Blog
IFRS 18: What Treasury Needs to Know Now
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out more
Rapid advancements in technology and globalization often require cutting- edge payment solutions for corporates with a diverse footprint, but be sure to bake in anti-fraud measures.
Payment fraud originating from within or outside an organization must be guarded against. Read on to learn how SAP Advanced Payment Management (APM) and Business Integrity Screening (BIS) can help.
Compliance requirements, audit needs and external factors like embargos, sanctions imposed by governments, and so on are additional imperatives for corporates and financial institutions (FIs) that want to secure their end-to-end payment lifecycle. Protection must be provided from the time of triggering a payment – or even before – until payment reaches the intended recipient.
In an increasingly digitized world with multiple cybersecurity threats, it is becoming even more important that the payment process is robust and ably supported by a strong technology infrastructure that provides security, speed, and efficiency.
Challenge for Corporates
The reality for many corporates is that they have multiple enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems – SAP or from other vendors – implemented over a period of time, or they have multiple systems due to merger and acquisition (M&A) activity in the past. Such corporates end up having lots of multi-banking relationships with different processes across the entire company, and different systems or banking portals for making payments. In an ideal world, moving to a single system with focused banking relationships, centralized treasury management and harmonized global processes is the end game that every company wants to achieve. But the process to get there is long.
SAP S/4 HANA
Companies using, or moving, to SAP as their primary ERP often aim for a single instance of the S/4 HANA landscape to get a single version of truth, but they may approach it in different ways. The journey most often is long and complex. But payment risk has to be mitigated sooner, rather than later.
Companies can adopt different strategies like ‘Central Finance’, ‘Treasury First’ or centralization of payments through a Payment Factory (PF) solution to enable certain quicker wins and security for the treasury and finance organization.
Advanced Payment Management Functionality
SAP introduced APM in 2019 to help payment centralization, visibility and oversight for those using its systems. APM alongside In-House Bank is its payment factory solution. SAP has continuously upgraded it since, with appropriate functionalities including anti-fraud measures available to users now.
APM allows for centralization of payments originating from any system – be it SAP or non-SAP – and facilitates:
These measures enable treasury to have central and near-real time visibility of all payments going out, allowing corporate treasurers to put controls and checks in place through a robust payment approval mechanism.
Having a strong and auditable payment approval process governed by a unified system will enable reductions in payment fraud. However, payment approval alone is somewhat of a reactive mechanism and relies on a human touch that can sometimes become time consuming, labor-intensive and prone to errors, which can potentially miss some transactions when done on a large scale. A more advanced way of managing payment risk efficiently is through an exception-based procedure, where only absolutely required payments go through a human touch, with low-risk transactions filtered through an automated rules engine that allows for targeted attention on high-risk payments.
The need for Business Integrity Screening
SAP Business Integrity Screening (BIS) is a solution that complements the payment engine of S/4 HANA, including the advanced payment management (APM) function. BIS is a SAP solution that can be enabled on S/4 HANA. At a high level, it is a rules-based engine designed to detect anomalies and third-party risk. It uses data to predict and prevent future occurrences of fraud risk.
By virtue of being on S/4 HANA, BIS handles large volumes of payments, processing through real-time simulations. SAP BIS also integrates with different process areas like master data management, invoice processing, payment execution (payment runs), and with APM for payments originating from other systems. This helps fraud prevention at a much earlier stage.
The below Figure 1 picture depicts a few of the features of BIS where a set of rules can be defined for different scenarios with certain SAP provided out-of-box rules – for example, identified risk factors might include:
Figure 1: SAP’s Business Integrity Screening (BIS) Key Features
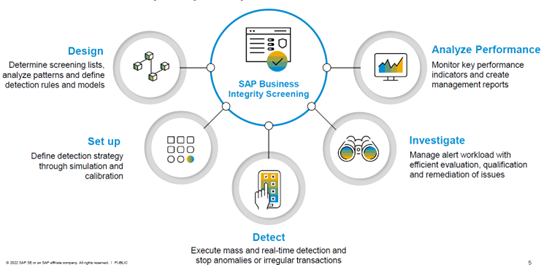
Source: SAP.
BIS has a highly flexible detection and screening strategy for business partners where new rules can be added and it can make composite rule scenarios, resulting in an overall risk score being awarded. For example, a weighted score may be determined based on individual Rules like:
Using the power of S/4 HANA, every payment is processed through all the rules and strategies defined to detect anomalies as early as possible, with real-time alert mechanisms providing further security. Implementations can leverage out-of-the-box rules and create new rules based on internal knowledge to refine anti-fraud measures going forward. BIS also has powerful analytics through the SAP Analytics Cloud solution for evaluating the performance of each strategy and rule, enabling refinements to be made.
BIS & APM Integration
For customers operating a single system environment, BIS was previously integrated with Payment Run functionality. With a multi-ERP Payment Factory landscape, BIS now integrates directly with APM. This means payments across the enterprise can be routed through screening for exception-based handling.
BIS combined with APM has two possibilities (as of writing this article):
Rules can be set based on the size of payments as well – for example, Low value payments can be set for batch screening, while high value transactions can be set for online screening.
In the current release BIS 1.5 (FPS00), there are pre-defined scenarios specifically for APM. These check recipient bank accounts – for example, in high-risk countries and so on – and business partner (payee) bona fides for sanction screening/embargo checks at the payment order/payment item level. Custom scenarios can be created, and further custom code enhancements built within SAP-provided enhancement points.
While screening online, APM payment orders are validated through BIS detection rules. Payments without any anomalies or risk scores below threshold are automatically approved and processed for further normal processing through APM outbound processing. Payments which are suspicious will be ‘parked’ in BIS for user intervention to either release the payment – remembering, it could be a false positive scenario – or for blocking.
Any blocked payment in BIS automatically moves the APM payment order to the Exception Handling queue within Advanced Payment Management for further processing – for example, taking corrective actions in source systems, validating internal processes, contacting the vendor, cancelling/reversing a payment, and so on.
End-to-End Payment Fraud Prevention
There are different solutions available to cater to the specific needs of corporates across the payment lifecycle. A key first step is to centralize payments where Advanced Payment Management can help. A key benefit of Payment Centralization in a corporate landscape is the opportunity to initiate centralized payment screening and fraud prevention using BIS.
The integration between BIS and the APM Payment Factory enables effective payment fraud and sanction screening detection across the whole payment landscape. Adding Bank Communication Management for further approval control on an exceptions-basis will ensure a robust and automated payment process mechanism, with a strong focus on automated payment fraud prevention.
Once the payment process is secured, the next step is having secure connectivity to banks. This is where solutions like the SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity option can help.
If you are interested in any of the topics mentioned, or Sanction Screening & Fraud Detection more generally, we at Zanders encourage you to reach out to us via the ‘Get In Touch’ button. You can read more about Bank Connectivity Solutions & Advanced Payment Management: APM in our earlier articles.
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out moreBuilding on the June 2024 launch of the new EU AML/CFT framework and the creation of the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA), SupTech (short for Supervisory Technology) now stands as a key
Find out moreAs the European Union increasingly emphasizes robust digital resilience within the financial sector as of January 17th 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) has become a critical
Find out moreManaging banking book risk remains a critical challenge in today’s financial markets and regulatory environment. There are many strategic decisions to be made and banks are having trouble
Find out moreOn July 2nd, the European Banking Authority (EBA) published a Consultation Paper proposing amendments to its 2016 Guidelines on the application of the definition of default (DoD). As part of the
Find out moreArtificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, particularly with the emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs). Yet, in quantitative risk
Find out moreIn an industry where growth is often measured in multiples, and value creation is expected to be both scalable and repeatable, operational excellence is no longer a supporting function—it’s
Find out moreWith extreme weather events becoming more frequent and climate policy tightening across jurisdictions, banks are under increasing pressure to understand how climate change will impact their
Find out moreWith the introduction of CRR3, effective from January 1, 2025, the ‘extra’ guarantee on Dutch mortgages – known as the Dutch National Mortgage Guarantee (NHG) – will no longer be
Find out moreAccording to the IFRS 9 standards, financial institutions are required to model probability of default (PD) using a Point-in-Time (PiT) measurement approach — a reflection of present
Find out moreInflows from open reverse repos In May 2024 the EBA stated1 that inflows from open reverse repos cannot be recognised in LCR calculations unless the call option has already been
Find out moreThis article is intended for finance, risk, and compliance professionals with business and system integration knowledge of SAP, but also includes contextual guidance for broader audiences. 1.
Find out moreOur team at Zanders has been at the forefront of implementing BACS AUDDIS (Automated Direct Debit Instruction Service) with SAP S/4HANA, helping clients to streamline their direct debit
Find out moreThailand's e-Withholding Tax (e-WHT) system officially launched on October 27, 2020, in collaboration with 11 banks, marking a significant digital transformation with far-reaching benefits for
Find out moreIn today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, fortifying the Financial Risk Management (FRM) function remains a top priority for CFOs. Zanders has identified a growing trend among
Find out moreEmergence of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning The rise of ChatGPT has brought generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) into the mainstream, accelerating adoption across
Find out moreIntroduction In December 2024, FINMA published a new circular on nature-related financial (NRF) risks. Our main take-aways: NRF risks not only comprise climate-related risks,
Find out moreAs mid-sized corporations expand, enhancing their Treasury function becomes essential. International growth, exposure to multiple currencies, evolving regulatory requirements, and increased
Find out moreIndustry surveys show that FRTB may lead to a 60% increase in regulatory market risk capital requirements, placing significant pressure on banks. As regulatory market risk capital requirements
Find out moreFirst, these regions were analyzed independently such that common trends and differences could be noted within. These results were aggregated for each region such that these regions could be
Find out more
In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Fintegral.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired RiskQuest.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Optimum Prime.
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information