TCFD climate-related disclosure recommendations

The recommendations for the disclosure of climate-related financial information by the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), published in 2017, have become the de-facto disclosure standards world-wide.

An increasing number of policy makers and regulators have embedded the recommendations in industry guidance and laws. In this article we summarize the TCFD recommendations, taking into account the additional guidance that has been provided by the TCFD since the original recommendations were published.
Key takeaway:We recommend that firms begin collecting data and amend internal processes that enable them to disclose climate-related information in line with the recommendations of the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Background
The Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in December 2015 to develop climate-related disclosures that “could promote more informed investment, credit [or lending], and insurance underwriting decisions” and, in turn, “would enable stakeholders to understand better the concentrations of carbon-related assets in the financial sector and the financial system’s exposures to climate-related risks.” The TCFD finalized its recommendations in June 20171 and, based on the subsequent experience, published implementation guidance in 20212.
In line with this goal, the recommendations and implementation guidance are intended for all financial and non-financial organizations with public debt or equity. However, the TCFD encourages all organizations to implement the recommendations. An increasing number of firms are doing so and indicate explicitly as part of their annual report or financial filing where they have disclosed information in relation to individual TCFD recommendations3.
Climate-related risks and opportunities
To be able to disclose relevant climate-related information, an organization first needs to understand its exposure to climate-related risks and the opportunities that the execution of the Paris Agreement offers. Hence, it needs to evaluate the potential negative impacts of climate change on its own operations and the full value chain (covering both physical and transition risks) as well as the opportunities it offers for new products, services and markets. Subsequently, the impact of the identified risks and opportunities on revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities, and capital and financing needs to be assessed. This is summarized in the following chart.
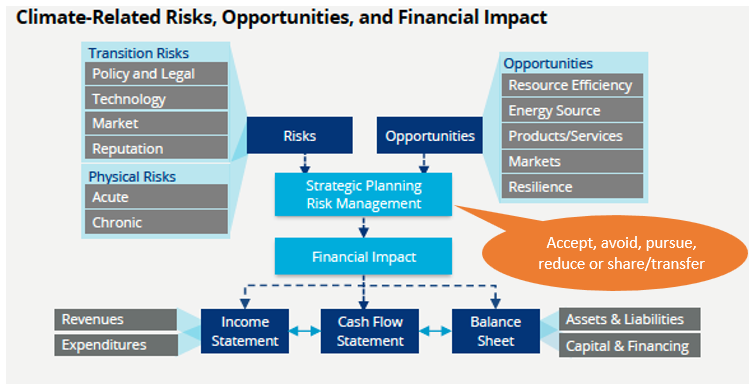
Source: TCFD, Implementing the Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, October 2021, page 9.
Appendix 1 of the TCFD implementation guidance provides examples how climate-related risks and opportunities can impact the financial statements.
The TCFD Recommendations
The TCFD has issued 11 recommendations in four main areas: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics and Targets. These are summarized in the table below.
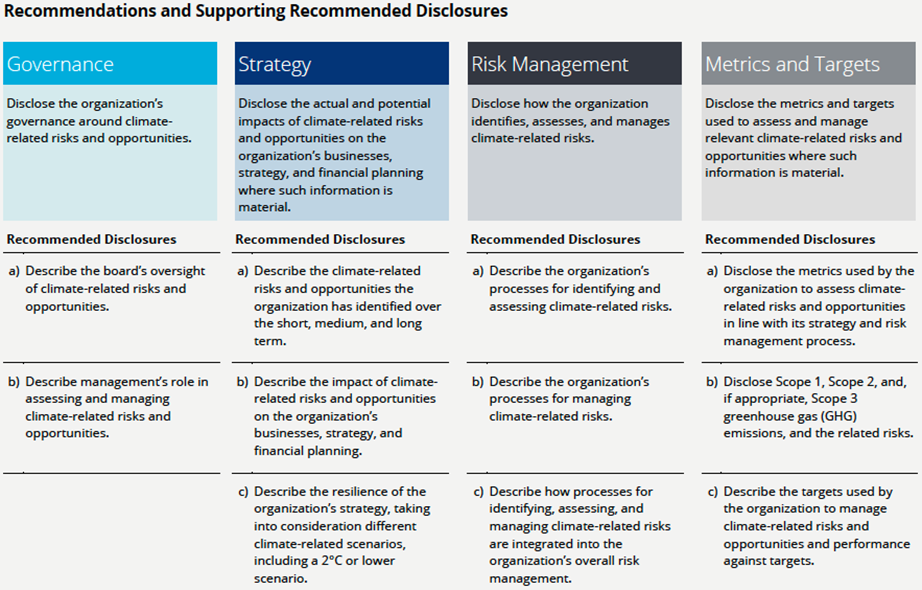
Source: TCFD, Implementing the Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, October 2021, page 15.
For banks, insurance companies, asset owners, asset managers and non-financial industries that are more likely to be financially impacted by climate-related risks4, the TCFD provides additional guidance for some of the recommended disclosures.
For banks, the additional guidance entails:
- Describe significant concentrations of credit exposure to carbon-related assets through the lending and financial intermediary business (Strategy – sub a).
- Characterize their climate-related risks in the context of traditional banking industry risk categories such as credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk (Risk Management – sub a).
- Disclose GHG emissions for their lending and other financial intermediary business activities where data and methodologies allow, calculated in line with the Global GHG Accounting and Reporting Standard for the Financial Industry developed by the Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF Standard) or a comparable methodology (Metrics and Targets – sub b).
Metrics and targets: Additional guidance
For the metrics, the TCFD provides the following suggestions for all organizations:
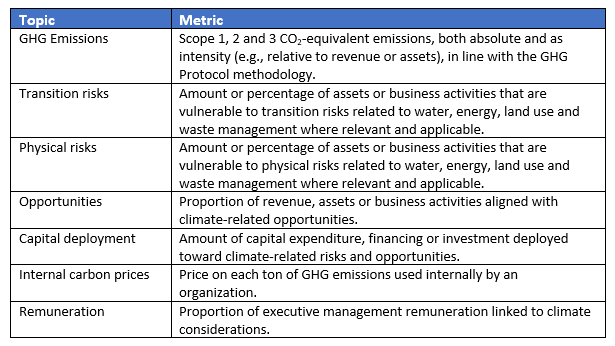
Targets can be established by specifying the planned reduction or increase in each of the metrics over a chosen time horizon, including a comparison to regulatory requirements, market constraints or other goals.
In conclusion
As the TCFD recommendations are increasingly used as basis for climate-related disclosure standards in national laws and regulatory guidance, firms are advised to start collecting data and amend internal processes that enable them to disclose climate-related information in line with these recommendations. Zanders has supported various financial institutions on climate-related topics that have a bearing on the TCFD disclosure recommendations. If you want to learn more, please do not hesitate to contact us or call at +41 44 577 70 10.
Footnotes
[1] TCFD, Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, June 2017, see TCFD Recommendations
[2] TCFD, Implementing the Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, October 2021, see TCFD Publications
[3] TCFD, 2022 Status Report, October 2022, see TCFD Publications
[4] Comprising the following sectors: energy, transportation, materials and buildings, and agriculture, food and forest products.
[5] TCFD, Guidance on Metrics, Targets and Transition Plans, October 2021, see TCFD Publications













