Sustainability in Switzerland: Recent developments

Sustainability poses risks and offers opportunities for the financial sector.

The Federal Council in Switzerland wants to make sure that the Swiss financial sector will play a leading role in sustainability. To help accomplish this, it published an action plan in December for the period 2022-2025. Furthermore, the Swiss supervisory authority FINMA issued additional guidance on how financial institutions need to account for sustainability in their strategy, governance, risk management and disclosure. In this article we provide an overview of recent developments in the area of sustainability in Switzerland that are relevant for Swiss financial institutions.
Key takeaways:
- In November 2022, a law was approved that requires all Swiss firms above a minimum size (hence including financial institutions) to disclose climate-related information in line with the recommendations from the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) as of 1 January 2024. This comes on top of the existing law that came into force on 1 January 2022, requiring all firms to disclose more broadly their management of risks to the environment, social engagement, employee interests, human rights and avoidance of corruption (for the first time as part of their annual disclosure over 2023).
- In January 2023, Swiss supervisory authority FINMA published additional guidance in which it highlights its expectation that banks and insurance companies in Switzerland proactively engage with the recent guidance and recommendations issued by the BCBS and IAIS. FINMA will intensify its supervision of the measures that institutions are taking to address climate risks and it will expand this to cover a larger number of institutions (current focus is on the largest institutions, those in FINMA categories 1 and 2). In November 2022, FINMA also published recommendations for improvements of disclosures about climate-related financial risks by category 1 and 2 institutions to satisfy existing climate-related disclosure rules, which came into effect on 1 July 2021.
- In December 2022, the Swiss Federal Council (‘Bundesrat’) published its action plan ‘Sustainable Finance in Switzerland – Areas for action for a leading sustainable financial centre 2022-2025’. The action plan contains 15 initiatives to improve the availability of comprehensive and comparable sustainability data for the full Swiss economy, enhance transparency in the financial sector with respect to climate and biodiversity risks, promote impact investments and green bonds, and support international initiatives for the pricing of environmental damage.
Disclosure requirements in line with the TCFD
From 1 January 2024, all firms above a minimum size1 are legally required to disclose climate-related information in line with the recommendations from the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) (see media release). An overview of the TCFD disclosure recommendations can be found in this separate article.
This law provides details on climate-related reporting requirements in relation to a law that entered into force on 1 January 20222. This earlier law requires firms to disclose their management of risks in relation to climate change and the environment, social engagement, employee interests, human rights and avoidance of corruption. Firms have to report on this for the first time as part of their annual disclosure over 2023, at the latest by end of June 2024. This law is based on, and in some aspects extends, the EU directive 2014/95 on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reporting from 20143.In addition, this law requires firms that import and/or process minerals from conflict or high-risk regions as well as firms which offer products or services for which the use of child labour in its supply chain is likely, to establish and report on due-diligence measures that have been implemented to manage these risks in line with international agreements.
FINMA: Guidance with respect to the management of climate risks
FINMA issued additional guidance for the management of climate risks by banks and insurance companies in January 20234. This guidance follows the publication of documents by international supervisory bodies in the financial sector, specifically:
- ‘Application paper on the Supervision of Climate-related Risks in the Insurance Sector’ by the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS) in May 2021 (See IAIS)
- ‘Principles for the effective management and supervision of climate-related financial risks’ by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) in June 2022 (See BCBS Principles and for a summary, see our recent article)
- ‘Frequently asked questions’ by the BCBS in December 2022 (See BCBS FAQ), intended to facilitate a globally uniform interpretation of the existing Pillar 1 standards in relation to climate risk5.
In the guidance, FINMA reiterates that climate risks in the form of transition, physical, legal and reputational risks should not be seen as separate risk categories, but as risk drivers for existing risk categories. It further emphasizes that banks and insurance companies are expected to implement the recommendations as contained in the above papers by the BCBS and IAIS. The areas of the recommendations are summarized in the table below.
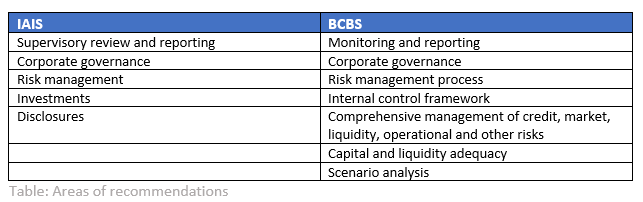
In its supervision of climate-related risks, FINMA is currently focusing on the institutions in FINMA categories 1 (currently UBS and Credit Suisse, no insurance companies) and 2 (currently Raiffeisen, PostFinance and the Zürcher Kantonalbank (ZKB) as well as five insurance companies). FINMA is also gathering initial experiences with climate scenario analysis. Over time, FINMA intends to generally intensify its supervision of the measures that institutions are taking to address climate risks and it will expand this to cover a larger number of institutions.
Institutions in supervisory categories 1 and 2 were already subject to climate-related disclosure rules from FINMA as of 1 July 2021, as embedded in the disclosure circulars 2016/1 (for banks) and 2016/2 (for insurers). The required disclosure covers:
- The governance structure in place to identify, assess, measure and monitor climate-related financial risks
- The impact of climate-related financial risks on the business and risk strategy as well as on the existing risk categories in the short, medium and long term
- Risk management structures and processes to identify, assess and manage climate-related financial risks
- Quantitative information (metrics and targets) employed, including the measurement methodologies used
In November 2022, FINMA issued an evaluation of climate-related disclosures by these institutions in their 2021 annual reports against the disclosure rules. FINMA concludes that the institutions largely met the disclosure obligations but observes that it is still difficult for readers to get a clear picture about the effective relevance of climate-related financial risks for the individual institutions. According to FINMA, it proved difficult to find the specific disclosures on climate-related financial risks in the annual and/or other (e.g., sustainability) reports and it expects institutions to more clearly present this. Furthermore, FINMA suggests the following improvements:
- More specific information on how climate risk is managed as part of the overall governance structure. This should include internal reporting of climate-related financial risks, which FINMA views as a part of embedding them in the internal governance
- More detailed information on how climate-related risks impact the business and risk strategy, including the results of a materiality assessment and differentiation of short-, medium- and long-term impact
- More transparent information about the risk management structures and processes in place to identify, assess and manage climate-related financial risks
- Clarification of the connection between climate-related financial risks and the metrics and targets that are disclosed, and which (sub)portfolios are covered by the metrics
FINMA notes that the disclosures did not give sufficient transparency about the criteria and assessment methods by institutions to evaluate the materiality of climate-related financial risks.
Swiss Federal Council: Sustainable Finance Action plan 2022-20256
The Sustainable Finance Action plan 2022-2025 of the Swiss Federal Council (“Bundesrat”) is written against the background of fulfilling the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030. However, the focus is on risks and opportunities in relation to the mitigation of climate change in line with the Paris Agreement and of biodiversity loss. The action plan consists of 15 measures in four main areas:
A: Sustainability data from all sectors of the economy
B: Transparency in the financial sector
C: Impact investments and green bonds
D: Pricing of environmental damage
An overview of the individual actions, grouped by main area, is shown in the following chart.
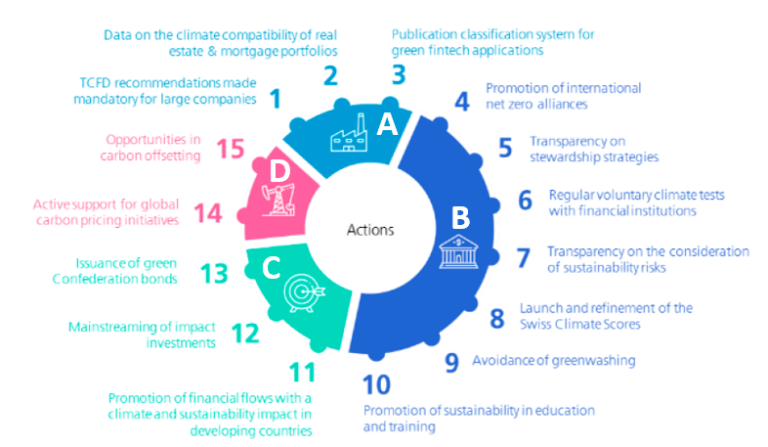
Source: Swiss Federal Council, Sustainable Finance in Switzerland – Areas for action for a leading sustainable financial centre, 2022–2025, 16 December 2022 (media release)
Below we summarize each of the 15 actions on which the Swiss government will focus, following the numbering in the graph above. Some of the actions will benefit investors and involve additional effort from financial institutions (such as those leading to additional rules or disclosure requirements in actions 1, 5, 7, 8 and 9) while others aim to benefit financial institutions (such as actions 2, 3 and 10). Some actions will affect or benefit society at large (actions 6 and 11 to 15).
A – Sustainability data from all sectors of the economy
1. This action corresponds to the law with climate-related financial disclosure requirements according to the TCFD recommendations, which we described earlier in this article. In addition, the Federal Council will continue to follow and participate in international discussions regarding biodiversity-related financial disclosures.
2. The Swiss government will increase the availability of data about the climate-friendliness of buildings in Switzerland (CO2 emissions, energy efficiency and alignment with the Swiss climate goals) in the Gebäude- und Wohnungsregister (GWR)
3. Support the introduction of a green fintech classification system (see website), which can help existing players in the Swiss financial sector to obtain access to and/or process sustainability related data in a more efficient manner.
B- Transparency in the financial sector
4. The Swiss government encourages financial institutions to join international Net-Zero-Alliances. Furthermore, it collaborates in the international Climate Data Steering Committee (CDSC) to establish a database to create transparency about the commitment of reduction in greenhouse gas emissions of individual financial institutions.
5. In December 2022, the Federal Council recommended that financial institutions and pension funds publish information on how their client engagement strategy and the exercise of equity voting rights aligns with the own net-zero strategy.
6. The government will continue to conduct regular, voluntary climate tests of the financial sector, to provide transparency how the financial sector as a whole aligns with achieving the goals of the Paris agreement (results of the 2022 test can be found on this website).
7. Already in 2020, the Federal Council recommended that financial institutions publish the methods and strategies employed for taking account of climate and environmental risks when managing clients’ assets, in accordance with the existing legal duties of loyalty and due diligence.
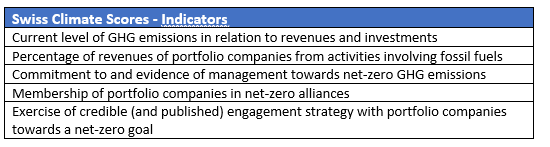
8. In June 2022, the Federal Council recommended that financial institutions use comparable and meaningful information about alignment of financial investments and client portfolios with global (net-zero) climate goals. To support this, it introduced the ‘Swiss Climate Scores’ (see Climate Scores website). These Swiss Climate Scores comprise indicators for both the current and prospective alignment with global (net-zero) climate goals, which are summarized in the table below.
9. Establish rules to avoid greenwashing of financial products and services, ensuring that products and services that are labeled as sustainable are aligned with, or contribute to the achievement of at least one specific sustainability goal.
10. Promote sustainable finance education
C. Impact investments and green bonds
11. Promote impact investments in developing countries, for example by establishing the ‘Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Impact Finance initiative’ in 2021 and the goals of the ‘Swiss Investment Fund for Emerging Markets (SIFEM) 2021-2024’.
12. Examine, in collaboration with the industry and FINMA, how financial market legislation can be amended to promote the expansion of impact investments.
13. Issue green Swiss Confederation bonds.
D – Pricing of environmental damage
14. Active support of multi-lateral initiatives to establish an equitable global carbon price.
15. Investigate what role the federal government can play to exploit opportunities for the Swiss financial market in the area of CO2-compensation.
In conclusion
Pressure on firms in Switzerland is increasing to be more transparent on how climate and environmental risks are identified, assessed and managed as part of the regular course of business. Zanders has supported various financial institutions on climate and environmental risk-related topics in the EU as they need to adhere to detailed expectations from the European Central Bank (ECB) and the European Union (EU). If you want to learn more, please contact us or call at +41 44 577 70 10.
Footnotes
[1] At least 500 FTE and a balance sheet total of at least CHF 20 million and/or revenues of at least CHF 40 million on a consolidated basis
[2] See media release.
[3] Within the EU, this is generally referred to as the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). On 5 January 2023 the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) entered into force, succeeding the NFRD (details can be found here). The CSRD extends the scope of the companies covered to all large and all listed companies, requires the audit (assurance) of reported information and strengthens the standardisation of reported information by empowering the Commission to adopt sustainability reporting standards.
[5] The EBA published a discussion paper on the inclusion of environmental risks in Pillar 1 capital requirements, see EBA and for a summary EBA summary https://zandersgroup.com/en/latest-insights/are-climate-change-risks-properly-captured-in-the-prudential-framework/.
[6] See media release













