Blog
IFRS 18: What Treasury Needs to Know Now
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out more
This article describes the current status of the IFRS 9 landscape, six years after the IFRS 9 accounting standards replaced IAS 39.
We touch upon the main difficulties experienced by financial institutions in the Netherlands based on a combination of project experience, results of a survey, main attention points from the eyes of the regulator and observations from publicly available annual reports. Interested to learn more about the IFRS 9 framework components banks struggle with the most and whether these challenges can be easily solved? Find out in the remainder of this article.
The main objective of this article is to provide insight into market practices and common challenges within the IFRS 9 landscape of Dutch financial institutions. In this light, Zanders conducted a survey amongst Dutch financial institutions. Six main IFRS 9 framework components form the basis of the survey: data quality, model components (PD, LGD, EAD), SICR & staging, macroeconomic scenarios, out-of-model adjustments and the relation between IFRS 9 and other models within the bank. An example of a full IFRS 9 framework overview is presented in Figure 1. The questionnaire was followed up by a roundtable in which the most noticeable results from the survey were discussed with the participants.
Besides the survey, the IFRS 9 monitoring report published by the European Banking Authority (IFRS 9 Monitoring report, EBA (November 2023)) provides insights into the key IFRS 9 attention points from a regulatory perspective (e.g. as identified by EBA). In this article, we discuss the key differences between the difficulties experienced by banks versus attention points highlighted in the monitoring report. Lastly, this article uses publicly available information from annual reports to illustrate the diverging modelling practices and model behavior amongst market peers.
Figure 1: IFRS 9 framework overview.
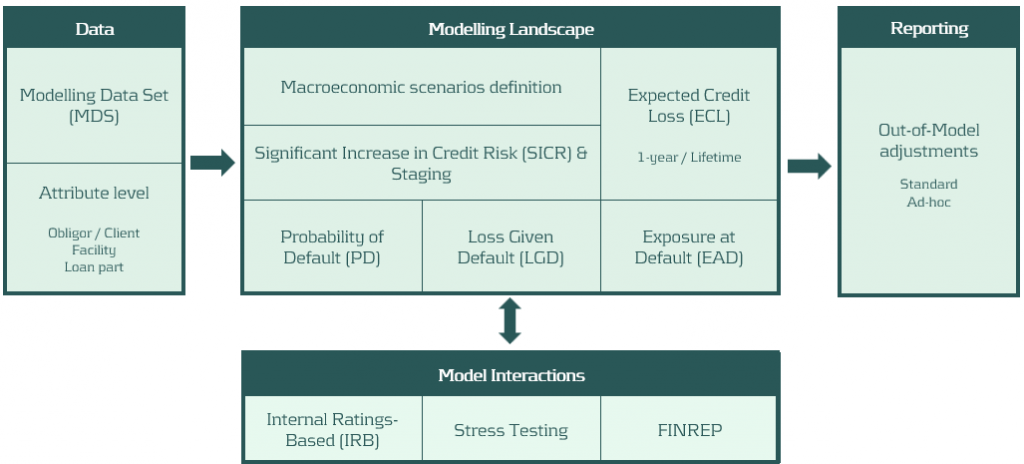
The IFRS 9 survey held in Q4 2023 was centered around the six framework components as stated in the introduction section and which are graphically presented in Figure 1. The participating banks were asked in which areas of the framework they experience difficulties. Consequently, each area was explored deeper by means of questions directly related to each area.
All participating banks except one indicate difficulties in the areas of data quality and out-of-model adjustments (e.g. overlays). For data quality, changing policies (e.g. Definition of Default, loan quality assessment), limited loss realizations for LGD (as well as limited detail of the loss realization data) and dealing with unrepresentative data from the Covid-19 period are examples of reasons for the difficulties experienced in this area. With regards to out-of-model adjustments, it becomes apparent that many banks struggle with pressure from the regulator and audit, triggering banks to find an escape in overlays on the IFRS 9 model outcomes. Overlays are applied on a wide variety of topics, in various ways (e.g. calculated, constant, periodic, expert based, etc.) and sometimes constitute the majority of the total provisions. Altogether, this illustrates the need to have out-of-model adjustments in place that are sufficiently qualitatively substantiated and, whenever possible, are applied on the model component level. At the same time, we are of the opinion that out-of-model adjustments are sometimes over-used to make up for model deficiencies. Especially when out-of-model adjustments constitute the majority of the total provisions, compliance of the model with the IFRS 9 best-estimate principle should be questioned.
Surprisingly, only one third of the respondents experiences difficulties in the framework areas that came into existence with the introduction of IFRS 9; SICR & staging and macroeconomic scenarios. A possible explanation for this is that the responsibility for these framework areas is often distributed across multiple departments. Macroeconomic predictions and scenario weights are usually determined by a separate macroeconomic scenario department or committee, and staging assessments are often placed outside the scope of IFRS 9 modelling teams. From a governance perspective, we are of the opinion that more alignment over the full IFRS 9 provisioning chain is desired.
Want to know more about the survey results? Download our white paper.
The EBA published a monitoring report in November 2023 on the current status of the IFRS 9 model landscape (IFRS 9 Monitoring report, EBA (November 2023)). In this report the EBA highlights several takeaways, which are shown in Figure 2. One of these takeaways is the manner in which SICR is modelled at the moment. The EBA is not convinced that non-collective approaches are more suitable than collective approaches. In the results of the survey however, it was shown that most respondents did not indicate SICR as one of the main challenges in their IFRS 9 landscape. This raises the question whether banks in the Netherlands are aware of the EBA’s remark on the current SICR approaches, or whether Dutch banks are outliers when it comes to the SICR modelling approaches.
Furthermore, the report indicates that out-of-model adjustments should be applied on the model parameter level and not on the outcome level. During the roundtable it was discussed that several participants recognize this desire from the regulator, but that they still apply it on the outcome level because the available data only allows for this level. This discrepancy could lead to further scrutiny from the regulator in the near future.
Figure 2: Key takeaways from the IFRS 9 monitoring report (EBA, 2023).

In the Dutch banking market, a variety of modelling practices is observed when it comes to IFRS 9 models for calculating credit loss provisions. Besides gaining insights into these IFRS 9 modelling practices via a survey, annual reports are analyzed to identify potential differences (or similarities) from information that is publicly available.
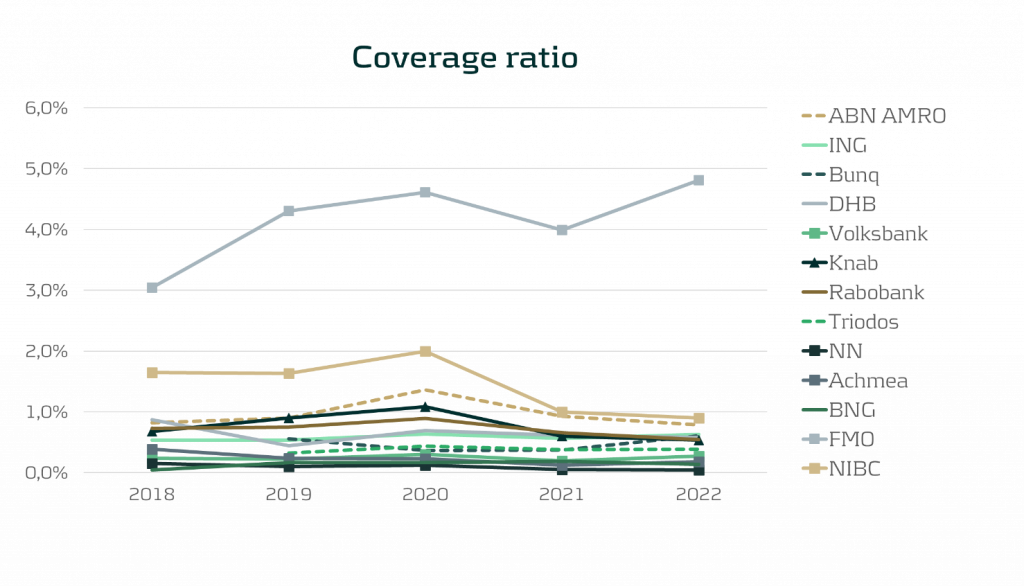
One of the observations from comparing annual reports is that no common level is observed for the Provisioning Coverage Ratio (PCR), i.e. the percentage of funds set aside for covering losses due to bad debts. Characteristics such as portfolio type/composition and loan maturity likely explain these differences. In 2020, almost all banks show an increase in the PCR due to increased allowances in response to the Covid-19 pandemic. Note that this was not necessarily caused by models picking up changing macroeconomic dynamics, but because of model overlays. PCR levels stabilized again in 2021 and 2022.
Figure 3: Coverage ratio over the years 2018 till 2022 . All results were gathered from public annual reports.
Although not all banks report macroeconomic scenario weights in their annual reports, it is worth noting that large differences exist in the scenario weights of banks that do report these figures. Especially weights assigned to the up and down scenarios vary significantly. In 2022, the weight percentage for the base scenario is generally between 40% and 60% (one bank uses a weight of 30%), whereas the weight percentage for the down scenario ranges from 20% to 60%. For the up scenario, percentage weights differ from 2% to 30%. It must be noted that the scenario weights cannot be judged without considering the actual scenario definitions/severity. Nonetheless, the wide variety in scenario weight percentages as well as large differences in the development of these scenario weights over time raises questions on the accuracy of macroeconomic predictions. In addition, it also complicates the comparability of IFRS 9 figures amongst banks.
We combine deep credit risk modelling expertise with relevant experience in regulation and programming:
Interested to learn more? Contact Kasper Wijshoff or Michiel Harmsen for questions on IFRS 9.
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out moreBuilding on the June 2024 launch of the new EU AML/CFT framework and the creation of the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA), SupTech (short for Supervisory Technology) now stands as a key
Find out moreAs the European Union increasingly emphasizes robust digital resilience within the financial sector as of January 17th 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) has become a critical
Find out moreManaging banking book risk remains a critical challenge in today’s financial markets and regulatory environment. There are many strategic decisions to be made and banks are having trouble
Find out moreOn July 2nd, the European Banking Authority (EBA) published a Consultation Paper proposing amendments to its 2016 Guidelines on the application of the definition of default (DoD). As part of the
Find out moreArtificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, particularly with the emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs). Yet, in quantitative risk
Find out moreIn an industry where growth is often measured in multiples, and value creation is expected to be both scalable and repeatable, operational excellence is no longer a supporting function—it’s
Find out moreWith extreme weather events becoming more frequent and climate policy tightening across jurisdictions, banks are under increasing pressure to understand how climate change will impact their
Find out moreWith the introduction of CRR3, effective from January 1, 2025, the ‘extra’ guarantee on Dutch mortgages – known as the Dutch National Mortgage Guarantee (NHG) – will no longer be
Find out moreAccording to the IFRS 9 standards, financial institutions are required to model probability of default (PD) using a Point-in-Time (PiT) measurement approach — a reflection of present
Find out moreInflows from open reverse repos In May 2024 the EBA stated1 that inflows from open reverse repos cannot be recognised in LCR calculations unless the call option has already been
Find out moreThis article is intended for finance, risk, and compliance professionals with business and system integration knowledge of SAP, but also includes contextual guidance for broader audiences. 1.
Find out moreOur team at Zanders has been at the forefront of implementing BACS AUDDIS (Automated Direct Debit Instruction Service) with SAP S/4HANA, helping clients to streamline their direct debit
Find out moreThailand's e-Withholding Tax (e-WHT) system officially launched on October 27, 2020, in collaboration with 11 banks, marking a significant digital transformation with far-reaching benefits for
Find out moreIn today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, fortifying the Financial Risk Management (FRM) function remains a top priority for CFOs. Zanders has identified a growing trend among
Find out moreEmergence of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning The rise of ChatGPT has brought generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) into the mainstream, accelerating adoption across
Find out moreIntroduction In December 2024, FINMA published a new circular on nature-related financial (NRF) risks. Our main take-aways: NRF risks not only comprise climate-related risks,
Find out moreAs mid-sized corporations expand, enhancing their Treasury function becomes essential. International growth, exposure to multiple currencies, evolving regulatory requirements, and increased
Find out moreIndustry surveys show that FRTB may lead to a 60% increase in regulatory market risk capital requirements, placing significant pressure on banks. As regulatory market risk capital requirements
Find out moreFirst, these regions were analyzed independently such that common trends and differences could be noted within. These results were aggregated for each region such that these regions could be
Find out more
In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Fintegral.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired RiskQuest.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Optimum Prime.
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information