised cost in terms of IT support – the so-called ‘cost of ownership’. The more systems and types of format are used, the greater the cost of making any modification to each system. CN wanted more independence.
Zanders partner Judith van Paassen worked closely with CN on this issue. She explains that: “The ‘cost of ownership’ of maintaining the current multiple types of file formats and bank connectivity was too high. CN needed more standardization to reduce this cost and to ‘future-proof’ its treasury and payments operations. But first, treasury and IT needed to convince other departments that this would be both necessary and beneficial.”
The solution put forward in CN’s vision and roadmap was to simplify the systems landscape and number of interfaces. CN already had Swift’s Alliance Lite2.0 in place but this was only used for treasury payments and wires and, in any case, was unsuitable for the volume of commercial payments for a company of CN’s size.
Tawel explained that the aim is to adopt a standardized, bank-agnostic communication channel for all bank communications: “We want to leverage our Swift communication platform, but in future we may need a Swift Service Bureau. This will take time, and as we are already on Swift, we see it as primarily an IT project.”
A communication strategy was needed across the organization to get all departments aligned with the best practice identified by treasury and IT in the areas of bank connectivity and payment formats harmonization. Van Paassen adds: “We advised the treasury and IT teams to view this project as a long-term strategy. It was a challenge to get departments such as A/R and A/P to support this vision, but CN’s treasury succeeded.”
CN was vindicated in its long-term strategy for banking relationships, bank connectivity, and payment formats. It has already been able to reduce its banking fees significantly via the bank RFI and RFP phase and in future expects to improve security and simplify the process of making commercial payments.
Vision and roadmap
Having already selected two relationship banks and with its vision for future bank connectivity and payments firmly established, CN is now planning the initial steps along its roadmap, which will take it up to 2021. In early 2016, treasury began looking at document solution design and payment formats. Van Paassen says: “The challenge will be in the implementation, but we are confident that we helped treasury see the bigger picture, which will enable them to make the necessary changes.”
A factor that was vital to the project’s success was getting buy-in from several different teams. While some departments initially questioned the need for the proposed changes, they reached a consensus, helped by the objective, fact-based methodology used during the RFI and RFP phase and the bank communication standardization project. Irene Kwan, senior manager, treasury operations, at CN, said that at the end of the project, treasury’s vision was shared and supported across all departments. She says: “The project was well received in the company. Everyone was on board and everyone was clear about what we wanted to achieve. In my view, it would be really beneficial to carry out projects on best practices more frequently.”
Would you like to know more about bank connectivity or other treasury challenges? Contact us today.