Blog
IFRS 18: What Treasury Needs to Know Now
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out more
Credit Risk Suite – Expected Credit Losses Methodology article
The IFRS 9 accounting standard has been effective since 2018 and affects both financial institutions and corporates. Although the IFRS 9 standards are principle-based and simple, the design and implementation can be challenging. Specifically, the difficulties that the incorporation of forward-looking information in the loss estimate introduces should not be underestimated. Using our hands-on experience and over two decades of credit risk expertise of our consultants, Zanders developed the Credit Risk Suite. The Credit Risk Suite is a calculation engine that determines transaction-level IFRS 9 compliant provisions for credit losses. The CRS was designed specifically to overcome the difficulties that our clients face in their IFRS 9 provisioning. In this article, we will elaborate on the methodology of the ECL calculations that take place in the CRS.
An industry best-practice approach for ECL calculations requires four main ingredients:
The overall ECL calculation is performed as follows and illustrated by the diagram below:
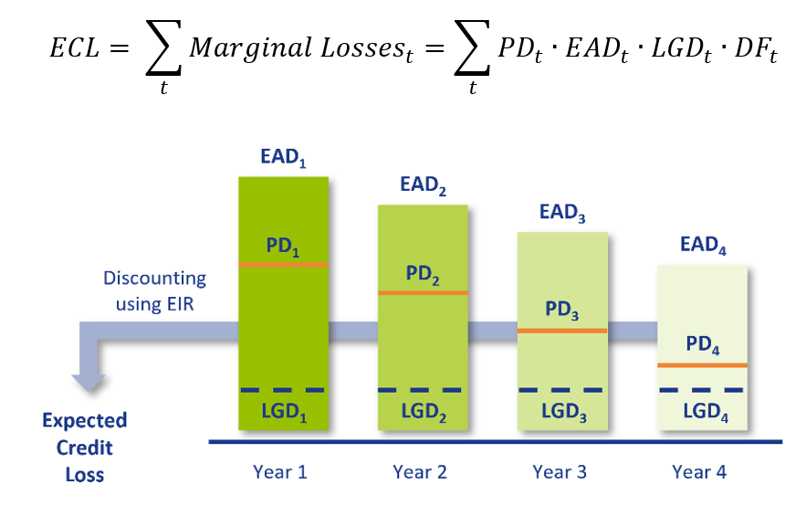
The CRS consists of multiple components and underlying models that are able to calculate each of these ingredients separately. The separate components are then combined into ECL provisions which can be utilized for IFRS 9 accounting purposes. Besides this, the CRS contains a customizable module for scenario-based Forward-Looking Information (FLI). Moreover, the solution allocates assets to one of the three IFRS 9 stages. In the component approach, projections of PDs, EADs and LGDs are constructed separately. This component-based setup of the CRS allows for customizable and easy to implement approach. The methodology that is applied for each of the components is described below.
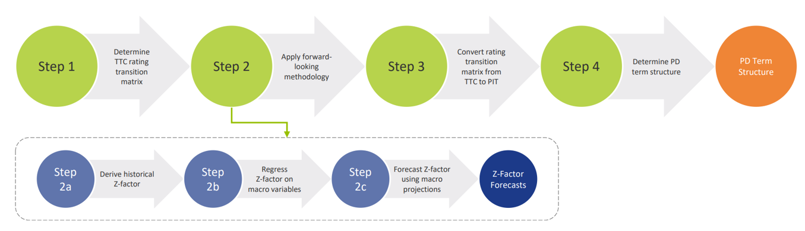
For each projected month, the PD is derived from the PD term structure that is relevant for the portfolio as well as the economic scenario. This is done using the PD module. The purpose of this module is to determine forward-looking Point-in-Time (PIT) PDs for all counterparties. This is done by transforming Through-the-Cycle (TTC) rating migration matrices into PIT rating migration matrices. The TTC rating migration matrices represent the long-term average annual transition PDs, while the PIT rating migration matrices are annual transition PDs adjusted to the current (expected) state of the economy. The PIT PDs are determined in the following steps:
The result of this is a forward-looking PIT PD term structure for all transactions which can be used in the ECL calculations.
For any given transaction, the EAD consists of the outstanding principal of the transaction plus accrued interest as of the calculation date. For each projected month, the EAD is determined using cash flow data if available. If not available, data from a portfolio snapshot from the reporting date is used to determine the EAD.
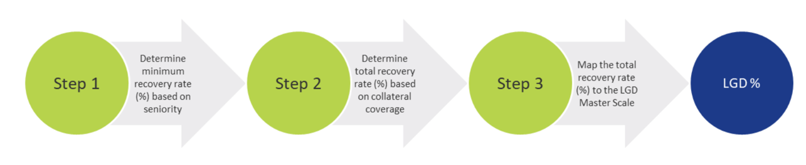
For each projected month, the LGD is determined using the LGD module. This module estimates the LGD for individual credit facilities based on the characteristics of the facility and availability and quality of pledged collateral. The process for determining the LGD consists of the following steps:
Once all expected losses have been calculated for all scenarios, the weighted average one-year and lifetime loss are calculated for each transaction , for both 1-year and lifetime scenario losses:
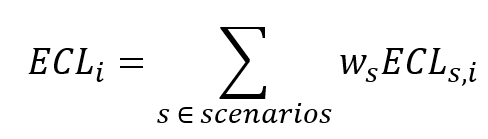
For each scenario , the weights are predetermined. For each transaction , the scenario losses are weighted according to the formula above, where is either the lifetime or the one-year expected scenario loss. An example of applied scenarios and corresponding weights is as follows:
This results in a one-year and a lifetime scenario-weighted average ECL estimate for each transaction.
Lastly, using a stage allocation rule, the applicable (i.e., one-year or lifetime) scenario-weighted ECL estimate for each transaction is chosen. The stage allocation logic consists of a customisable quantitative assessment to determine whether an exposure is assigned to Stage 1, 2 or 3. One example could be to use a relative and absolute PD threshold:
If either of the criteria are met, Stage 2 is assigned. Otherwise, the transaction is assigned Stage 1.
The provision per transaction are determined using the stage of the transaction. If the transaction stage is Stage 1, the provision is equal to the one-year expected loss. For Stage 2, the provision is equal to the lifetime expected loss. Stage 3 provision calculation methods are often transaction-specific and based on expert judgement.
IFRS 18 introduces significant changes to FX classification and reporting requirements by January 2027. Despite that this adoption date still feels quite far away, there is quite some time
Find out moreBuilding on the June 2024 launch of the new EU AML/CFT framework and the creation of the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA), SupTech (short for Supervisory Technology) now stands as a key
Find out moreAs the European Union increasingly emphasizes robust digital resilience within the financial sector as of January 17th 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) has become a critical
Find out moreManaging banking book risk remains a critical challenge in today’s financial markets and regulatory environment. There are many strategic decisions to be made and banks are having trouble
Find out moreOn July 2nd, the European Banking Authority (EBA) published a Consultation Paper proposing amendments to its 2016 Guidelines on the application of the definition of default (DoD). As part of the
Find out moreArtificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, particularly with the emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs). Yet, in quantitative risk
Find out moreIn an industry where growth is often measured in multiples, and value creation is expected to be both scalable and repeatable, operational excellence is no longer a supporting function—it’s
Find out moreWith extreme weather events becoming more frequent and climate policy tightening across jurisdictions, banks are under increasing pressure to understand how climate change will impact their
Find out moreWith the introduction of CRR3, effective from January 1, 2025, the ‘extra’ guarantee on Dutch mortgages – known as the Dutch National Mortgage Guarantee (NHG) – will no longer be
Find out moreAccording to the IFRS 9 standards, financial institutions are required to model probability of default (PD) using a Point-in-Time (PiT) measurement approach — a reflection of present
Find out moreInflows from open reverse repos In May 2024 the EBA stated1 that inflows from open reverse repos cannot be recognised in LCR calculations unless the call option has already been
Find out moreThis article is intended for finance, risk, and compliance professionals with business and system integration knowledge of SAP, but also includes contextual guidance for broader audiences. 1.
Find out moreOur team at Zanders has been at the forefront of implementing BACS AUDDIS (Automated Direct Debit Instruction Service) with SAP S/4HANA, helping clients to streamline their direct debit
Find out moreThailand's e-Withholding Tax (e-WHT) system officially launched on October 27, 2020, in collaboration with 11 banks, marking a significant digital transformation with far-reaching benefits for
Find out moreIn today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, fortifying the Financial Risk Management (FRM) function remains a top priority for CFOs. Zanders has identified a growing trend among
Find out moreEmergence of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning The rise of ChatGPT has brought generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) into the mainstream, accelerating adoption across
Find out moreIntroduction In December 2024, FINMA published a new circular on nature-related financial (NRF) risks. Our main take-aways: NRF risks not only comprise climate-related risks,
Find out moreAs mid-sized corporations expand, enhancing their Treasury function becomes essential. International growth, exposure to multiple currencies, evolving regulatory requirements, and increased
Find out moreIndustry surveys show that FRTB may lead to a 60% increase in regulatory market risk capital requirements, placing significant pressure on banks. As regulatory market risk capital requirements
Find out moreFirst, these regions were analyzed independently such that common trends and differences could be noted within. These results were aggregated for each region such that these regions could be
Find out more
In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Fintegral.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired RiskQuest.

In a continued effort to ensure we offer our customers the very best in knowledge and skills, Zanders has acquired Optimum Prime.
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information