Trade confirmations

Despite the tremendous push towards fully automating trade confirmations between banks and corporates in recent years, many transactions are still confirmed manually.

Manual confirmations are slow and error-prone, putting both sides of the trade at risk. In addition, many international regulations such as EMIR and Dodd-Frank have demanded an increase in automation.
Corporate treasurers often use SWIFT to standardize their confirmation messages. SWIFT is a cooperative that connects the financial community by providing highly secure financial messaging services that eliminate manual processing and makes inefficient paper confirmations redundant. More than 11,000 financial institutions, corporations, and other financial entities use SWIFT to exchange confirmations (SWIFT, 2019).
This article will explore several ways to confirm foreign exchange, money market, and currency option settlements through different solutions connected to SAP.
SWIFT Connectivity
Over the last several years, the SWIFT Network has experienced growing popularity with corporates of all sizes, stretching from large corporates with a high volume of transactions to small-to-medium corporates with a lower volume of transactions. As a result, corporates have several options when deciding on a connectivity solution:
- Direct in-house connectivity, where access to the SWIFT Alliance Gateway (SAG) is managed in-house by your IT (Information Technology) department. However, this solution is not recommended by SWIFT due to its high complexity and requirement for specialist SWIFT knowledge.

Figure 1: Direct Connectivity (SWIFT, 2019)
2. Alliance Lite2 is a packaged offering from SWIFT providing connectivity through a web browser or the embedded Lite2 for Business Applications (L2BA). Alliance Lite2 offers a simple, secure, cloud-based SWIFT connection. It connects to SWIFT through HTTPS and enables users to access the Alliance Lite 2 GUI. Since 2015, 61% of new corporate customers have opted for Alliance Lite2 (SWIFT, 2019).

Figure 2: Alliance Lite 2 (SWIFT, 2019)
3. SWIFT Service Bureaus (SSBs) provide a connection to the SWIFT network without the need to have an in-house IT department managing and maintaining the SWIFT connectivity. Furthermore, using an SSB can eliminate the need to undertake extra audit and compliance procedures. SSB providers vary in price but tend to be less expensive compared to direct in-house connectivity. It is still important to mention that initial investment is needed to set up the connectivity solution.

Figure 3: Swift Service Bureau (SWIFT, 2019)
4. Finastra Fusion Confirmation Matching Service (CMS) supports a hosted SWIFT connectivity through a Software as a Service (SaaS) application. It provides a confirmation matching solution for FX, Money Market, FX Options etc. This requires no upfront investment in infrastructure or implementation from the corporates availing of their services. It is directly hosted and managed and maintained by Finastra. Their File Transfer Service (FTS) is a secure process of moving messages between Misys CMS and clients ERP or TMS. FTS picks up and transfers files from the client to Misys CMS, converting the files to match trade data. After which, a matched message status is sent back to the client’s SAP TMS (Finastra, 2021).
Trading Platforms
Trading platforms such as 360T, Bloomberg and FXall offer automated back-office trade processing with SWIFT confirmation messages and trade matching.
The service allows corporate treasurers and banks to exchange deal confirmations directly on the trading platform. Messages are sent via the SWIFT networks directly to and from the banks, with the outgoing (incoming confirmation) and incoming messages (bankside confirmation) being automatically processed on the platform.
SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity
SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) is SAP’s offering of a SWIFT connection embedded within Business Applications. This cloud-based solution offers a multi-bank digital channel between SAP and partner banks. In addition, SAP MBC is being provided as a SaaS solution by SAP.
A SWIFT Service provider is not needed for SAP customers to send confirmations messages through the SWIFT network, as SWIFT services are given by SAP through an embedded version of Alliance Lite 2. This streamlines trade confirmations for the TRM module, as message statuses are automatically updated directly in SAP. Moreover, the integration platform offers connectivity to partner banks through EBICS and Host-to-Host connection.
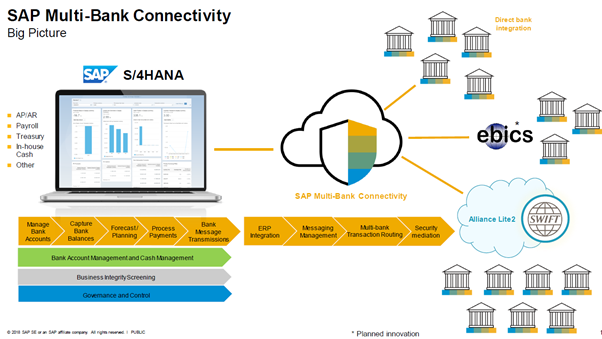
Figure 4: SAP MBC (SAP SE, 2018)
SAP Correspondence Monitor
This framework in SAP is an excellent tool to manage all correspondence objects. For example, back-office users can view incoming and outgoing messages and resend those messages previously failed to send. In addition, the monitor provides a historical overview of all the deals that have previously been confirmed.
Furthermore, it also allows you to view PDF messages that have been sent out, for example, to your internal counterparties. Through the t-code, technical users can customize messages when their requirements are not covered by standard functionality. For example, previously, SAP TRM did not offer MT305s as a standard message format. The user could then reconfigure standard functionality to fit different message types not provided in the standard TRM Module.
Below is an example of a corporates SAP TMS connected to the SWIFT network through a SWIFT Service Bureau.
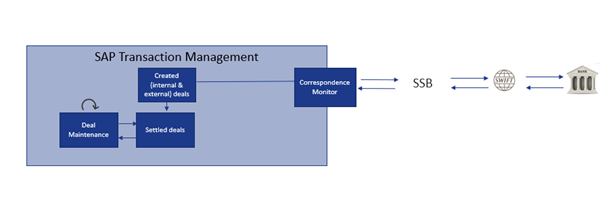
Figure 5: SAP Confirmation Connectivity
Conclusion
SWIFT Service Bureaus and Alliance Lite2 have been the most popular choice in sending out confirmations to and from the bank, with over 50% of all corporates accessing SWIFT through either connection. However, the offering of SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity is especially attractive to those corporates with a technology roadmap leading towards SAP as a key ERP provider. Nowadays, many corporates are transitioning towards their S/4 HANA transformations journey and are looking at their SWIFT connectivity options. Therefore, SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity is likely to compare favorably to SWIFT Service Bureaus in the coming years.
References
1) Finastra. (2021). From https://www.finastra.com/sites/default/files/file/2021-09/Confirmation-Matching-Service_FS_GL3800_FINAL.pdf
2) SAP SE. (2018). SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity.
3) SWIFT. (2019). S4C Workshop., (p. 95). Cape Town.












