But to seize the opportunities ESG must become an integrated part of a bank’s strategy, risk management and disclosure regimes. High-quality data is instrumental to identify and measure ESG risks, but it can be lacking. FIs need to improve their internal data and use of external private and public vendors like Moody’s or the IMF, while developing a framework that plugs any data gaps.
The lack of appropriate ESG data is considered one of the main challenges for many FIs, but proxies, such as using a building’s energy rating to work out its carbon emissions, can be used.
FIs need climate change-related data that isn’t always available if you don’t know where to look. This article will give you an overview of the most relevant data vendors and provide suggestions on how to treat missing data gaps in order to get a comprehensive ESG framework for the green future where carbon measurement, assessment, reporting and trading will be vital
The data challenge
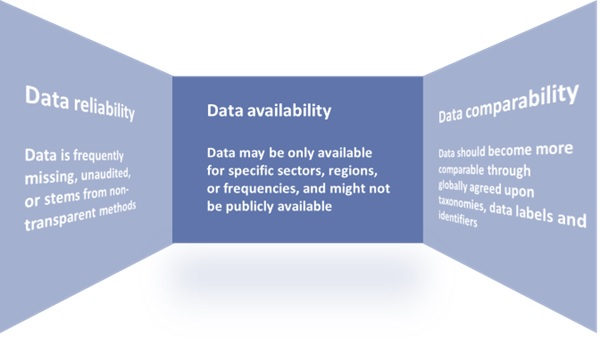
In May 2021, the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) published a ‘Progress report on bridging data gaps’. In this report, the NGFS writes that meeting climate-related data needs is a challenge that can be described along the following three dimensions:
- data availability,
- reliability,
- & comparability.
A further breakdown of the challenges related to these dimensions can be found in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The dimensions of the climate-related data challenge.
Source: Graphic adapted by Zanders from a NGFS report entitled: ‘Progress report on bridging data gaps’ (2021).
Key financial metrics
The NGFS writes that a mix of policy interventions is necessary to ensure climate-related data is based on three building blocks:
- Common and consistent global disclosure standards.
- A minimally accepted global taxonomy.
- Consistent metrics, labels, and methodological standards.
EU Taxonomy, CSRD & EBA’s 3 ESG risk disclosure standards
Several initiatives have started to ignite these needed policy interventions. For example, the EU Taxonomy, introduced by the European Commission (EC), is a classification system for environmentally sustainable activities. In addition, the recently approved Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) provides ESG reporting rules for large listed and non-listed companies in the EU, including several FIs. The aim of the CSRD is to prevent greenwashing and to provide the basis for global sustainability reporting standards. Another example of a disclosure standard is the binding standards on Pillar 3 disclosures on ESG risks developed by the European Banking Authority (EBA).
Even though policy, law and regulation makers have a big part to play in the data challenge, there are also steps that individual institutions could and should take to improve their own ESG data gaps. Regulatory bodies such as the EBA and the European Central Bank (ECB) have shared their expectations and recommendations on the management of ESG data with FIs.
To illustrate, the EBA recommends FIs “[identify] the gaps they are facing in terms of data and methodologies and take remedial action” and the ECB expects institutions to “assess their data needs in order to inform their strategy-setting and risk management, to identify the gaps compared with current data and to devise a plan to overcome these gaps and tackle any insufficiencies”
Collecting data
Collecting ESG data is a challenging exercise. A distinction can be made between collecting data for large market cap companies, and small cap companies and retail clients. Although large cap companies tend to be more transparent, the data often is dispersed over multiple reports – for example, corporate sustainability reports, annual reports, emissions disclosures, company websites, and so on.
For small cap companies and retail clients, the data is more difficult to acquire. Data that is not publicly available could be gathered bilaterally from clients. For example, one European bank has developed an annual client questionnaire to collect data from its clients.
Gathering data from various reports or bilaterally from clients might not always be the best option, however, because it is time consuming or because the data is not available, reliable, or comparable. Two alternatives are:
- Use tools to collect the data. For example, using open-source tooling from the Two Degrees Investing Initiative (2DII) to calculate Paris Agreement Capital Transition Assessment (PACTA) portfolio alignment.
- Collect data from other external data sources, such as S&P Global.
This could be forward-looking external data on macro-economic expectations, international climate scenarios, financial market data or sectoral climate developments. Below we discuss some sources for external ESG and climate change-related data.
External data
Some of Zanders’ clients resort to vendor solutions for acquiring their ESG data. The most commonly observed solutions, in random order, are:
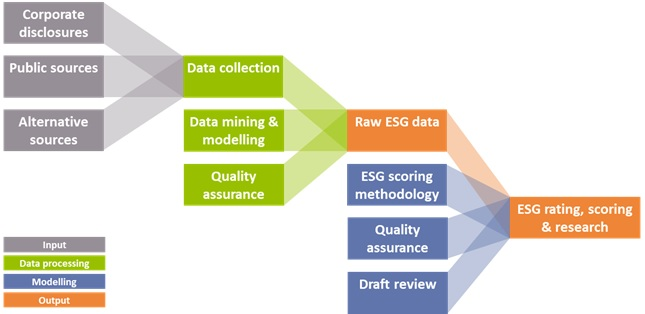
All the solutions above provide an aid to determine if climate related performance data is lacking, or can assist in reporting comparable and reliable data. They all apply a similar process of collecting the data and determining ESG scores, which is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Data collection process for ESG data solutions (Source: Zanders).
Additionally, public and non-commercial data and solution providers are available, such as:
Missing data
Given the data challenges, it is nearly impossible to create a complete data set. Until that is possible, there are several (temporary) methods to deal with missing data:
- Find a comparable loan, asset, or company for which the required data is available.
- Distribute sector data based on market share of individual companies. For example, assign 10% of the estimated emission of sector X to company Y based on its market share of 10%.
- Find a proxy, comparable or second-best metric. For example, by taking the energy label as a proxy for CO2 emission related to properties, or by excluding scope 3 emissions and focusing on scope 1 and 2 emissions.
- Change the granularity level. For example, by gathering data on sector level rather than on individual positions.
- Fill in the gaps with statistical or machine learning techniques.
Conclusion
The increased attention to integrating ESG risks into existing risk frameworks has led to a need for FIs to collect and disclose meaningful data on ESG factors. However, there is still a lack of data availability, reliability, and comparability.
Several regulatory and political efforts are ongoing to tackle this data challenge, such as the EU taxonomy. More policy interventions, however, are required. Examples are additional mandatory disclosure requirements, an audit and validation framework for ESG data, and social and governance taxonomies that classify economic activities that contribute to social and governance goals.
In the meantime, FIs have to find ways to produce meaningful insights and comply with regulatory requirements related to ESG risks. Zanders has experienced that there is no one-size-fits-all solution for defining, selecting, implementing, and disclosing relevant data and metrics. It is dependent on the composition of the asset and loan portfolio, the use of the data, and the data that is (already) available. Regardless of how the lack of data is solved, it is important that FIs are transparent about their choices and methodologies, and that the related metrics and scorings are explainable and intuitive.
Sources:
https://www.ngfs.net/sites/default/files/medias/documents/progress_report_on_bridging_data_gaps.pdf
https://ec.europa.eu/info/business-economy-euro/banking-and-finance/sustainable-finance/eu-taxonomy-sustainable-activities_en
https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/press-room/20220620IPR33413/new-social-and-environmental-reporting-rules-for-large-companies
https://zandersgroup.com/en/insights/blog/ebas-binding-standards-on-pillar-3-disclosures-on-esg-risks
https://www.eba.europa.eu/sites/default/documents/files/document_library/Publications/Reports/2021/1015656/EBA%20Report%20on%20ESG%20risks%20management%20and%20supervision.pdf
https://www.bankingsupervision.europa.eu/ecb/pub/pdf/ssm.202011finalguideonclimate-relatedandenvironmentalrisks~58213f6564.en.pdf
https://2degrees-investing.org/resource/pacta/