
A combination of external market volatility and internal structural change prompted our client, a global energy logistics business, to seek a more disciplined approach to interest rate risk management. Our team from Zanders stepped in, providing expert support to help the treasury benchmark their practices and strengthen their risk management framework.

Global market turbulence and the shifting interest rate environment have intensified uncertainty for corporate treasuries in recent years. This has forced greater attention on financial risk – particularly for businesses operating across multiple continents and managing exposure to volatile financing costs. For our global energy logistics client, these external pressures arrived at the same time as major internal changes, presenting an ideal opportunity to reassess existing treasury practices.
“There were a lot of new faces and new knowledge with the changes at the company – it seemed a logical moment to also review all the policies and procedures in place,” says a company treasurer. “This triggered a discussion on risk management – what policies we had in place and whether they were still fit for purpose.”
Time for pragmatism and validation
While hedging policies existed, they were informal and inconsistently applied. As market volatility increased, it became clear that the company needed a more formal, structured framework to provide the clarity now expected – both internally and by regulators.
“We decided it was time to formalize our policies,” the company treasurer adds. “There was more focus internally on how market volatility could impact our results. We were regularly being asked what was driving revaluations in our financials and how we could smooth this by structuring differently or applying hedge accounting.”
The treasury team embarked on a large-scale project to refresh and refine policies and document their future risk management approach. However, while internal discussions clarified objectives and processes, to have complete confidence in their approach required more than just internal agreement. They also needed to be sure that their policies were aligned with market best practices and that their hedging strategies would withstand the scrutiny of management, auditors and regulators.
“We realized we needed validation,” the client explains. “We wanted to know whether what we were doing was correct, whether we were missing something and how our approach compared to market practice. Were we under-hedged or over-hedged compared to peers?”
Making risk tangible
Zanders was a natural choice to conduct this benchmarking exercise and provide the independent, expert view the company needed. The treasury team trusted them from an earlier transfer pricing project and valued their approach – in particular the blend of technical depth and practical execution.
We like Zanders’ pragmatic approach.
Company Treasurer
“Once you start talking about hedging policies, many consultants immediately ask for SAP dumps going back 15 years and expect you to fill an entire data room. I was afraid of that. We weren’t at the start of a project – we were almost finished – we needed a partner who could validate our work without creating a massive administrative burden. Zanders understood this.”
Instead of a heavy data-driven exercise, Zanders designed a focused, efficient process structured around two interactive workshops: an exploratory session to discuss and map existing processes and a second session to validate conclusions.
It really helped to get validation from an external consultant, you want to know whether what you’ve built actually makes sense, whether you’re missing something, and how competitors approach the same issues.
Company Treasurer
Within just a few weeks, Zanders delivered a clear validation report accompanied by a set of practical recommendations. One of the most valuable was linking hedge decisions more closely to the company’s financial sensitivities – a shift that has made it far easier to communicate risk to senior management.
“These are really pragmatic solutions that have improved our policies, and our top management can see the results immediately,” says the company treasurer. “When we explain why we hedge, or what happens if we don’t, the impact becomes tangible. It’s no longer abstract. We can show: ‘If you do this, here’s the risk. If you do that, here’s the outcome.’ It makes presenting the figures much easier, and it helps management truly understand the numbers rather than just percentages.”
Reshaping perspectives on risk
By combining structured validation with practical recommendations, the project not only strengthened the company’s interest rate risk framework but also gave the treasury team renewed confidence in their approach.
“Overall, the outcome of the project wasn’t to radically change our approach – it confirmed we were on the right track,” says the company treasurer. “But it also led to changes that have created more awareness and understanding across the company about the importance of risk management.”
Perhaps most importantly, the exercise reframed the company’s view of risk in the core. “We used to think of risk management purely as minimizing risk,” the company treasurer says. “Now we see it as balancing risk, cost and impact – making informed decisions rather than automatic ones on multiple levels.”
Looking to elevate your interest rate risk strategy?
From volatility in global markets to rising expectations from boards, auditors and regulators, interest rate risk management has never been more critical. Zanders brings the expertise, structure and independent perspective needed to strengthen your framework and turn risk insights into strategic clarity.
Get in touch to discover how we can help you build a clearer, more resilient approach to interest rate risk – ensuring transparency, control and confidence across your financial decision-making.

Ready to transform your interest rate risk strategy?
Contact us
We explore the main challenges of computing Margin Value Adjustment (MVA) and share our insights on how GPU computing can be harnessed to provide solutions to these challenges.

With recent volatility in financial markets, firms need increasingly faster pre-trade and risk calculations to react swiftly to changing markets. Traditional computing methods for these calculations, however, are becoming prohibitively expensive and slow to meet the growing demand. GPU computing has recently garnered significant interest, with advances in the fields of advanced machine learning techniques and generative AI technologies, such as ChatGPT. Financial institutions are now looking at gaining an edge by using GPU computing to accelerate their high-dimensional and time-critical computing challenges.
The MVA Computing Challenge
The timely computation of MVA is essential for pre-trade and post-trade modeling of bilateral and cleared trading. Providing an accurate measure of future margin requirements over the lifetime of a trade requires the frequent revaluation of derivatives with a large volume of intensive nested Monte Carlo simulations. These simulations need to span a high-dimensional space of trades, time steps, risk factors and nested scenarios, making the calculation of MVA complex and computationally demanding. This is further complicated by the need for an increasing frequency of intra-day risk calculations, due to recent market volatility, which is pushing the limits of what can be achieved with CPU-based computing.
An Introduction to GPU Computing
GPU computing utilizes graphics processing units, which are specifically designed to handle large volumes of parallel calculations. This capability makes them ideal for solving programming challenges that benefit from high levels of parallelization and data throughput. Consequently, GPUs can offer substantial benefits over traditional CPU-based computing, thanks to their architectural differences, as outlined in the table below.
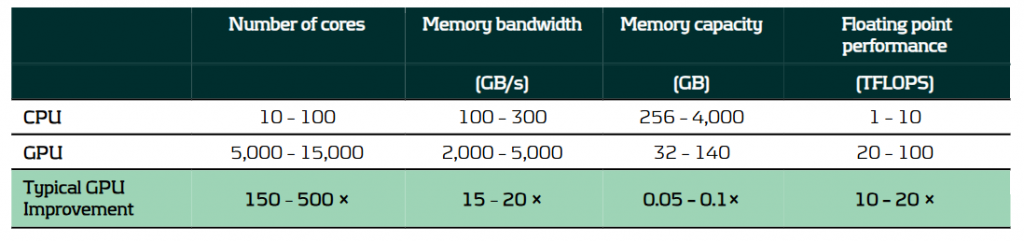
A comparison of the typical capabilities of enterprise-level hardware for CPUs and GPUs.
It is because of these architectural differences that CPUs and GPUs excel in different areas:
- CPUs feature fewer but more powerful cores, optimized for general-purpose computing with complex, branching instructions. They excel in performing serial calculations with high single-core performance.
- GPUs consist of a large number of less powerful cores and with higher memory bandwidth. This makes them ideal for handling large volumes of parallel calculations with high throughput.
Solving the MVA Computational Challenge with GPU Computing
The requirement to calculate large volumes of granular simulations makes GPU computing especially well-suited to solving the MVA computational challenge. The use of GPU computing can lead to significant improvements in performance for not only MVA but a range of problems in finance, where it is not uncommon to see improvements in calculation speed of 10 – 100x. This performance increase can be harnessed in several ways:
- Speed: The high throughput of GPUs provides results more quickly, providing faster risk calculations and insights for decision-making, which is particularly important for pre-trade calculations.
- Throughput: GPUs can more quickly and efficiently process large calculation volumes, providing institutions with more peak computing bandwidth, reducing workloads on CPU-grids that can be used for other tasks.
- Accuracy: With greater parallel processing capabilities, the accuracy of models can be improved by using more sophisticated algorithms, greater granularity and a larger number of simulations. As illustrated below, the difference in the number of Monte Carlo simulations that can be achieved by GPUs in the same time as CPUs can be significant.
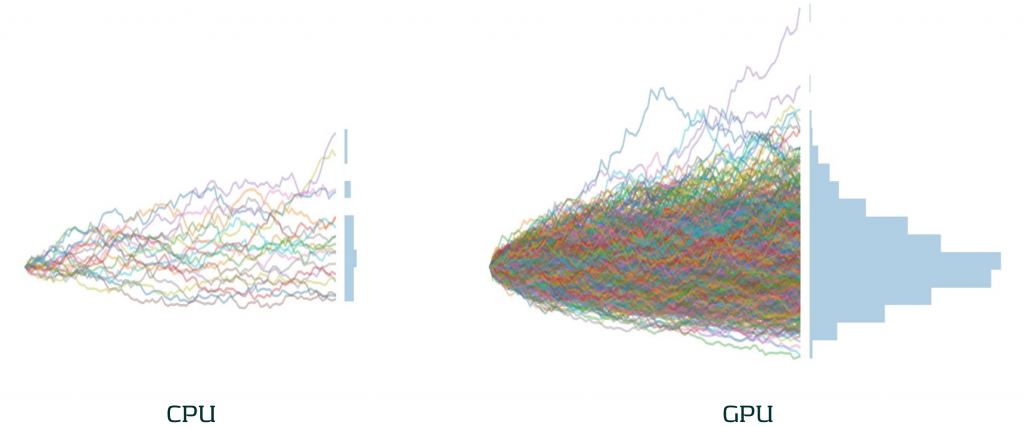
The difference in the number of Monte Carlo paths than can be simulated in the same time between an equivalent enterprise-level CPU and GPU.
Case Study: Our approach to accelerating MVA with GPUs
To illustrate the impact of GPU computing in a real situation, we present a case study of our work accelerating MVA calculations for a major bank.
Challenge: A large investment bank was seeking to improve the performance of their pre-trade MVA for more timely calculations. This was challenging as they needed to compute their MVA exposures over long time horizons, with a large number of paths. Even with a sensitivity-based approach, this process took close to 10 minutes using a single-threaded CPU calculation.
Solution: Zanders analyzed the solution and identified several bottlenecks. We developed and optimized a GPU-accelerated solution to ensure efficient GPU utilization, parallelizing the calculations across scenarios and risk factors.
Performance: Our GPU implementation improved MVA calculation speed by 51x. Improving calculation time from just under 10 minutes to 10 seconds. This significant increase in speed enabled more timely and frequent assessments and decisions on MVA.
Our Recommendation: A strategic approach to GPU computing implementations
There are significant benefits to be achieved with the use GPU computing. However, there are some considerations to ensure an effective use of resources:
We work with firms to develop bespoke solutions to meet their high-performance computing needs. Zanders can help in all aspects of GPU computing implementation, from initial design to the analysis, development and optimization of your GPU computing implementation.
Conclusion
GPU computing offers significant improvements in the speed and efficiency of financial calculations, typically boosting calculation speeds by factors of 10-100x. This enables financial institutions to manage their risk more effectively, including the computationally demanding calculations of MVA. By replacing CPU-based calculations with GPU computing, banks can dramatically improve their capacity to process greater volumes of calculations with higher frequency. As financial markets continue to evolve, GPU computing will play an increasingly vital role in their calculation infrastructure.
To find out more on how GPU computing can enhance your institution's risk management processes, please contact Steven van Haren (Director) or Mark Baber (Senior Manager).

Following the publication of its focus areas for IRRBB in 2024 and 2025, the European Banking Association (EBA) has now published an update regarding the implementation and explains the next steps.

The implementation update covers observations, recommendations and supervisory tools to enhance the assessment of IRRBB risks for institutions and supervisors.1 Main topics include non-maturing deposit (NMD) behavioral assumptions, complementary dimensions to the SOT NII, the modeling of commercial margins for NMDs in the SOT NII, as well as hedging strategies.
Some key highlights and takeaways from the results of sample institutions as per Q4 2023:
- Large dispersion across behavioral assumptions on NMDs is observed. The significant volume of NMDs as part of EU banks’ balance sheets, differences in behavior between customer / product groups and developments in deposit volume distributions, however, underline the need for more solid and aligned modeling. The EBA hence suggests NMD modeling enhancements and recommends (1) banks to consider various risk factors related to the customer, institution and market profile, as well as (2) a supervisory toolkit to monitor parameters / risk factors. Segmentation and peer benchmarking, (reverse) stress testing as well as (combining) expert judgment and historical data are paramount in this regard. The recommendations spark banks to reevaluate forward looking approaches, as shifting deposit dynamics render calibration solely based on historical data insufficient. Establishing a thorough expert judgment governance including backtesting is vital in this respect. Moreover, assessing and substantiating how a bank’s modeling relates to the market is more important than ever.
- Next to the NII SOT that serves as a metric to flag outlier institutions from an NII perspective, the EBA proposes additional dimensions to be considered by supervisors. These dimensions, which aim to reflect internal NII metrics, must complement the assessment and enhance the understanding of IRRBB exposures and management. The proposed dimensions include (1) market value changes of fair value instruments, (2) interest rate sensitive fees/commissions & overhead costs, and (3) interest rate related embedded losses and gains. It is important to note that it is not intended to introduce new limits or thresholds associated with these dimensions.
- Given concerns and dispersion regarding the modeling of commercial margins for NMDs in the NII SOT (38% of sample institutions assumed constant commercial margins versus the remainder not applying constant margins), the EBA now provided additional guidance on the expected approach. They recommend institutions to align the assumptions with those in their internal systems, or apply a constant spread over the risk-free rate when not available. Key considerations include the current spread environment, the context of zero or negative interest rates and lags in pass-through. The EBA’s clarification indicates that banks are allowed to apply a non-constant spread. This serves as an opportunity for banks still applying constant ones, as using non-constant spreads enhances the ability to quantify NII risk under an altering interest rate environment.
- Hedging practices vary significantly across institutions, although hedging instruments (i.e. interest rate swaps) to manage open IRRBB positions are aligned. Hedging strategies have significantly contributed to meeting regulatory requirements, with all institutions meeting the SOT EVE as per Q4 2023, compared to 42% that would not have complied if hedges were disregarded. For the SOT NII, however, 13% of the sample institutions would have been considered outliers if this regulatory measure had been applied in Q4 2023 (versus 21% when disregarding hedges). This result shows that it is key for banks to find a balance between value and earnings stability, and apply hedging strategies accordingly. As compliance with SOTs must be ensured under all circumstances, stressed client behavior and market dynamics must be accounted for.
In the upcoming years, the EBA will continue monitoring the impact of the IRRBB regulatory package, focusing on NMD modeling, hedging strategies, and potential scope extensions to commercial margin modeling. It will also assess Pillar 3 disclosure practices and track key regulatory elements such as the 5-year cap on NMD repricing maturity and Credit Spread Risk in the Banking Book (CSRBB)-related aspects. Additionally, the EBA will contribute to the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB's) Dynamic Risk Management (DRM) project and evaluate the impact of recalibrated shock scenarios from the Basel Committee.
The EBA publication triggers banks to take action on the four topics outlined above, as well as on hedge accounting (DRM) in the near future. Zanders has extensive relevant experience, and supported on:
- Numerous NMD topics, including modeling, validation and benchmarking. Furthermore, we published a series of whitepapers regarding NMD modeling concepts and approaches, deposit rate dynamics, forward looking perspectives and migration dynamics in deposits that is particularly relevant following this EBA publication.
- Drafting an IRRBB strategy, advising on coupon stripping and developing a hedging strategy, thereby carefully balancing value and NII risks (SOT EVE / NII).
- Validating a hedge accounting framework, developing a hedge account model and hedge accounting outsourcing. Zanders moreover held a survey on DRM as well as published an extensive series of articles on the DRM project of the IASB and its implications for banks.
Contact Jaap Karelse, Erik Vijlbrief (Netherlands, Belgium and Nordic countries) or Martijn Wycisk (DACH region) for more information.
Citations
The European Banking Authority (EBA) has updated its supervisory outlier test (SOT) threshold for a ‘large decline’ in net interest income (NII).

The new threshold is set at a 5% decline of Tier 1 capital, replacing the previous level of 2.5%. The EBA plans to review and update the threshold regularly and may revise the methodology in the longer term. The NII SOT is an additional metric in the supervisory review of institutions’ exposures to interest rate risk in the banking book (IRRBB). The EBA states that a breach would not lead to automatic supervisory measures. Integrating the threshold into institutions’ internal systems would not necessarily require recalibration actions.
This increase in the threshold is not deemed sufficient, however, by the banking sector. According to Risk.net, the sector proposes a 7.5% limit. The EBA has calibrated the limit such that the number of banks violating the Economic Value of Equity (EVE) SOT should be similar as for the NII SOT. The sector claims that a 7.5% NII SOT will ensure this, as the original 2.5% was estimated in a low interest rate environment. The new threshold must still be approved by the European Commission (EC). Without this approval, the status of both the SOT for Economic Value of Equity (EVE) and NII is unclear.
Meanwhile, the European Central Bank (ECB) has started to analyse the unrealized losses that banks (could) face due to the recent interest rate movements. The ECB has requested banks to provide detailed information on their interest rate risk models and how they are affected by rising rates. The ECB states that it will use, among other, the results of the ongoing stress test to analyze the resilience of the banks.
In the broader context of banking supervision, the Financial Stability Institute (FSI) of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) has highlighted the impact of rapid interest rate hikes on banks’ solvency and liquidity positions. Banks’ accounting choices, balance sheet characteristics, and business models play a role in how these effects are experienced. While Pillar 1 sets baseline requirements, rising interest rates and declining asset values expose vulnerabilities that require robust supervision under Pillar 2. Supervisors need to assess risks such as IRRBB and unsustainable business models. Market turmoil has emphasized the need for additional measures, both quantitative and qualitative, to address bank-specific vulnerabilities and enhance risk management. Implementing Pillar 2 consistently across jurisdictions is a challenge, however, that may require further guidance.

BNG Bank, established to offer low-rate loans to the Dutch government and public interest institutions, helps lower the cost of public amenities, but its balance sheet’s sensitivity to financial market fluctuations highlights the need for a robust interest rate risk framework.

BNG Bank was founded more than 100 years ago – firstly under the name Gemeentelijke Credietbank – as a purchasing association with the main task of bundling the financing requirements of Dutch local authorities so that purchasing benefits could be obtained on capital markets. In 1922, the name was changed to Bank voor Nederlandsche Gemeenten and even today the main aim is, in essence, the same. What has changed is the role of local authorities, says John Reichardt, a member of the Board of BNG Bank. He explains: “Over the past few years they have diversified. Many of their responsibilities are now independent or even privatized. Hospitals, electricity boards and housing companies, for example, were in the hands of local authorities but now operate independently. They are, however, still our clients because they provide public services.”
Different to Other Banks
To satisfy the financing requirements of its clients, BNG Bank collects money on the international capital markets to realize ‘bundled’ purchasing benefits. “And we pass these benefits on to our customers,” says Reichardt. “While our customers have become more diverse over time, our product portfolio has widened. Some thirty years ago we became a bank, with a comprehensive banking license, and this meant we could take up short-term loans, make investments, and handle our customers’ payments. We try to be a full-service bank, but then only for services our customers need.”
The state holds half of the shares and the remainder belongs to local authorities and provinces/counties. “Because of this we always have the dilemma: should we go for more profit and more dividend, or should our strong purchasing position be reflected immediately in our prices by means of a moderate pricing strategy? Our goal is to be big in our market – we think we should keep 35 to 50 percent of the total outstanding debt on our balance sheet. We are not striving for maximum profit, and that differentiates us from many other banks. Although we are a private company, we do also feel we are a part of the government,” says Reichardt.
Changed Worlds
BNG Bank has only one branch in The Hague, with 300 employees. The bank has grown considerably, mainly over the past few years. As of the start of the financial crisis, a number of services from other parties have disappeared, so BNG Bank was often called upon to step in. Now, partly as a result of this, it has become one of the systematically important Dutch banks. “From a character point of view, we are more of a middle-sized company, but as far as the balance sheet is concerned, we are a large bank. We earn our money by buying cheaply, but also by trying to pass this on as cheaply as possible to our customers – with a small commission. This brings with it a strong focus on risk management, including managing our own assets and the associated risks. These are partly credit risks, but we have fewer risks than other banks – because, thanks to the government, our customers are usually very creditworthy.”
BNG Bank also runs certain interest rate risks that have to be controlled on a day-to-day basis. “We have done this in a certain way for a long time, but in the meantime the world has changed,” says Hans Noordam, head of risk management at BNG Bank. “So we thought it was time to give the method a face-lift to test whether we are doing it right, with the right instruments and whether we are looking at the right things? We also wanted someone else to take a good look at it.”
So BNG Bank concluded that the interest rate risk framework had to be revised. “Our approach once was state of the art but, as always with the dialectics of progress, we didn’t do enough ourselves to keep up with changes in that respect,” Reichardt explains. “When we looked at the whole management of interest rate risk, on the one hand it was about the departments involved, and on the other hand the measurement system – the instruments we used and everything associated with them used to produce information which enabled decision-making on our position strategy. That is a big project.
Project Harry
Over the past few years various developments have taken place in the area of market risk. When BNG Bank changed its products and methods, various changes also took place in the areas of risk management and valuation, including extra requirements from the regulator. “So we started a preliminary investigation and formed one unit within risk management,” says Reichardt. At the end of 2012, BNG Bank appointed Petra Danisevska as head of risk management/ALM (RM/ALM). “We agreed not to reinvent the wheel ourselves, but mainly to look closely at best market practices,” she says.
Zanders helped us with this. In May 2013 we started an investigation to find out which interest rate risks were present in the bank and where improvement levels could be made.
Petra Danisevska, Head of risk management/ALM (RM/ALM) at BNG Bank
Noordam explains that they agreed on suggested steps with the Asset Liability Committee (ALCO), which also provided input and expressed preferences. A plan was then made and the outlines sketched. To convert that into concrete actions, Noordam says that a project was initiated at the beginning of 2014: Project Harry. “This gets its name from BNG Bank’s location, also the home of a Dutch cartoon character, called Haagse Harry. He was the symbol of the whirlwind which was to whip through the bank,” says Noordam.
Within ALCO Limits
“During the (economic) crisis, all sorts of things happened which influenced the valuation of our balance sheet,” Reichardt explains. “They also had many effects on the measurement of our interest rate risk. We had to apply totally different curves – sometimes with very strange results. Our company is set up in a way that with our economic hedging and our hedge accounting, we can buy for X and pass it on to our customers for X plus a couple of basis points, which during the period of the loan reverts to us. We retain a small amount and on the basis of this pay out a dividend – our model is that simple. However, since the valuations were influenced by market changes, we were more or less obliged to take measures in order to stay within our ALCO limits. These measures, with respect to managing our interest position, would not have been realizable under our current philosophy; simply because they weren’t necessary. We knew we had to find a solution for that phenomenon in the project. After much discussion we were able to find a solution: to be more reliable within the technical framework of anticipating market movements which strongly influence valuation of financial instruments. In other words: the spread risk and the rate risk had to be separately measured and managed from one another. The world had changed and our interest rate risk management, as well as reporting and calculations based upon it, had to as well.”
After revision of the interest rate risk framework, as of the second half of 2015, all interest-rate risk measurements, their drivers and reporting were changed. The market risks as a result of the changes in interest rate curves, were then measured and reported on a daily basis by the RM/ALM department. “There is definitely better management of the interest rate risk; we generate more background data and create more possibilities to carry out analyses,” Danisevska explains. “We now have detailed figures that we couldn’t get before, with which we can show ALCO the risk and the accompanying, assumed return.”
More proactive
Noordam knew that Project Harry would involve a considerable effort. “The risk framework would inevitably suffer quite a lot. It had to be innovated on the basis of calculated conditions, while the implementation required a lot of internal resources and specific knowledge. Technical points had to be solved, while relationships had to be safeguarded; many elements with all sorts of expertise had to be integrated. The European Central Bank was stringent – that took up a lot of time and work. We had an asset quality review (AQR) and a stress test – that was completely new to us. Sometimes we were tempted to stay on known ground, but even during those periods we were able to carry on with the project. We rolled up our shirtsleeves and together we gained from the experience.”
Reichardt says: “It was a tough project for us, with complex subject matter and lots of different opinions. In total it took us seven quarters to complete. However, I think we have accomplished more than we expected at the beginning. With a combination of our own people and external expertise, we have managed to make up for lost ground. We have exchanged the rags for riches and we have been successful. Where do we stand now? As well as the required numbers, we have a clear view of what our thoughts are on ‘what is interest rate risk and what isn’t’. The only thing we still have to do is to fine-tune the roles: what can you expect from risk managers and risk takers, and how will they react to this? We will continue to monitor it. RM/ALM as a department is in any case a lot more proactive – that was an important goal for us. We can be more successful, but the department is really earning its spurs within the bank and that means profit for everyone.”

Ballast Nedam, with support from Zanders’ expertise in hedge accounting and financial valuation, effectively manages financial risks in long-term infrastructure projects through public-private partnerships.

Building houses, mobility, energy and nature – these are the areas in which Ballast Nedam is active. Customers are large and middle-sized companies, private and public. In addition to building roads and houses, the company installs foundations for offshore wind farms, invests in alternative fuel, extracts gravel, and works to make homes more sustainable. Ballast Nedam aims to be involved in the entire life cycle of projects – development, realization, management, recycling, and funding. This enables an integral approach.
An example is the approach of highway A2 through Maastricht, commissioned by the Ministry of Infrastructure and the Environment, where Ballast Nedam, as part of the combination Avenue 2, is working on an integral solution. The tunnel roof of the dual-layered tunnel will become at a later stage a green strip of nature that reconnects the different city parts of Maastricht. Large projects like these will in most cases be executed through a consortium with other contractors, to spread the risk. Just like the Kromhout military base in Utrecht, a project for the Ministry of Defense, with a value of more than EUR 450 million on an area of 19 hectares.
Life cycle thinking and doing
A public-private partnership (PPP), such as the Kromhout military base, is a form of cooperation between the government and one or more parties. In an increasing number of cases, Ballast Nedam is also taking on the responsibility, after the building phase, of management and maintenance. Such outsourcing of the management means clarity and cost savings for the government. For the construction firm, it is a secure source of income, which in certain cases also increases the room to maneuver when designing the project.
In another PPP-project for the construction of the A15 Maasvlakte-Vaanplein highway, the government posed a mobility question and requested a complete solution, starting with a list of concrete demands. This project is about the widening of the A15 at a busy section and the building of a new Botlek bridge. Ballast Nedam is part of the consortium A-Lanes A15, which is responsible for the design, building, and funding of the project plus 20 years of maintenance, with a value of approximately EUR 1.5 billion. Because of the management component, such projects last longer, sometimes even 30 years.
“These sorts of requests, where the government engages in a contract for many years and outsources the management, are relatively new,” explains Bart Buyck, financial controller at Ballast Nedam Concessions.
They have been in the market for about 10 years and have seen strong growth in this sort of contract in the past five years. That is why Ballast Nedam established its Concessions arm to focus on what we call ‘life cycle projects,’ public-private partnerships with a long completion time. Concessions acts within Ballast Nedam as financier. So how can Ballast Nedam finance these large long-duration projects?
Thinking outside the box
For every PPP-project, a Special Purpose Company (SPC) is established. The project is based around that SPC, which is the link between customer, financier, shareholder (Ballast Nedam and other investors), builder, and manager. With all these parties, the SPC concludes agreements. A PPP-project, with a contract value of sometimes hundreds of millions of euros, will for the largest part – 80-90 percent – be funded privately, by a bank. Depending on the size and the risk of the project, Ballast Nedam is involved in a certain portion, varying from 20 to 100 percent.
Ballast Nedam Concessions acts in the SPC as project manager, quality assurance manager, and process manager. Preferably, it will assume responsibility for the entire project. “In that case, you can make a difference at bids,” Buyck says. “If you continue to think inside the box, you will not achieve optimization. Designer, builder, and manager should decide together what the smartest, most efficient solution is. Only by doing so will you be able to break out of the box.”
Interest rate swaps
For the duration of the contract, the customer periodically pays a fixed amount of interest, repayment, and services. Buyck says: “An interest component is included on the customer’s invoice. When offering a PPP-project, you need to consider the impact of that interest rate and hence fix it. The funding is based on a floating interest rate. Because you receive a fixed interest rate and pay a floating interest, an interest rate risk arises. This risk limits financing possibilities and can have a negative effect on the return. To hedge interest rate risks, the SPC concludes an interest rate swap: it pays a fixed rate to the bank and receives a floating interest rate in return. That is how one can hedge that sort of risk.”
With hedged risks, all parties involved know where they stand. But from an accounting perspective, not all conditions will have been met. Ballast Nedam reports as a listed company under IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards). IFRS contains rules for the preparation of annual statements and for other periodical financial reporting.
That is the moment when the expertise of Zanders Valuation Desk is required.
Bart Buyck, financial controller at Ballast Nedam Concessions.
“At this moment we have five of this kind of SPCs. In 2008 we were confronted for the first time with IFRS requirements with regard to the valuation of interest rate hedges on SPCs. We engaged Zanders at that time to value the interest rate swaps. Together we set up and refined the methodology.”
Hedge Accounting
Derivatives like interest-rate swaps have to be valued in the books at market value in accordance with IAS 39. Changes in market value must be accounted for in the profit and loss account. This can cause undesired temporary volatility in the result. To remedy that, IAS 39 allows for hedge accounting; a company can – provided certain conditions are met – put the market value of derivatives temporarily on its balance sheet.
Buyck notes: “Every quarter Zanders performs two things for us. Firstly, they determine the market value of the instrument using current yield curves. Secondly, they apply hedge accounting; they use an effectiveness test to determine the degree to which the hedge instrument is still in line with the premises on which it was originally concluded and the underlying funding position. We provide them with our loan positions and the forecasts for the future.”
If you do not apply hedge accounting, you must account for changes in market value in your profit and loss account. If you do apply hedge accounting and you comply with the requirements, you may put it as a provision on your balance sheet. “It is a very technical and specific area,” Buyck says. “All sorts of things are involved in this; the valuation methodology, the accounting in connection with that and finally the financial reporting both internally and vis-à-vis the auditor. But it does create transparency. Thanks to swaps – while causing accounting complexity – we have secure cash flows. This will make it easier to find funding for all the great projects we are still going to do.”
Zanders’ Valuation Desk provides and validates valuations of financial products for all market segments. In addition, experts study the financial markets and analyze market developments. The valuations and analyses of the Valuation Desk are objective and independent. The services of the Valuation Desk include periodic valuations (for example for commodity derivatives), hedge accounting, research, and support when calculating margin calls.
Would you like to know more? Contact us today.


