Combining SAP ERP and a third-party TMS

The recent decade has brought notable developments in both ERP and treasury management system (TMS) markets.

On one hand, the trend towards ERP system consolidation has progressed, most companies have centralized all their global entities and processes in a single environment with unique master data. At the same time, the trend towards cloud solutions has brought innovation and increased competition also to the TMS area. In this context, we are often asked: should the treasury function follow into the centralized ERP solution as well, or does a separate TMS instance have its justification?
Nowadays, all established TMS solutions are also available in the cloud or have disappeared from the market. The cloud technology brings disruption to the TMS market – high scalability of the cloud solutions has brought a number of new players to the global market – originally regional leaders seek to expand their footprint in other regions, some of them challenging the traditional market leaders. Established cloud TMS providers expand their functional covering in a very high pace and at relatively low marginal costs, which leads to increased competition in both functional capabilities and pricing.
In the segment of companies with more than USD 1 billion revenue, SAP occupies a special position among both ERP and TMS vendors (see numbers here) – it offers both a leading ERP system and a TMS with very broad functional coverage.
Benefit areas
In what areas can you find the benefits from integrating the TMS into ERP? We list them for you.
- Process integration
Treasury is usually involved closely in the following three cross-functional processes, with the following implications:
(a) Cash management
Short- and mid-term cash forecast reflects accounts payable and accounts receivable, but purchase and sales orders can also be used to enrich the report. Even when commercial accounts are cash-pooled to treasury accounts, expected movements on these accounts can be used to plan cash pool movements on treasury accounts.
(b) Payments
Various levels of integration can be found among the companies. While some leave execution of commercial payments locally, others implement payments factories to warehouse all types of payments centrally. Screening against payment frauds and sanction breach is facilitated with centralized payment flow. Centralized, well-maintained bank master used at payment origination helps to avoid the risk of declined payments.
(c) Exposure hedging
FX and commodity hedging activities are usually centralized with the treasury team.
In case FX or commodity exposure arises from individual purchase and sales orders or contracts, the treasury team needs tools to be directly involved in the exposure identification and hedge effectiveness controlling.
- System integration
Streamlined processes described above have implications for the required system integration. Depending on frequency and criticality of the data flows, different integration approaches can be considered.
All TMS on the market support file integration with the ERP systems in a reasonable way. They are also often very strong in supporting API integration with trading platforms and bank connectivity providers, but usually lag behind in API integration with the ERPs. Claims of available API integration need to be always critically reviewed on their maturity. API integration is preferred.
What are the benefits of API-based integration?
- It offers real-time process integration between the systems and empowers treasury to be tightly integrated in the cross-functional processes. It can be important when intraday cash positions are followed, payments are executed daily or exposure needs to be hedged continuously.
- It keeps the data flow responsibility with the users. Interfaces often fail because of master data are not aligned between the participating systems. If message cannot be delivered because of this reason, user receives the error message immediately and can initiate corrective actions. On the other hand, file-based interfaces are usually monitored by IT and errors resolution needs to be coordinated with multiple parties, requiring more effort and time.
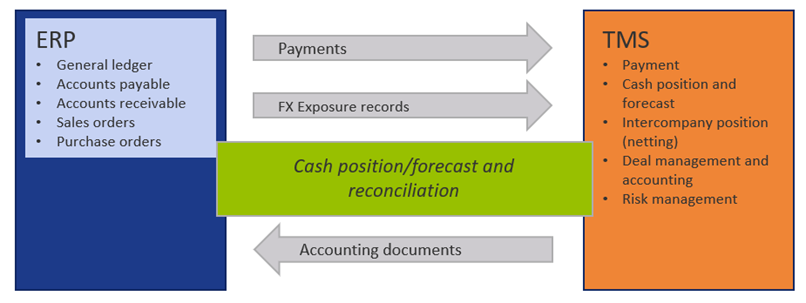
Figure 1 Usual data flow between ERP and TMS
- Parallel maintenance of master data
Integration flows require harmonization decisions in the area of master data. Financial master data (G/L accounts, cost centers, cost elements) are involved as well as bank master data and payment beneficiaries (vendors). TMS systems rarely offer an interface to automatically synchronize the master data with the ERP system – dual manual maintenance is assumed. Using one of the systems as leading system for the respective master data (e.g. bank masters) is usually not an available option.
- Redundant capabilities
Both the ERP and TMS systems need to cover certain functionalities for different purpose. ERP to support payments and cash management in purchase-to-pay and order-to-cash, while TMS supports the same in treasury process. Both systems need to cover creation of payment formats, reconciliation of electronic bank statement, update of cash position for their area. These functionalities need to be maintained in parallel, or specific solution defined, to avoid the redundancy.
Conclusion
So, should the treasury function follow into the centralized ERP solution as well, or does a separate TMS instance have its justification? The answer to this question depends strongly on your business model and the degree of functional centralization. If functional centralization and streamlined business operations across your global entities is important in your business, you are probably already very advanced in ERP centralization as well. You can expect benefits from integrating the treasury function into such system setup.
On the other hand, if the above does not apply, you may benefit from the rich choice of various TMS solutions available at competitive prices to fit your specific needs.
Every business runs differently. We are happy to support you in your specific situation.












