Optimizing Trade Execution through SAP Trade Platform Integration

Traditionally the SAP Treasury functionality has been heavily focused on accounting, reporting, and monitoring of treasury transactions that have already been executed. But now, pre-trade processes can be optimized with SAP Trade Platform Integration (TPI).

In any SAP Treasury implementation, conversation will eventually turn to the integration of external systems and providers for efficient straight-through processing of data and the additional controls it provides. SAP has introduced the TPI functionality to manage one of the more challenging of these interfaces which is the integration between SAP and the external trade platforms.
The general outline for any trade integration solution would contain the following high-level components:
- The ability to collect the trade requirements in the form of FX orders from all relevant sources.
- A trade dashboard for the dealers to view and manage all requested orders.
- Ability to send the FX orders to an external trade platform for trade execution.
- Capturing of the executed trade in the treasury module, ensuring that the FX order data is also recorded to identify the purpose of the FX transaction.
There are many levels of complexity of how each of these components have been developed in the past for different organizations, from the simplest Excel templates to the most complex bespoke modules with live interfaces to manage the end-to-end trading needs.
The choice of how much an organization would want to invest in these complex solutions would depend on the volume, importance of the trading function, need for enhanced control around trading, and the level of enriched data to be recorded automatically on the deals. Now, with a standard alternative available from SAP, an extensive business case may no longer be necessary to incorporate the more complex of these requirements, as the improved controls and efficiency of processing data is available with less risk and investment than previously considered.
The solution can be broadly defined under the SAP S/4 HANA functionality and the SAP Cloud Platform (SCP) functionality as seen below.
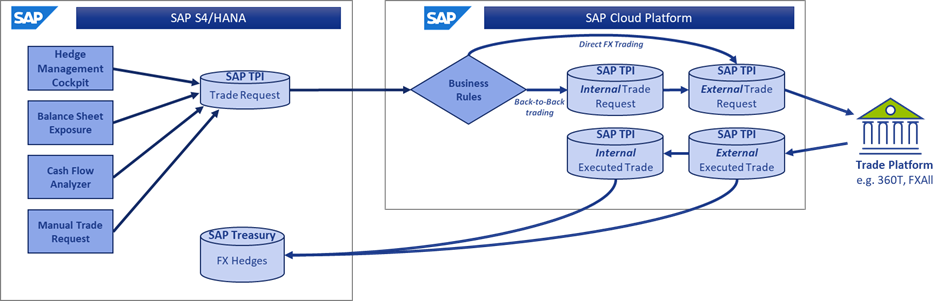
Figure 1
SAP S/4 HANA – Trade Platform Integration
The S/4 HANA functionality covers the first of the components mentioned before. Here SAP has introduced an entirely new database in the SAP environment to manage and control Trade Requests – the SAP equivalents of FX orders.
These Trade Requests may be created automatically off the back of other SAP tools such as Cash Management, Hedge Management Cockpit, Balance Sheet Hedging or simply from manual requests. The resulting Trade Request contains the same data categorizations that apply to a deal in TRM, such as portfolio, characteristics, internal references, and other fields normally found under Administration. All of this data collected prior to trading will be carried to the actual deal once executed, ensuring the dealers will not be responsible for accurately capturing this information on the deal that may not be relevant to them but necessary for further processing.
The clear benefit of this new integration is that it bridges the gap between the determination of trade requirements from Cash Management or FX risk reporting, and the dealers who are to execute and fulfil the trades. This allows the information related to the purpose of the trade (e.g.; the portfolio, exposure position, profit center, etc.) to be allocated to the Trade Request and subsequently to the executed trade automatically without the need of any manual enrichment.
Specially within the context of the Hedge Management Cockpit, this is very useful in the further automatic assignment of trades to hedge relationships, as the purpose of the trade is carried throughout the process.
SAP Cloud Platform – Trade Platform Integration
While the database in S/4 HANA remains the central transaction data source throughout the process, the functionality in SCP provides a set of tools for the dealers to manage the trades requests as needed.
This begins with some business rules to help differentiate how the trades will be fulfilled, either directly externally with a bank counterparty or internally via the treasury center.
All the external trades now can be found on the central Trade Request dashboard “Manage Trade Requests”, which acts as an order book from where the dealers/front office have a clear view on all deal requests that are been triggered from different areas of the organization and where in addition to being able to manage all the trade requests centrally, the status of each trade request is available to ensure no duplicate trading.
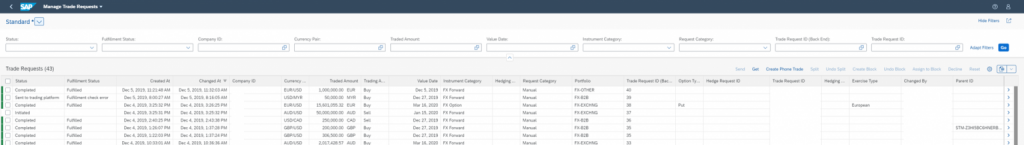
Figure 2
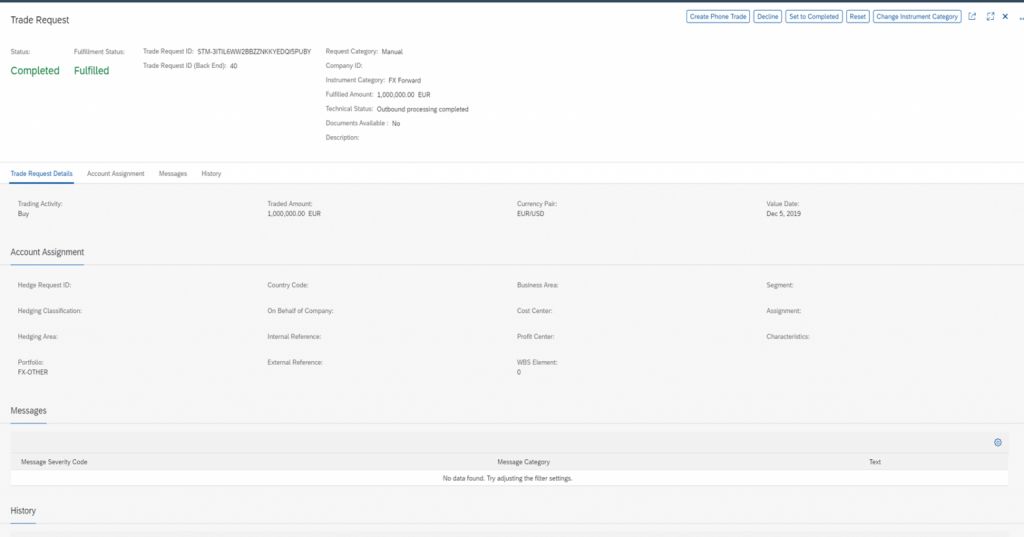
Figure 3
From the dashboard, a dealer can choose to group trades into a block, split the trades and edit them as necessary or alternatively the Trade Requests may be cancelled or manually traded as a “Phone Trade”.
The Send function on the dashboard will trigger the interface to the external trade platform for the selected trade requests taking into account the split and block trade requirements. The requests will then be executed and fulfilled on the external platform where the executed trade details such as rate and counterparty are captured back in the application, which in turns triggers the automatic creation of the FX deal in SAP S/4 HANA. The executed trade details can then be displayed on SCP application “Manage Trades”.

Figure 4
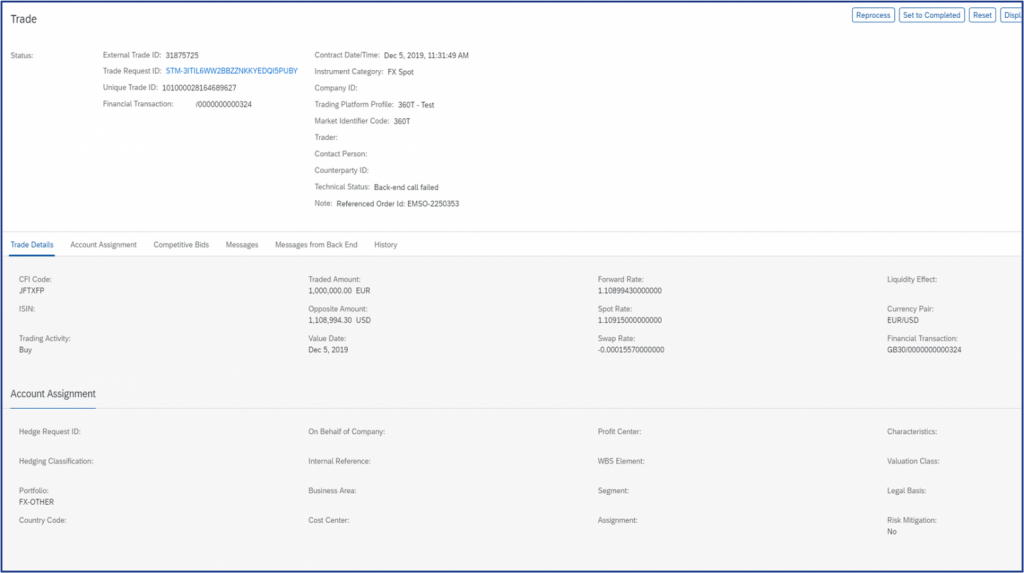
Figure 5
Internal trade requests can be automatically fulfilled at a price determined by the business rules defined by the users. This includes pricing based on the associated external deal rate (back-to-back scenario) with a commission, or pricing based on market data with a commission element.
The deals captured in SAP S/4 HANA whether internal or external, all contain the enriched data with all the originating information relating to the trade request, so that the FX deal itself accurately reflects the purpose of the position for further reporting.
Future SAP Roadmap
Although initially only the FX instruments were included in scope, SAP is now extending the ability to execute Money Market Fund purchases and sales through the platform including the associated dividend and rebate flows. This is another step to truly set up the TPI function as a central trade location for front office to operate from, covering not only FX risk requirements, but also the management of cash investment transacting.
Credit risk management is also now on the table, with pre-trade credit risk analyzer information integrated to the TPI application so that counterparty limits may be checked pre-trade to give the opportunity to exclude certain counterparties from quotation. This is certainly an improvement on the historical functionality of SAP TRM where a breach would only be noted after the deal has already been executed.
Conclusion
The recent SAP advancements in the area of TPI provide many opportunities for an organization to incorporate additional control, efficiency and transparency to the dealing process, not only for the front office, but also for the rest of the treasury team. While dealers benefit from a central platform where they can best execute the trades, middle office can get immediate feedback on their FX exposure positions as the deal immediately reflects with the correct characteristics, while the cash management team benefits from a simple ability to request and monitor the FX and investment decisions that have been sent to the dealers. The accounting team stands to benefit greatly as the accounting parameters on the deal are no longer the domain of a front office trader, but rather can be determined by the purpose of the original trade request which dictates the accounting treatment, including the automatic assignment to hedge relationships.
The SAP TPI solution therefore optimizes not only the dealers’ execution role, but also ties together the preceding and dependent processes into one fully straight through process that will benefit the whole treasury organization.












