
With support for their long-standing hedge accounting models ending in 2025, global asset finance company, DLL, sought a partner capable of not just replicating their existing models but enhancing and futureproofing them – on a tight timeline. To guide the company’s treasury through this critical crossroad, DLL turned to Zanders.

DLL (De Lage Landen) is a global asset finance company headquartered in Eindhoven, the Netherlands, and a wholly owned subsidiary of Rabobank. Operating in more than 25 countries, it delivers leasing and asset-based financing solutions across a variety of industry sectors, including agriculture, construction, energy transition, food, healthcare, industrial, technology, and transportation. With a strong focus on responsible finance, the company supports businesses to access capital, manage risk, and make the transition to more sustainable business models.
Central to the company’s financial infrastructure is its global treasury function, based in Dublin, Ireland. This team manages the liquidity and Treasury risk management needs of the group. The team consists of an experienced group of highly qualified financial services professionals who are dedicated to meeting the treasury needs of DLL, covering everything from cash management to foreign exchange and interest rate hedging.
A critical turning point
A core element of DLL’s risk strategy is the use of interest rate swaps to mitigate exposure to interest rate volatility. Given the size and complexity of its global lending portfolio and the direct impact that interest rate movements can have on company earnings, these instruments are essential for maintaining financial stability and predictability.
“We have two large portfolios – euro interest rate swaps and US dollar interest rate swaps,” explains Coyle, Head of Hedge Accounting at DLL. “To mitigate the fair value movements of those swaps, we run macro fair value hedge accounting models in euros and dollars.”
These models allow DLL to align the value of derivatives with the risks they offset. This reduces earnings volatility, provides a transparent view of the company’s risk position, and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
For years, DLL’s hedge accounting models were developed and maintained by a previous provider. Due to regulatory requirements they were no longer allowed to support the models beyond 2025.
Faced with a tight deadline to transition to a new solution, DLL launched a competitive tender process to identify a partner capable of building fair value macro hedge accounting models for both their euro and dollar swap portfolios. To prevent disruption to DLL’s hedge accounting process, replacement models needed to be ready for testing in early 2025, ahead of full deployment a few months later. This challenging timeline relied on delivering a complete, fully tested and operational solution as quickly as possible, rather than following a more gradual, phased approach.
Zanders’ approach stood out because they proposed building a Python-based application from the start – delivering the end product we needed, and within the timeline that we wanted.
Coyle, Head of Hedge Accounting at DLL.
“Another provider suggested an Excel build first, then a Python version later – essentially two separate projects, which would not only take a lot longer but also impacted on the price as well.”
Rapid prototyping and agile development
Once selected in late 2024, Zanders began working on replicating the models. Despite having no access to the original model’s codebase, the Zanders team was able to reverse engineer DLL’s hedge accounting methodology in just a few weeks based.
“They started in December, and by the end of January we had our first models ready for testing,” Coyle recalls.
From February to March, both Zanders and DLL conducted independent back testing using the legacy model as a benchmark to validate outputs. This rigorous comparison helped ensure consistency and build confidence in the new models.
“This gave us comfort that we were on the right road,” Coyle says. “We did find a few things that we wanted to change – such as adding certain risk controls – and the Zanders team was very open to suggestions. These were implemented quickly, and it was a very easy process.”
By the end of March, the new Python-based applications was fully operational, enabling a seamless transition with no disruption to DLL’s interest rate risk strategy.
Faster, simpler, more integrated
While the primary focus of the project was the replication of DLL’s existing models, it ultimately evolved into an opportunity to streamline and modernize the company’s hedge accountancy processes.
“The new model is much quicker,” explains Marais, Treasury Hedge Accountant at DLL. “The old model had features we didn’t really use that slowed down performance. This was a chance to simplify and focus on what we needed.”
One of the most valuable technical gains was improved alignment with DLL’s internal treasury systems.
“With the new model, we are now able to utilize reports from our own treasury system – that was a significant improvement,” says Marais. Previously, the team had to rely on reports from Rabobank systems and model calculations, but the new model directly interfaces with DLL's internal system. “This makes our work process much quicker and more efficient compared to previously,” Marais adds.
Beyond the technical delivery, the project also stood out for the way it was executed. Working under a tight deadline, collaboration between the teams was critical and made a real difference to the overall experience. The DLL team particularly appreciated Zanders’ responsive and collaborative approach.
IT projects can be quite stressful, but this one was remarkably stress-free. That’s a reflection of a robust, collaborative process and great people. If someone asked whether we’d recommend the Zanders team for a project like this, we wouldn’t hesitate.
Coyle, Head of Hedge Accounting at DLL.
Interested in transforming your treasury infrastructure?
Whether you're navigating regulatory change, replacing legacy models, or looking to gain deeper insights into your risk exposure, Zanders combines advanced modeling with deep industry expertise to deliver accurate and audit-ready valuations.
Find out more about how Zanders can support your treasury and risk management transformation.

Ready to transform your treasury infrastructure?
Contact us
With IFRS 18 introducing fundamental changes to FX reporting, treasuries must act now to prepare for the 2027 compliance deadline.

IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time required in order to be compliant. Treasury Management Systems and ERP platforms must be updated to ensure compliance with new operating, investing, and financing categorizations. Introduced by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) in April 2024, IFRS 18 is required to be implemented by January 2027 at the latest. The new standard addresses how companies classify foreign exchange (FX) gains and losses, particularly affecting treasury operations.
In the past, for simplicity and pragmatic reasons, many organizations reported all FX results as part of operating income. Under IFRS 18 however, guidance on the treatment of these FX results is more explicit and must now be categorized into three groups: operating, investing, and financing dependent on the nature of the underlying exposure.
While this is a simple requirement conceptually, certain challenges may exist in creating a holistic transparent view on the FX impacts, particularly when considering the treatment of FX derivatives. This shift means that businesses must reassess their accounting practices and treasury and hedging strategies to ensure compliance.
Key Changes Under IFRS 18:The primary change in IFRS 18 is the requirement to classify FX gains and losses based on their source:
- Operating: FX results from accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) transactions fall into this category.
- Investing: FX fluctuations linked to investments are recorded here.
- Financing: FX changes related to loans and borrowings belong in this section.
Key Date: Full implementation required by January 2027
The P&L impact from FX derivatives should also be considered in these changes, where the selection of P&L category is determined based on the nature of the exposure. IFRS 18 does allow for the P&L classification from FX derivatives to be entirely posted as Operating in the case where it is not practical to uniquely identify the nature of the underlying exposure.
This may be a common occurrence, specifically in the example of Balance Sheet FX hedging, where it is not common to hedge the individual elements of the balance sheet separately. While posting to Operating for derivatives is easier to achieve, it would create inconsistencies in categorization between the FX result from hedging, and the FX result from source.
The goal of IFRS 18 is to create clearer and more comparable financial statements across different businesses, therefore the treatment of FX results from hedging activities should be carefully considered.
Treasury’s Role in the Transition
The treasury department will play a crucial role in implementing IFRS 18. While the new classification rules are straightforward, their practical application requires an in-depth review of the drivers of FX exposure and the applied hedging strategies. Determining which department takes primary responsibility for IFRS 18 implementation can be challenging. The cross-functional nature of the project requires clear ownership and accountability structures to ensure successful implementation. This coordination challenge makes a strong case for external advisory support to facilitate collaboration between treasury, finance, accounting, and IT teams.
One major challenge of IFRS 18 is the potential mismatch between FX hedging strategies and accounting classifications. Traditionally, companies have managed FX risk through balance sheet hedging, using a single FX deal to cover multiple exposures. However, with the new classification rules, companies may need to adjust their hedging approach to ensure that hedge results align with the appropriate classification.
For example, if a company hedges a foreign currency loan, and the loan’s FX impact is now categorized under financing, the FX gain or loss from the hedge should also be classified under financing. If it remains under operating income, the company may see artificial volatility in financial statements, which could misrepresent its risk management effectiveness.
Operational and Systemic Adjustments
Beyond policy updates, IFRS 18 requires changes to Treasury Management Systems (TMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. These systems must be configured to ensure that FX transactions are correctly classified into operating, investing, or financing categories. This may involve adding new data fields, updating existing reporting structures, or even implementing new hedging processes.
Challenges and Considerations:
Companies may face several key challenges in implementing IFRS 18:
- Instance Structure Differences: Companies must determine how to apply classification rules across different subsidiaries and business units. Classification of operating for a finance company like the Treasury center may differ from that of a regular business operation.
- Chart of Accounts Adjustments: Treasury teams must assess whether existing FX hedging strategies need to be revised.
- System Updates: IT teams must modify TMS and ERP systems to support the new classification structure.
- Cross-Department Coordination: Treasury, finance, and accounting teams must work together to ensure a smooth transition.
How Zanders Can Help
Zanders, a leading treasury advisory firm, offers support to companies transitioning to IFRS 18. Our expertise extends beyond compliance, helping organizations develop effective hedging policies, update financial systems, and align their reporting strategies. Our services include:
- Reviewing FX exposure and hedging strategies.
- Identifying and resolving classification challenges.
- Developing a step-by-step plan for IFRS 18 compliance.
- Assisting with system updates and configuration changes in TMS and ERP platforms.
By addressing IFRS 18 proactively, treasury teams can not only comply with the new standard but also enhance their overall risk management approach. Zanders is committed to helping organizations navigate these changes efficiently.
Conclusion
IFRS 18 represents a significant shift in how FX gains and losses are reported and viewed through accounting principles and hedging strategies. While the standard itself is not overly complex, its impact on hedging and financial reporting requires careful planning, BI preparation, and compliance validation.
With the compliance deadline approaching in January 2027, now is the time to act. Zanders is ready to assist companies in this transition, providing both strategic guidance and practical implementation support to ensure a seamless adaptation to IFRS 18.
To find out more about IFRS 18 and key changes for treasury, please contact Jonathan Tomlinson or Mitchell Ponder.

Since its launch just over a decade ago, Nationaal Warmtefonds has grown from a niche financing platform to a driving force in promoting residential energy efficiency across the Netherlands. Over the last five years, our partnership has deepened and developed, with Zanders reshaping its support to adapt to every operational challenge and growth stage.

Nationaal Warmtefonds was established in 2013 as an experimental fund backed by the Dutch government to help homeowners make their houses more energy efficient. Today, it's a key player in the Netherlands’ climate ambitions, granting over 1.8 billion euro of loans and helping more than 130.000 households make their homes more sustainable.
From cautious beginnings
In the early stages, Nationaal Warmtefonds-backed loans were only offered to homeowners who could afford traditional credit. But in 2015, the Paris Agreement was signed, setting new international climate targets and raising action on energy efficiency to a national priority. This sparked a rapid extension of the fund’s mandate. Notably, the decision was made to expand from financially stable owners to provide access to funding to households with lower incomes. This led to a surge in the scale and impact of the fund.
“Initially the fund grew steadily – in the first year we financed €5 million,” says Ernst Jan Boers, Chairman of Nationaal Warmtefonds. “But within five years, we were doing €150 million a year and it became clear we had to reshape ourselves. The fund was expected to double in size and to support this growth, we needed more than just a loan administrator – we needed the full second and third lines.”
As Nationaal Warmtefonds’ objectives became more ambitious, so did the need for specialist risk management, compliance, and treasury functions. These were services beyond the capabilities of the organization and its existing administrative providers. So, five years ago, the fund set out to find an advisor that could support their growth strategy. This led them to Zanders.
“In the early stages, it was about managing the funds with boots on the ground,” says Ernst Jan.
Zanders offered treasury knowledge, but they were also willing to do the day-to-day work – and the same applied for compliance and risk. We needed a role that we called ‘fund director’ and Zanders filled that position.
Ernst Jan Boers, Chairman of Nationaal Warmtefonds
Tasked with managing the fund, coordinating with other service providers, and supporting the board, the Zanders team was quickly embedded into day-to-day operations, providing advice and hands-on support across risk, compliance, and treasury. And as the fund rapidly grew to over €400 million a year, Zanders’ role also expanded as it helped the fund navigate growth and the challenges it presented.
Navigating the challenges of fund expansion
A strengthening moment in the partnership came with the near collapse of a large, multi-million-euro eco-renovation of an apartment building, involving more than 180 homeowners. When the construction firm went bankrupt mid-way through the build, the future of the project plunged into uncertainty. Zanders played an important role in enabling the project to proceed – mediating between homeowners, authorities, and internal credit committees, while also designing a financial restructuring plan. With this hands-on, credit management, Zanders helped Nationaal Warmtefonds not only rescue the project (it was ultimately completed to almost zero-emission standards) but also reshape future governance and credit approval processes to reduce risk going forward.
Large, high-stakes projects like this highlighted how fast the fund was evolving and how far its role had expanded beyond its original scope.
“We started with a lifetime from 3 to 6 years for the fund,” Ernst Jan reflects. “But if you look at the scale of the transition and how embedded we’ve become in the national climate effort, we’ll likely be doing this work through to 2050.”
The impact of this growth is that the somewhat short-term nature of Nationaal Warmtefonds’ operational structure was no longer sufficient to manage the growing complexity and scale of its role.
“About a two years ago, things were moving so fast and we realized it was time to become a real organization,” admits Ernst Jan. “Up until that point, we had a board of just four people, each working only one or two days a week. Everything was outsourced – risk, finance, and loan administration. We had good controls, but no one on payroll, and not even a physical office. We were becoming too big for that model and, more importantly, we realized we’re not temporary – we’re actually here to stay.”
At this point Nationaal Warmtefonds decided to insource key service providers, and at the same time, the board transitioned from a part-time structure to working three to four days a week.
“As part of this shift, the role of fund director was no longer needed in the same way,” says Ernst Jan.
Zanders continues to support us – especially in areas like risk, compliance, and treasury – but the nature of the support has changed again. It's now more advisory and less operational, because we’ve built the internal structure to handle much of it ourselves.
Ernst Jan Boers, Chairman of Nationaal Warmtefonds
This marks a new, more consultancy-driven era for our partnership, where Zanders empowers Nationaal Warmtefonds with the expertise, guidance and strategic support to continue to grow the fund and proactively manage risk.
Flexible foundations for the future
From providing hands-on crisis management during complex projects to shifting towards a more advisory role as internal capacity grew, Zanders’ support for Nationaal Warmtefonds has evolved in line with the fund’s growth and changing needs. This flexibility has been crucial in navigating the challenges of rapidly scaling the fund as climate action has climbed the national agenda.
Looking to the future, as the energy transition deepens and new challenges arise, our partnership will keep adapting, continually re-balancing operational support with strategic advice to ensure Nationaal Warmtefonds is positioned to respond effectively and continue to drive forward the energy transition in the Netherlands.
To find out more about how we can support the growth strategy of your business and fund, please contact Eva de Lange.

This article outlines key focus areas for an evolving treasury function, detailing how it can effectively support the organization’s growth trajectory and ensure long-term financial resilience.

As mid-sized corporations expand, enhancing their Treasury function becomes essential. International growth, exposure to multiple currencies, evolving regulatory requirements, and increased working capital demands are key indicators of the need for a well-structured Treasury function. These factors heighten the risk of challenges such as limited cash visibility, foreign exchange fluctuations, and a greater need for centralization and diverse financing sources—making a solid policy framework essential. A Treasury function built around a clear Target Operating Model (TOM) is critical for managing this complexity and enabling sustainable growth.
Zanders has deep experience in helping companies of all sizes define and optimize their Treasury TOM—from small businesses to global multinationals. Across industries from pharmaceuticals to manufacturing, we support organizations at every stage of treasury maturity. A well-designed TOM gives you a roadmap to transform Treasury into a strategic, scalable capability.
Benchmarking your Treasury Performance: Know Where You Stand
A treasury benchmark study provides a clear and objective view of how your treasury function compares to peers and industry best practices. It helps to identify strengths, spot inefficiencies, and uncover opportunities to enhance performance and resilience.
This kind of assessment is especially valuable during periods of rapid growth, when your treasury must adapt to increasing complexity. It also proves to be critical during major events such as mergers, acquisitions, or shifts in the market, where quick adaptation is key.
Benchmarking is more than a comparison exercise. It delivers clarity on your current state and defines what’s needed to evolve. That insight becomes the foundation for targeted improvements, stronger risk management, and the development of a TOM that aligns with your organization’s goals.
In the sections below, we outline two key areas to consider and how benchmarking provides the insights needed to build your optimal treasury roadmap.
Strategic Alignment in Action: Optimizing Organizational Structures for Sustainable Growth
As organizations grow, it becomes increasingly important to clearly define treasury responsibilities separately from those of the broader finance function. At the same time, integrating Treasury into the interconnected structure of the Office of the CFO helps build a stronger and more resilient finance organization. A common challenge in change management arises when legacy definitions of roles and responsibilities remain unaddressed. For example, certain processes—such as reconciliation—may continue to be performed within the ERP system simply because “that’s how it’s always been done,” even if it’s no longer the most efficient approach. In some cases, the accounting team may lack the capacity to take ownership of such tasks, resulting in inefficiencies and blurred accountability.
A TOM review creates the opportunity to redefine treasury roles, policies, and processes. This should be revisited regularly to keep it aligned with the organization's structure and goals.
Key Opportunities for Policy and Procedure Optimization:
- Consolidation and Standardization: Implementing unified policies and procedures can enhance efficiency and consistency across the organization. This involves consolidating knowledge, standardizing processes, and ensuring that all departments operate in alignment with organizational goals.
- Enhancing Segregation of Duties: Reviewing and refining the organizational structure can better support the segregation of duties, reducing risks and improving operational integrity. This involves defining clear roles and responsibilities to ensure effective internal controls.
- Streamlining Operations: Centralizing certain activities currently performed locally can lead to streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and reduced costs. Centralization allows for standardized procedures, clearer decision-making processes, and improved resource utilization.
- Strategic Resource Realignment: Redirecting treasury resources from routine operational tasks to strategic initiatives can significantly enhance the treasury's value proposition. By automating non-core activities, the treasury can focus on high-impact projects and internal consulting roles, driving business growth and strategic alignment
Alongside a review and assessment of the organizational structure, a deep dive into the treasury technology landscape of an organization is another key aspect to consider when transforming a treasury.
Technology as a tool
While large organizations typically have an ERP or TMS in place, many small to mid-sized companies have not yet reached that level of maturity. In these organizations, treasury functions often rely heavily on spreadsheets, which can be cumbersome and prone to error. Additionally, treasurers must log into multiple bank portals to gather essential data for reconciliation and forecasting. As the company grows, the time spent on these manual processes increases, along with the risk of mistakes and inefficiencies.
Recognizing the need for modernization, treasurers are increasingly focusing on upgrading treasury technology. As mid-sized corporations scale and face greater financial complexity, the reliance on outdated, custom-developed solutions and manual processes becomes more problematic. This makes the need for an enhanced treasury management system even more critical to efficiently manage financial operations and reduce operational risks.
Key opportunities for a Treasury Technology Upgrade:
- Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: Upgrading to cloud-based treasury management systems (TMS) can provide greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency compared to traditional onsite systems. This allows for easier access and management of treasury operations across different locations and teams.
- Advanced Reporting Capabilities: Real-Time Financial Insights: Implementing a more advanced TMS can address reporting challenges by providing accurate, real-time financial insights. This capability enables treasurers to make timely and informed decisions, enhancing overall financial management and strategic planning.
- Streamlined Operations: Upgrading to a system with seamless integration capabilities can automate processes, reduce operational delays, and minimize errors. This integration ensures that all systems communicate effectively, fostering a more efficient and cohesive treasury environment.
- Efficient Cost Management and Regulatory Compliance: A modern TMS can help achieve significant cost savings and improve compliance by supporting segregation of duties and multi-level approval processes. This ensures adherence to regulatory requirements while optimizing operational expenses.
- Improved Cash Management: Access to real-time data, such as global cash positions, is crucial for effective decision-making and cash management. Upgrading to a system that provides these insights can enhance treasury operations by allowing for proactive management of liquidity and financial risks.
Organizations should carefully evaluate when and how to upgrade their TMS, recognizing signs of inadequacy, understanding the benefits, and identifying essential features. A suitable TMS will not only optimize treasury operations but also provide the necessary tools for effective financial management, maintaining a competitive edge in an evolving landscape.
Build a Strategic Roadmap
With the insights gained from benchmarking, organizations can define their long-term target state and build a tailored solution design. This becomes the foundation for a strategic roadmap that outlines the initiatives needed to elevate your treasury function. Whether the focus is on technology upgrades, process improvements, or resource realignment, each initiative should shape a treasury function that is agile, efficient, and growth ready. A fit-for-purpose treasury is not just a support function; it is a strategic asset that underpins long-term performance and resilience.
If you wish to learn more about how we can support the growth of your organization through the treasury function, please contact Ernest Huizing or Vincent Casterman.

Strengthen strategic decision-making by bridging the FX impact gap. Empower Treasury as a proactive partner in predicting and minimizing global and local FX risks through advanced analytics

In a world of persistent market and economic volatility, the Corporate Treasury function is increasingly taking on a more strategic role in navigating the uncertainties and driving corporate success.
Even in the most mature organizations, the involvement of the Treasury center in FX risk management often begins with collecting forecasted exposures from subsidiaries. However, to fundamentally enhance the performance of the FX risk management process, it is crucial to understand the nature of these FX exposures and their impacts on the upstream business processes where they originate.
Enabling this requires the optimization of the end-to-end FX hedging lifecycle, from subsidiary financial planning and analysis (FP&A) that identifies the exposure to Treasury hedging. Improvements in the exposure identification process and FX impact analytics necessitate the use of intelligent systems and closer cooperation between Treasury and business functions.
Traditional models
While the primary goal of local business units is to enhance the performance of their respective operations, fluctuating FX rates will always directly impact the overall financial results and, in many cases, obscure the true business performance of the entity. A common strategy to separate business performance from FX impacts is to use constant budgeting and planning rates for management reporting, where the FX impact is nullified. These budgeting and planning rates typically reflect the most likely hedged rates achieved by Treasury, considering the hedging policies and forecasted hedging horizons. However, this strategy can lead to unexpected shocks in financial reporting and obscure the impacts of FX exposure forecasting and hedging performance.
When these shocks occur, conclusions about their causes, such as over or under-hedging or unrealistic planning rates, can only be drawn through retrospective analysis of the results. Unfortunately, this analysis often comes too late to address the underlying issues.
The most common Treasury tools used to measure the accuracy of business forecasting are Forecast vs. Forecast and Actual vs. Forecast accuracy reporting. These tools help identify recurring trouble areas that may need improvement. However, while these metrics indicate where forecasting accuracy can be improved, they do not easily translate into a quantification of the predicted or actual financial impact required for business planning purposes.
End-to-End FX risk management in a Treasury 4.x environment
Finance transformation projects, paired with system centralization and standardization, may offer an opportunity to create better integration between Treasury and its business partners, bridging the information gap and providing better insight and early analysis of future FX results. Treasury systems data related to hedging performance, together with improved up-to-date exposure forecasting, can paint a clearer picture of the up-to-date performance against the plan.
While some principles may remain the same, such as using planning and budgeting rates to isolate the business performance for analysis, the expected FX impacts at a business level can equally be analyzed and accounted for as part of the regular FP&A processes, answering questions such as:
- What is the expected impact of over- or under-hedging on the P&L?
- What is the expected impact from late hedging of exposures?
- What is the expected impact from misaligned budgeting and planning rates compared to the achieved hedging rates?
The Zanders Whitepaper, "Treasury 4.x – The Age of Productivity, Performance, and Steering," outlines the enablers for Treasury to fulfill its strategic potential, identifying Productivity, Performance, and Steering as key areas of focus.
In the area of Performance, the benefits of enhanced insights and up-to-date metrics for forecasting the P&L impacts of FX are clear. Early identification of expected FX impacts in the FP&A processes provides both time and opportunity to respond to risks sooner. Improved insights into the causes of FX impacts offer direction on where issues should be addressed. The outcome should be enhanced predictability of the overall financial results.
In addition to increased Performance, there are additional benefits in clearer accountability for the results. In the three questions above, the first two address timely forecasting accuracy, while the third pertains to the Treasury team's ability to achieve the rates set by the organization. With transparent accountability for the FX impact, Treasury gains an additional tool to steer the organization toward improved budgeting processes and create KPIs to ensure effective strategy implementation. This provides a valuable addition to the commonly used forecast vs. forecast exposure analysis, as the FX impacts resulting from that performance can be easily identified.
Conclusion
Although FP&A processes are crucial for clear strategic decision-making around business operations and financial planning, the FX impact—potentially a significant driver of financial results—is not commonly monitored with the same extent and detail as business operations metrics.
Improving the FX analytics of these processes can largely bridge the information gap between business performance and financial performance. This also allows Treasury to be utilized as a more engaged business partner to the rest of the operations in the prediction and explanation of FX impact, while providing strategic direction on how these impacts can be minimized, both globally and at local operations levels.
Implementing such an end-to-end process may be intimidating, but data and technology improvements embraced in the context of finance transformation projects may open the door to exploring these ideas. With cooperation between Treasury and the business, a true end-to-end FX risk management process may be within reach.

Discover the full potential of bank connectivity with EBICS. From strategies for secure and cost-efficient bank connectivity to tips and quick wins and an update on EBICS 3.0, this article provides food for thought for sustainable and secure banking architecture.

Security in payments is a priority that no corporation can afford to overlook. But how can bank connectivity be designed to be secure, seamless, and cost-effective? What role do local connectivity methods play today, and how sustainable are they? This article provides an overview of various bank connectivity methods, focusing specifically on the Electronic Banking Internet Communication Standard (EBICS). We'll examine how EBICS can be integrated into global bank connectivity strategies, while comparing it to alternative methods. The following section offers a comparison of EBICS with other connectivity solutions.
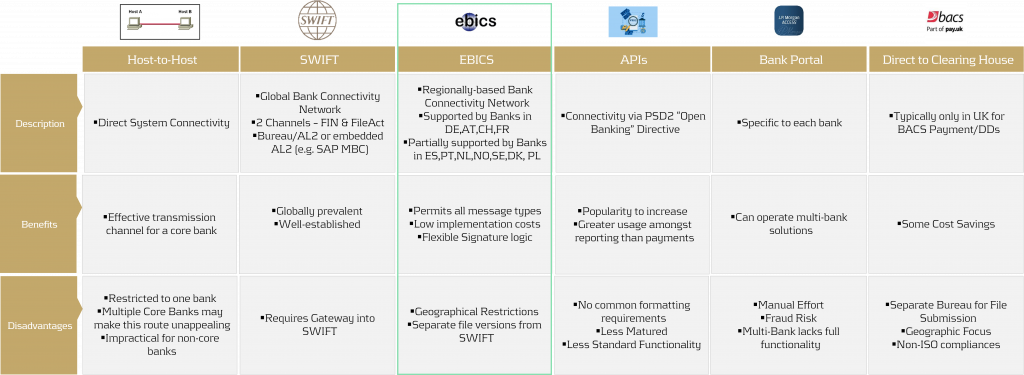
For a comprehensive overview of bank connectivity methods, including insights from an SAP perspective, we recommend the article Bank connectivity – Making the right choices.
Compared to alternatives, EBICS contracts are cost-effective, and EBICS connectors, along with supporting online banking software, are equally affordable. Whether through standalone solutions provided directly by banks or SAP ERP-integrated systems, EBICS consistently proves to be the most cost-effective option when compared to SWIFT or individual host-to-host connections.
The downside of EBICS? Outside the GSA region (Germany, Switzerland, Austria) and France, there are significant variations and a more diverse range of offerings due to EBICS' regional focus. In this article, we explore potential use cases and opportunities for EBICS, offering insights on how you can optimize your payment connectivity and security.
EBICS at a Glance
EBICS, as a communication standard, comes with three layers of encryption based on Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). In addition to a public and a private key, so-called EBICS users are initialized, which can present a significant advantage over alternative connection forms. Unlike Host-to-Host (H2H) and SWIFT, which are pure communication forms, EBICS has an intelligent signature process integrated into its logic, following the signing process logic in the GSA region. EBICS, developed by the German banking industry in 2006, is gaining increasing popularity as a standardized communication protocol between banks and corporates. The reason for this is simple—the unbeatable price-performance ratio achieved through high standardization.
Furthermore, EBICS offers a user-specific signature logic. Primary and secondary signatures can be designated and stored in the EBICS contract as so-called EBICS users. Additionally, deliveries can be carried out with so-called transport users (T-transport signature users).
In practice, the (T) transport signature user is used for tasks such as retrieving account statements, protocols, or sending payments as a file without authorization.
It is worth noting that for the intelligent connectivity of third-party systems or even service providers that create payments on behalf of clients, the T user can be utilized. For example, an HR service provider can send an encrypted payment file using the provided T user to the bank server. The payment file can be viewed and signed separately on the bank server via the relevant treasury or EBICS-compatible banking software.
Furthermore, through EBICS, individual records and thus personal data in the case of HR payments can be technically hidden. Only header data, such as the amount and the number of items, will be visible for approver.
Is the signature logic too maintenance-intensive? Fortunately, there is an alternative available to the maintenance of individual users. A so-called Corporate Seal User can be agreed upon with the bank. In this case, the bank issues an EBICS user based on company-related data in the (E) Single signature version. The (E) signature is transmitted directly to the bank for every internally approved payment, which is comparable to connectivity via SWIFT or Host-to-Host.
Strategic Adjustments with EBICS
Regional standards like EBICS can be used to connect regional banks and send or receive messages over the bank's internal SWIFT network through a so-called request for forwarding, also known as European Gateway or SWIFT Forwarding. Using this service, it is not necessary to connect every bank directly via Host-to-Host or SWIFT in order to become cost-efficient in your corporate banking.
A SWIFT Forwarding agreement is drafted and signed with your individual bank. Payment files are sent to the bank via a defined order type intended solely for forwarding. The bank acts here as a mere transmitter of the message. Incidentally, the same principle can also be adapted for account statements. Several banks in the GSA-region and France proactively market the service as an additional cash management service to their corporate customers. Account statements are centrally collected via the bank's SWIFT network and sent to the corporate via the existing EBICS channel. This procedure saves implementation efforts and simplifies the maintenance.
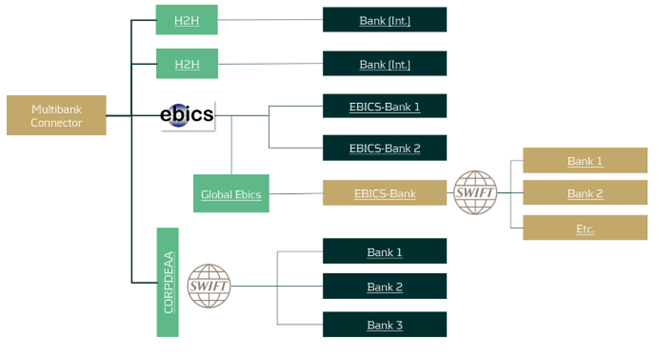
We like to summarize the advantages and disadvantages of integrating SWIFT forwarding via the EBICS channel:
Advantages
- High maintenance Host-to-Host connections are avoided.
- A dedicated SWIFT connection can be avoided without neglecting the benefits.
Disadvantages
- A bank with a well-developed interbank network is required.
- Transport fees per message may apply.
In general, corporates can take advantage of this specific EBICS setup when dealing with banks that manage a small portion of their transaction volume or when the technical connections with certain banks are more challenging. This approach is especially beneficial for banks that are difficult to access through local connectivity methods and have medium-to-low transaction volumes. However, for banks with high transaction volumes, connectivity via Host-to-Host or even a dedicated SWIFT connection may be more appropriate. Each situation is unique, and we recommend evaluating the best banking connectivity setup on a case-by-case basis to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Future of EBICS: Changes Until 11/2025
Since November 2023, banks have been offering EBICS 3.0 as the most recent and up-to-date version. This version is binding in the GSA (Germany, Switzerland, Austria) region until approximately November 2025.
Here is a summary of the most important changes:
- Increased Standardization: Local EBICS “flavors” are unified to simplify implementation.
- Enhanced Encryption: Since version 2.5, the minimum encryption level has been 2048 bits. This is continuously increased with the EBICS 3.X version.
- XML Only for EBICS-specifics: Protocols like PTK are migrated to pain.002 HAC.
The new version of EBICS increases the security of the communication standard and makes it more attractive in the EU given its updates. In addition to Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and France, we observe the communication standard is increasingly offered by banks in Spain, Portugal, the Netherlands, as well as in the Nordic countries. Recently, the first banks in Poland have started to offer this communication standard–a rising trend.
In summary, EBICS is a cost-effective and powerful standard that can do much more than just bank connectivity. For companies that mainly use Host-to-Host or SWIFT for bank connectivity within the Eurozone, it may be worthwhile to look at EBICS and consider switching their connectivity method, provided their banking partner offers EBICS.

We explore six common challenges facing treasuries today and how Zanders’ Treasury Business Services could help you to ride out the storm.

In brief
- Despite an upturn in the economic outlook, uncertainty remains ingrained into business operations today.
- As a result, most corporate treasuries are experiencing operational challenges that are beyond their control.
- Treasuries that adapt by embedding more resilience and flexibility into their operations will be the ones that forge ahead.
- Zanders created Treasury Business Services to provide a customizable suite of niche expertise and flexible resourcing options for treasuries.
Treasuries today are expected to adapt faster than ever to challenges that are largely beyond their control. Here we outline the six most pressing issues affecting treasuries today that you not only need to be aware of, but also proactively planning for.
The financial headwinds that have weighed down on investment activity, liquidity, and returns in recent times are gradually easing. And while optimism is creeping back into our outlooks, it’s not necessarily an end to uncertainty for treasury teams. That appears to be here to stay. Talent shortages, a more transient workforce, an expanding treasury role, large-scale digitalization, the lingering impact of recent global crises and unexpected opportunities too. Deeply engrained uncertainty means there are a lot of plates to keep spinning when you’re running a treasury function today. The following six challenges are making this balancing act more arduous for the corporate treasurer, emphasizing the urgent need to build greater resilience and agility into their operations.
1. Peak load scenarios where performance is non-negotiable
There are situations where treasury simply must deliver. Period. Even when it does not have the resources. M&A and IT-related projects are good examples but there are many more. When these peak load scenarios occur, treasuries need to be prepared to handle them in a fast, flexible, and efficient way.
2. Demand for specialist treasury IT knowledge
A 2023 Treasury Technology survey found 53% of respondents were already using a TMS and a further 16% planned to implement within the next two years. It’s undeniable that technology now commands a dominant role in treasury processes, with investment in ERPs, TMSs, payment factories and e-banking portals a priority across the industry. However, the talent to implement and manage these complex IT systems is scarce, and costly to recruit and retain. And even when someone with the right skills and experience is identified and convinced to join, it often becomes apparent that a dedicated full-time employee might be excessive for the requirements of the role. This makes it even more difficult to fill this critical skills gap effectively and cost-efficiently.
3. The paradox of lowering labor costs while delivering more
Treasury has never been a department with a high headcount, but it’s still not immune to company-wide edicts to reduce labor expenditure. In this cost-cutting environment, the best most treasuries can hope for is a cap on their existing headcount. So, while treasuries are increasingly called on to deliver more and faster, they’re required to perform this expanded role without increasing headcount.
4. The evolution from a cost center to a performance-oriented business partner
Like the rest of your company, treasury must show a tangible contribution to the improvement of productivity and performance. This was the subject of our recent white paper – Treasury 4.x, the Age of Productivity, Performance & Steering. There are lots of ways to enable treasury to transition into this new more value-driven role – from introducing more automation, improving methodologies, and increasing use of data, to outsourcing certain activities. But all this comes with additional demands on budget, skills, and resources.
5. The talent pool isn’t sufficient to keep treasuries today afloat
The 2023 Association for Financial Professionals (AFP) Compensation Report suggests it has become increasingly difficult to fill open treasury positions. According to the survey, almost 60% of treasury and finance professionals said their organization was tackling a talent shortage. There are many reasons given for this. A competitive job market is certainly a dominant cause (as stated by 73% of organizations in the survey). But treasury is also facing a dearth of candidates with the necessary skills for their roles (indicated by 47% of organizations in the survey). As a result, treasury talent shortages are not only due to the general demographic challenges affecting all companies but also because treasury remains underrepresented in the higher education system.
6. A continually expanding treasury agenda
ESG, increased regulatory demands, the burden of administering digital payments – a constantly shifting treasury landscape not only requires additional resources but also niche skillsets and significant cross-departmental collaboration. In addition, the unprecedented challenges businesses have faced in recent years have placed a spotlight on treasury management as a critical resource for businesses. In 2022, an AFP survey found 35-43% treasury professionals were reporting a consistent increase in communication between treasury and the CFO. Further to this, a 2023 TIS survey found almost 50% of treasury professionals have become strategic partners with the CFO. This is further fueling an expanded and more complex treasury agenda, creating another pressure on skillsets and resources.
Uncertainty meets its match
These challenges are triggering uncertainty in treasuries. Do you have the resources and skill profiles you need? How can you give your team more bandwidth to deliver a constantly expanding treasury role? Who is going to manage the TMS you’ve just implemented? And what would happen if you unexpectedly lost a member of your team? We created our Treasury Business Services solution to support you as you maneuver uncertainty, enabling you to execute rapid performance improvements when you need them most.
TBS is a special unit of Zanders offering a wide range of niche treasury expertise and flexible resourcing options to treasuries. From running your treasury-IT platform and covering routine back-office tasks, to taking care of highly specialized activities and filling your temporary resource needs – our service is deliberately broad to give you optimal flexibility and more control to shape the support you need.
To find out more contact Carsten Jäkel.

Unlock Treasury Efficiency: Exploring SAP’s GROW and RISE Cloud Solutions

As organizations continue to adapt to the rapidly changing business landscape, one of the most pivotal shifts is the migration of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to the cloud. The evolution of treasury operations is a prime example of how cloud-based solutions are revolutionizing the way businesses manage their financial assets. This article dives into the nuances between SAP’s GROW (public cloud) and RISE (private cloud) products, particularly focusing on their impact on treasury operations.
The "GROW" product targets new clients who want to quickly leverage the public cloud's scalability and standard processes. In contrast, the "RISE" product is designed for existing SAP clients aiming to migrate their current systems efficiently into the private cloud.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
The public cloud, exemplified by SAP's "GROW" package, operates on a shared infrastructure hosted by providers such as SAP, Alibaba, or AWS. Public cloud services are scalable, reliable, and flexible, offering key business applications and storage managed by the cloud service providers. Upgrades are mandatory and occur on a six-month release cycle. All configuration is conducted through SAP Fiori, making this solution particularly appealing to upper mid-market net new customers seeking to operate using industry-standard processes and maintain scalable operations.
In contrast, the private cloud model, exemplified by the “RISE” package, is used exclusively by a single business or organization and must be hosted at SAP or an SAP-approved hyperscaler of their choice. The private cloud offers enhanced control and security, catering to specific business needs with personalized services and infrastructure according to customer preferences. It provides configuration flexibility through both SAP Fiori and the SAP GUI. This solution is mostly preferred by large enterprises, and many customers are moving from ECC to S/4HANA due to its customizability and heightened security.
Key Differences in Cloud Approaches
Distinguishing between public and private cloud methodologies involves examining factors like control, cost, security, scalability, upgrades, configuration & customization, and migration. Each factor plays a crucial role in determining which cloud strategy aligns with an organization's vision for treasury operations.
- Control: The private cloud model emphasizes control, giving organizations exclusive command over security and data configurations. The public cloud is managed by external providers, offering less control but relieving the organization from day-to-day cloud management.
- Cost: Both the public and private cloud operate on a subscription model. However, managing a private cloud infrastructure requires significant upfront investment and a dedicated IT team for ongoing maintenance, updates, and monitoring, making it a time-consuming and resource-intensive option. Making the public cloud potentially a more cost-effective option for organizations.
- Security: Both GROW and RISE are hosted by SAP or hyperscalers, offering strong security measures. There is no significant difference in security levels between the two models.
- Scalability: The public cloud offers unmatched scalability, allowing businesses to respond quickly to increased demands without the need for physical hardware changes. Private clouds can also be scaled, but this usually requires additional hardware or software and IT support, making them less dynamic.
- Upgrades: the public cloud requires mandatory upgrades every six months, whereas the private cloud allows organizations to dictate the cadence of system updates, such as opting for upgrades every five years or as needed.
- Configuration and Customization: in the public cloud configuration is more limited with fewer BAdIs and APIs available, and no modifications allowed. The private cloud allows for extensive configuration through IMG and permits SAP code modification, providing greater flexibility and control.
- Migration: the public cloud supports only greenfield implementation, which means only current positions can be migrated, not historical transactions. The private cloud offers migration programs from ECC, allowing historical data to be transferred.
Impact on Treasury Operations
The impact of SAP’s GROW (public cloud) and RISE (private cloud) solutions on treasury operations largely hinges on the degree of tailoring required by an organization’s treasury processes. If your treasury processes require minimal or no tailoring, both public and private cloud options could be suitable. However, if your treasury processes are tailored and structured around specific needs, only the private cloud remains a viable option.
In the private cloud, you can add custom code, modify SAP code, and access a wider range of configuration options, providing greater flexibility and control. In contrast, the public cloud does not allow for SAP code modification but does offer limited custom code through cloud BADI and extensibility. Additionally, the public cloud emphasizes efficiency and user accessibility through a unified interface (SAP Fiori), simplifying setup with self-service elements and expert oversight. The private cloud, on the other hand, employs a detailed system customization approach (using SAP Fiori & GUI), appealing to companies seeking granular control.
Another important consideration is the mandatory upgrades in the public cloud every six months, requiring you to test SAP functionalities for each activated scope item where an update has occurred, which could be strenuous. The advantage is that your system will always run on the latest functionality. This is not the case in the private cloud, where you have more control over system updates. With the private cloud, organizations can dictate the cadence of system updates (e.g., opting for yearly upgrades), the type of updates (e.g., focusing on security patches or functional upgrades), and the level of updates (e.g., maintaining the system one level below the latest is often used).
To accurately assess the impact on your treasury activities, consider the current stage of your company's lifecycle and identify where and when customization is needed for your treasury operations. For example, legacy companies with entrenched processes may find the rigidity of public cloud functionality challenging. In contrast, new companies without established processes can greatly benefit from the pre-delivered set of best practices in the public cloud, providing an excellent starting point to accelerate implementation.
Factors Influencing Choices
Organizations choose between public and private cloud options based on factors like size, compliance, operational complexity, and the degree of entrenched processes. Larger companies may prefer private clouds for enhanced security and customization capabilities. Startups to mid-size enterprises may favor the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of public clouds during rapid growth. Additionally, companies might opt for a hybrid approach, incorporating elements of both cloud models. For instance, a Treasury Sidecar might be deployed on the public cloud to leverage scalability and innovation while maintaining the main ERP system on-premise or on the private cloud for greater control and customization. This hybrid strategy allows organizations to tailor their infrastructure to meet specific operational needs while maximizing the advantages of both cloud environments.
Conclusion
Migrating ERP systems to the cloud can significantly enhance treasury operations with distinct options through SAP's public and private cloud solutions. Public clouds offer scalable, cost-effective solutions ideal for medium-to upper-medium-market enterprises with standard processes or without pre-existing processes. They emphasize efficiency, user accessibility, and mandatory upgrades every six months. In contrast, private clouds provide enhanced control, security, and customization, catering to larger enterprises with specific regulatory needs and the ability to modify SAP code.
Choosing the right cloud model for treasury operations depends on an organization's current and future customization needs. If minimal customization is required, either option could be suitable. However, for customized treasury processes, the private cloud is preferable. The decision should consider the company's lifecycle stage, with public clouds favoring rapid growth and cost efficiency and private clouds offering long-term control and security.
It is also important to note that SAP continues to offer on-premise solutions for organizations that require or prefer traditional deployment methods. This article focuses on cloud solutions, but on-premises remains a viable option for businesses that prioritize complete control over their infrastructure and have the necessary resources to manage it independently.
If you need help thinking through your decision, we at Zanders would be happy to assist you.

Commodity risk management has become a top CFO priority in some companies recently. Mastering commodity risk requires an integrated approach across business functions. SAP’s comprehensive solution can make a difference.

The recent periods of commodity price volatility have brought commodity risk management to the spotlight in numerous companies, where commodities constitute a substantial component of the final product, but pricing arrangements prevented a substantial hit of the bottom line in the past calm periods.
Understanding Commodity Risk Management is ingrained in the individual steps of the whole value chain, encompassing various business functions with different responsibilities. Purchasing is responsible for negotiating with the suppliers: the sales or pricing department negotiates the conditions with the customers; and Treasury is responsible for negotiating with the banks to secure financing and eventually hedge the commodity risk on the derivatives market. Controlling should have clarity about the complete value chain flow and make sure the margin is protected. Commodity risk management should be a top item on the CFO's list nowadays.
SAP's Solution: A Comprehensive Overview

Each of these functions need to be supported with adequate information system functionality and integrated well together, bridging the physical supply chain flows with financial risk management.
SAP, as the leading provider of both ERP and Treasury and risk management systems, offers numerous functionalities to cover the individual parts of the process. The current solution is the result of almost two decades of functional evolution. The first functionalities were released in 2008 on the ECC 6.04 version to support commodity price risk in the metal business. The current portfolio supports industry solutions for agriculture, oil, and gas, as well as the metal business. Support for power trading is considered for the future. In the recent releases of S/4HANA, many components have been redeveloped to reflect the experience from the existing client implementations, to better cover the trading and hedging workflow, and to leverage the most recent SAP technological innovations, like HANA database and the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP).
Functionalities of SAP Commodity Management
Let us take you on a quick journey through the available functionalities.
The SAP Commodity Management solution covers commodity procurement and commodity sales in an end-to-end process, feeding the data for commodity risk positions to support commodity risk management as a dedicated function. In the logistics process, it offers both contracts and orders with commodity pricing components, which can directly be captured through the integrated Commodity Price Engine (CPE). In some commodity markets, products need to be invoiced before the final price is determined based on market prices. For this scenario, provisional and differential invoicing are available in the solution.
The CPE allows users to define complex formulas based on various commodity market prices (futures or spot prices from various quotation sources), currency exchange translation rules, quality and delivery condition surcharges, and rounding rules. The CPE conditions control how the formula results are calculated from term results, e.g., sum, the highest value, provisional versus final term. Compound pricing conditions can be replicated using routines: Splitting routines define how the formula quantity will be split into multiple terms, while Combination routines define how multiple terms will be combined together to get the final values.
Pricing conditions from active contracts and orders for physical delivery of commodities constitute the physical exposure position. Whether in procurement, in a dedicated commodity risk management department, or in the treasury department, real-time recognition and management of the company’s commodity risk positions rely on accurate and reliable data sources and evaluation functionalities. This is provided by the SAP Commodity Risk Management solution. Leveraging the mature functionalities and components of the Treasury and Risk Management module, it allows for managing paper trades to hedge the determined physical commodity risk position. Namely, listed and OTC commodity derivatives are supported. In the OTC area, swaps, forwards, and options, including the Asian variants with average pricing periods, are well covered. These instruments fully integrate into the front office, back office, and accounting functionalities of the existing mature treasury module, allowing for integrated and seamless processing. The positions in the paper deals can be included within the existing Credit Risk Analyser for counterparty risk limit evaluation as well as in the Market Risk Analyser for complex market risk calculations and simulations.
Managing Commodity Exposures
Physical commodity exposure and paper deals are bundled together via the harmonized commodity master data Derivative Contract Specification (DCS), representing individual commodities traded on specific exchanges or spot markets. It allows for translating the volume information of the physical commodity to traded paper contracts and price quotation sources.
In companies with extensive derivative positions, broker statement reconciliation can be automated via the recent product SAP Broker Reconciliation for Commodity Derivatives. This cloud-based solution is natively integrated into the SAP backend to retrieve the derivative positions. It allows for the automatic import of electronic brokers' statements and automates the reconciliation process to investigate and resolve deviations with less human intervention.
To support centralized hedging with listed derivatives, the Derivative Order and Trade execution component has been introduced. It supports a workflow in which an internal organizational unit raises a Commodity Order request, which in turn is reviewed and then fully or partially fulfilled by the trader in the external market.
Innovations in SAP Commodity Management
Significant innovations were released in the S/4HANA 2022 version.
The Commodity Hedge Cockpit supports the trader view and hedging workflow.
In the area of OTC derivatives (namely commodity swaps and commodity forwards), the internal trading and hedging workflow can be supported by Commodity Price Risk Hedge Accounting. It allows for separating various hedging programs through Commodity Hedging areas and defining various Commodity Hedge books. Within the Hedge books, Hedge specifications allow for the definition of rules for concluding financial trades to hedge commodity price exposures, e.g., by defining delivery period rules, hedge quotas, and rules for order utilization sequence. Individual trade orders are defined within the Hedge specification. Intercompany (on behalf of) trading is supported by the automatic creation of intercompany mirror deals, if applicable.
Settings under the hedge book allow for automatically designating cash flow hedge relationships in accordance with IFRS 9 principles, documenting the hedge relationships, running effectiveness checks, using valuation functions, and generating hedge accounting entries. All these functions are integrated into the existing hedge accounting functionalities for FX risk available in SAP Treasury and Risk Management.
The underlying physical commodity exposure can be uploaded as planned data reflecting the planned demand or supply from supply chain functions. The resulting commodity exposure can be further managed (revised, rejected, released), or additional commodity exposure data can be manually entered. If the physical commodity exposure leads to FX exposure, it can be handed over to the Treasury team via the automated creation of Raw exposures in Exposure Management 2.0.
Modelled deals allow for capturing hypothetical deals with no impact on financial accounting. They allow for evaluating commodity price risk for use cases like exposure impact from production forecasts, mark-to-intent for an inventory position (time, location, product), and capturing inter-strategy or late/backdated deals.
Even though a separate team can be responsible for commodity risk management (front office) - and it usually is - bundling together the back office and accounting operations under an integrated middle and back office team can help to substantially streamline the daily operations.
Last but not least, the physical commodity business is usually financed by trade finance instruments. SAP has integrated Letters-of-Credit, as well as Guarantees into the Treasury module and enhanced the functionality greatly in 2016.
All-in-all, every commodity-driven business, upstream or downstream, consumer or producer, works under different setups and business arrangements. The wide variety of available functionalities allows us to define the right solution for every constellation. Especially with commodity management functionalities active in the supply chain modules of the ERP system, SAP commodity risk management can offer a lot of efficiencies in an integrated and streamlined solution. We are happy to accompany you on the journey of defining the best solution for your enterprise.

Mergers, divestments, and other M&A activities reshape Treasury management, posing strategic challenges for Treasurers as they navigate disentanglement and build Treasury functions for stand-alone companies.

The corporate landscape is continuously reshaped by strategic realignments such as mergers, divestments, and other M&A activities, wherein a company divests a portion of its business or acquires other businesses to refocus its operations or unlock shareholder value. These transactions greatly affect Treasury management, influencing cash flow, banking structures, financial risk management, financing, and technology. This article explores the challenges Treasurers face during the disentanglement or carve-out process, emphasizing the need for strategic realignment of Treasury activities and focusing on the Treasury perspective of a divesting company. It acknowledges the transitional complexities that arise and the demand for agile response strategies to safeguard against financial instability. We will have a look at the special carve-out situation of building a Treasury function for a stand-alone company in a second part of this article.
Treasury Challenges in Carve-Out Situations
In the dynamic world of corporate restructuring, carve-outs present both a new frontier of opportunity and a multifaceted challenge for Treasurers. While divesting a part of an organization can streamline focus and potentially increase shareholder value, it can place unique pressures on treasury management to reassess and realign financial strategies.
When a corporation decides to execute a carve-out, the Treasury immediately takes on the critical task of separating financial operations and managing transitional service agreements. From the perspective of the divesting company, preserving liquidity and ensuring compliance with financial covenants is a key priority. This intricate division process demands the disentanglement of complex cash flows, re-evaluation and unwinding of cash pooling and internal as well as external debt structures, as well as a review of financial risk and investment policies. Such an endeavour requires rigorous planning and flawless execution to ensure that operational continuity is maintained. Additionally, it requires going into the details, such as the allocation of planning objects (e.g., vendor contracts, machines, vehicles) to the right business for purposes of liquidity forecasting.
Our experience shows that factors like company revenue, industry complexity, and operating countries affect the volume and frequency of treasury transactions. This can increase complexity and workload, especially for intricate transactions. An interesting remark is that carve-out transactions also impact the remaining group. Potentially, the geographic footprint is smaller, or the number of individual business models within the group is less than before – with a significant impact on Treasury.
The Role of Technology in Carve-Outs
A key component in the disentanglement process is represented by Treasury technology. In evaluating treasury technology during a carve-out, scrutiny of the landscape and meticulous planning are paramount to ensuring a smooth transition. The systems must not only handle specific needs such as segmenting data, independent entity reporting, and tracking discrete cash flows and risks, but they must also facilitate a seamless detachment and swift reconfiguration for the newly autonomous entities in the course of the disentanglement of a business. It is essential that these systems support operational independence and continuity with minimal disruptions during the restructuring process.
Implementing the right technology for the new entity, e.g., to cover stand-alone requirements, is crucial. It must meet current transaction needs and be robust enough to handle future demands. Given our breadth of experience across various technological domains and in various M&A scenarios, we have enriched many discussions on which solutions possess the adaptability and scalability necessary to accommodate the evolving needs of a redefined business. 'Right-sizing' the systems, structures, and processes, tailored specifically to the unique contours of the carved-out entity, is a decisive factor for laying the groundwork for sustainable success post-divestiture.
Strategic Realignment for Treasury
Any M&A transaction significantly changes the Treasury Process Map for both the remaining group and the carved-out entity. It has inherited risk and different risk types. We think that Treasury should deal with operational risks first, such as filling resource needs and/or stabilizing business operations. The resource issue requires an analysis of the available employees and their specific skill sets. Onboarding interim resources and back-filling resource gaps until the onboarding of dedicated new staff are alternative options to cover shortfalls.
The operational issue focuses on the impact on cash management and payment operations. Treasury needs to assess the impact on the existing banking and cash management structure and on liquidity as funds received by one entity are required by another. Bank relationships are foundational to Treasury operations and must be revisited and sometimes reinvented. Treasuries must work diligently to maintain trust and communication with old and new banking partners, articulating changes in the company's profile, needs, objectives, and strategies. Beyond negotiation and administration, the process often entails renegotiating terms and ensuring that the newly formed entity's financial needs will continue to be met effectively. The technical and operational ability to execute and receive payments through the company’s (new) bank accounts is a core requirement, which needs to be at the top of the list of priorities. Next, centralization of liquidity and cash structures is essential to avoid cash drag if inflows cannot be invested and/or concentrated in a relatively short time.
Treasury may also deal with different types of financial risk, such as interest rate or foreign exchange exposures. The financial risk management perspective is a crucial one for companies, but in the context of carve-out activities, it is often a second-order priority (depending on the financial risk profile of a company). However, proper identification and assessment of financial risk shall always be a top priority in a disentanglement process. Process implementation can be approached following the establishment of sound business and treasury processes if there is no significant financial risk.
If your organization is contemplating or in the midst of a carve-out, contact Zanders for support. Our consultative expertise in Treasury is your asset in ensuring financial stability and strategic advantage during and post-carve-out. Let Zanders be your partner in transforming challenges into successes.


