WACC: Practical Guide for Strategic Decision- Making – Part 3

Hybrids, Expensive Debt or Cheap Equity?

Hybrids are financial instruments that combine certain elements of debt and equity. Examples are preferred equity, convertible bonds, subordinated debt and index-linked bonds. For the issuers, hybrid securities can combine the best features of both debt and equity: tax deductibility for coupon payments, reduction in the overall cost of capital, and a strengthening of senior credit ratings.
This article describes the reasons behind the increased interest among corporates in using hybrid instruments to optimize their capital structure and the impact of hybrids on the WACC and shareholder value. It also takes a look at treatment by accountants, tax regulation and rating agencies.
Over €8bn of capital was raised in 2005 by corporates in Europe in the hybrid category, according to The Treasurer, April 2006. Over the past decade, it has primarily been financial institutions who have been frequent issuers of hybrids to optimize their capital structure. However, corporates are now also increasingly tapping this segment.
This growing interest can be explained both by new insights regarding the accounting and rating benefits of these instruments, as well as an increased appetite by investors who are drawn by the opportunity to make an additional yield in the current low-interest rate and credit spreads environment.
Accounting Treatment
A hybrid instrument can be structured to achieve equity treatment from an IFRS perspective. IAS 32 (Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation) requires a hybrid to have optional payment for all coupons and that the instrument should have no defined economic maturity.
If the instrument is structured to achieve equity accounting, the coupon is accounted for as a ‘preferred’ dividend distribution. This way, there is no interest expense and the reported net income is not affected. Likewise, earnings per share (EPS) are unchanged as for the purposes of the EPS calculation, preferred dividends are deducted from earnings.
However, if the instrument is treated as equity there is no IAS 39 (Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement) hedge accounting available for any associated swaps. The resulting P&L volatility may lead issuers to choose to have the instruments structured so that they are accounted for as debt.
View of Rating Agencies
Credit rating agency Moody’s published its Tool Kit for Assessing Hybrid Securities, a framework to determine the relative debt and equity characteristics of hybrid instruments, in December 1999. Since then, the rating agency has assessed hundreds of instruments, positioning them along the debtequity continuum in baskets from A (more debtlike) to E (more equity-like). Each basket on this continuum translates into the following percentages of equity and debt for the purpose of financial ratio calculations:
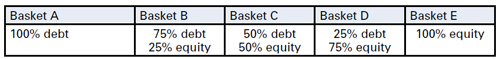
To illustrate, a €100m hybrid placed by Moody’s in Basket D will result in a €75m increase in equity and a €25m increase in debt. All relevant ratios, which include either debt or equity, will be adjusted accordingly by the agency.
In February 2005, Moody’s announced its revised methodology for the category, significantly increasing the acknowledgement of the equity-like features of the instruments and rewarding higher equitycredit to structures which meet specifically required features, particularly regarding subordination, coupon deferral and permanence in the capital structure. Moody’s revision has made it possible for corporates to achieve meaningful equity-credit of 50 per cent or more, and has prompted increased corporate activity in this area.
Standard & Poor’s and Fitch Ratings have also clarified their thinking on hybrids, and the three big rating agencies are now roughly in line in their treatment of hybrid capital.
Tax Treatment
The recent flow of corporate transactions has started in Europe thanks to favourable tax legislation in several European countries that makes it easier than in the US to develop new hybrid products that both improve rating treatment and qualify as debt for tax purposes. In the UK, however, the corporate tax law contains several provisions that challenge the tax deduction on interest paid on debt with ‘excessive’ equity characteristics.
The potential to achieve a more robust tax opinion may lead issuers choosing to have the instrument structured to be accounted for as debt. In article seven of this series on the WACC, ‘Reducing the WACC by Utilizing Tax Opportunities’; more tax angles related to this topic will be covered.
Impact on the WACC and Shareholder Value
Optimizing the WACC and maximizing returns to shareholders is a top priority for corporate treasurers.
Hybrid instruments strengthen the capital base by creating a buffer between senior creditors and shareholders. Hybrid capital offers an opportunity, when correctly structured and used as a substitute for more expensive and less flexible common equity, to lower the WACC.
Hybrid issues typically price between 50 and 200 basis points over senior debt. This means that the marginal cost of funding can be significantly lower than funding achieved through traditional debt and equity funding sources. This cost-effectiveness can be illustrated with the following example.
A company wants to raise €100m of capital with half of it qualifying as equity for rating purposes. It has, simply put, two options:
- €50m each of traditional debt and equity.
- €100m of hybrid capital with an equity treatment by the rating agencies of 50 per cent.
We assume the following rates apply to this company:

The marginal cost of capital for option 1 (traditional capital) would be:

The marginal cost of capital for option 2 (hybrid capital) would be
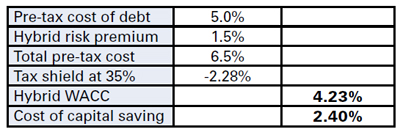
Please note: this calculation assumes full tax deductibility of the hybrid instrument.
By issuing hybrid capital with 50 per cent equity treatment the company achieves a cost of capital saving of 2.4 per cent. The advantage could be bigger still with 75 per cent equity treatment. The example shows that when hybrids are applied to substitute expensive equity, they offer an opportunity to lower the WACC of the issuer.
Conclusion
Hybrids offer corporates the opportunity to strengthen or maintain their credit ratings and balance sheet ratios, while funding acquisitions, share repurchases or pension deficits.
The economics achievable in current markets are an additional driving factor in the continuing rise in the number of hybrid instruments issued by corporates.
As a non-dilutive instrument, hybrid capital is particularly suitable for issuers who have limited access to equity or have dilution concerns. Raising hybrid capital offers the opportunity to lower the marginal cost of capital and therefore increase the return to shareholders.
To return to the question in the title of this article, hybrid capital can indeed be considered cheap equity. The additional cost on top of the normal cost of senior debt does not preclude the potential overall reduction in the cost of capital.
For companies with sufficient debt capacity within their current ratings, however, raising cheaper financing (not only in terms of spreads but also in terms of upfront fees) through traditional debt markets could still be a more attractive option. Possible changes in tax regimes and rating methodologies should also be taken into account when deciding on which funding instrument to choose.












