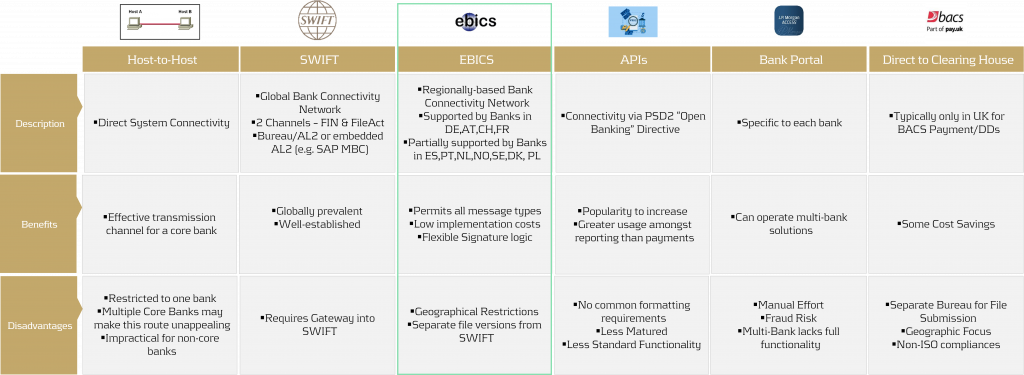
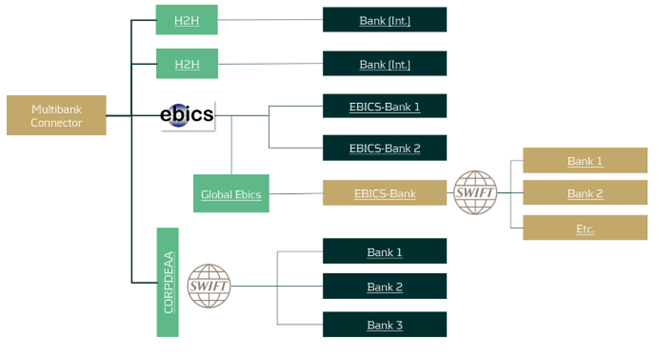
Security in payments is a priority that no corporation can afford to overlook. But how can bank connectivity be designed to be secure, seamless, and cost-effective? What role do local connectivity methods play today, and how sustainable are they? This article provides an overview of various bank connectivity methods, focusing specifically on the Electronic Banking Internet Communication Standard (EBICS). We'll examine how EBICS can be integrated into global bank connectivity strategies, while comparing it to alternative methods. The following section offers a comparison of EBICS with other connectivity solutions.
For a comprehensive overview of bank connectivity methods, including insights from an SAP perspective, we recommend the article Bank connectivity – Making the right choices.
Compared to alternatives, EBICS contracts are cost-effective, and EBICS connectors, along with supporting online banking software, are equally affordable. Whether through standalone solutions provided directly by banks or SAP ERP-integrated systems, EBICS consistently proves to be the most cost-effective option when compared to SWIFT or individual host-to-host connections.
The downside of EBICS? Outside the GSA region (Germany, Switzerland, Austria) and France, there are significant variations and a more diverse range of offerings due to EBICS' regional focus. In this article, we explore potential use cases and opportunities for EBICS, offering insights on how you can optimize your payment connectivity and security.
EBICS at a Glance
EBICS, as a communication standard, comes with three layers of encryption based on Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). In addition to a public and a private key, so-called EBICS users are initialized, which can present a significant advantage over alternative connection forms. Unlike Host-to-Host (H2H) and SWIFT, which are pure communication forms, EBICS has an intelligent signature process integrated into its logic, following the signing process logic in the GSA region. EBICS, developed by the German banking industry in 2006, is gaining increasing popularity as a standardized communication protocol between banks and corporates. The reason for this is simple—the unbeatable price-performance ratio achieved through high standardization.
Furthermore, EBICS offers a user-specific signature logic. Primary and secondary signatures can be designated and stored in the EBICS contract as so-called EBICS users. Additionally, deliveries can be carried out with so-called transport users (T-transport signature users).
In practice, the (T) transport signature user is used for tasks such as retrieving account statements, protocols, or sending payments as a file without authorization.
It is worth noting that for the intelligent connectivity of third-party systems or even service providers that create payments on behalf of clients, the T user can be utilized. For example, an HR service provider can send an encrypted payment file using the provided T user to the bank server. The payment file can be viewed and signed separately on the bank server via the relevant treasury or EBICS-compatible banking software.
Furthermore, through EBICS, individual records and thus personal data in the case of HR payments can be technically hidden. Only header data, such as the amount and the number of items, will be visible for approver.
Is the signature logic too maintenance-intensive? Fortunately, there is an alternative available to the maintenance of individual users. A so-called Corporate Seal User can be agreed upon with the bank. In this case, the bank issues an EBICS user based on company-related data in the (E) Single signature version. The (E) signature is transmitted directly to the bank for every internally approved payment, which is comparable to connectivity via SWIFT or Host-to-Host.
Strategic Adjustments with EBICS
Regional standards like EBICS can be used to connect regional banks and send or receive messages over the bank's internal SWIFT network through a so-called request for forwarding, also known as European Gateway or SWIFT Forwarding. Using this service, it is not necessary to connect every bank directly via Host-to-Host or SWIFT in order to become cost-efficient in your corporate banking.
A SWIFT Forwarding agreement is drafted and signed with your individual bank. Payment files are sent to the bank via a defined order type intended solely for forwarding. The bank acts here as a mere transmitter of the message. Incidentally, the same principle can also be adapted for account statements. Several banks in the GSA-region and France proactively market the service as an additional cash management service to their corporate customers. Account statements are centrally collected via the bank's SWIFT network and sent to the corporate via the existing EBICS channel. This procedure saves implementation efforts and simplifies the maintenance.
We like to summarize the advantages and disadvantages of integrating SWIFT forwarding via the EBICS channel:
Advantages
- High maintenance Host-to-Host connections are avoided.
- A dedicated SWIFT connection can be avoided without neglecting the benefits.
Disadvantages
- A bank with a well-developed interbank network is required.
- Transport fees per message may apply.
In general, corporates can take advantage of this specific EBICS setup when dealing with banks that manage a small portion of their transaction volume or when the technical connections with certain banks are more challenging. This approach is especially beneficial for banks that are difficult to access through local connectivity methods and have medium-to-low transaction volumes. However, for banks with high transaction volumes, connectivity via Host-to-Host or even a dedicated SWIFT connection may be more appropriate. Each situation is unique, and we recommend evaluating the best banking connectivity setup on a case-by-case basis to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Future of EBICS: Changes Until 11/2025
Since November 2023, banks have been offering EBICS 3.0 as the most recent and up-to-date version. This version is binding in the GSA (Germany, Switzerland, Austria) region until approximately November 2025.
Here is a summary of the most important changes:
- Increased Standardization: Local EBICS “flavors” are unified to simplify implementation.
- Enhanced Encryption: Since version 2.5, the minimum encryption level has been 2048 bits. This is continuously increased with the EBICS 3.X version.
- XML Only for EBICS-specifics: Protocols like PTK are migrated to pain.002 HAC.
The new version of EBICS increases the security of the communication standard and makes it more attractive in the EU given its updates. In addition to Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and France, we observe the communication standard is increasingly offered by banks in Spain, Portugal, the Netherlands, as well as in the Nordic countries. Recently, the first banks in Poland have started to offer this communication standard–a rising trend.
In summary, EBICS is a cost-effective and powerful standard that can do much more than just bank connectivity. For companies that mainly use Host-to-Host or SWIFT for bank connectivity within the Eurozone, it may be worthwhile to look at EBICS and consider switching their connectivity method, provided their banking partner offers EBICS.