Converging on resilience: Integrating CCR, XVA, and real-time risk management

In a world where the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) commands much attention, it’s easy for counterparty credit risk (CCR) to slip under the radar.
However, CCR remains an essential element in banking risk management, particularly as it converges with valuation adjustments. These changes reflect growing regulatory expectations, which were further amplified by recent cases such as Archegos. Furthermore, regulatory focus seems to be shifting, particularly in the U.S., away from the Internal Model Method (IMM) and toward standardised approaches. This article provides strategic insights for senior executives navigating the evolving CCR framework and its regulatory landscape.
Evolving trends in CCR and XVA
Counterparty credit risk (CCR) has evolved significantly, with banks now adopting a closely integrated approach with valuation adjustments (XVA) — particularly Credit Valuation Adjustment (CVA), Funding Valuation Adjustment (FVA), and Capital Valuation Adjustment (KVA) — to fully account for risk and costs in trade pricing. This trend towards blending XVA into CCR has been driven by the desire for more accurate pricing and capital decisions that reflect the true risk profile of the underlying instruments/ positions.
In addition, recent years have seen a marked increase in the use of collateral and initial margin as mitigants for CCR. While this approach is essential for managing credit exposures, it simultaneously shifts a portion of the risk profile into contingent market and liquidity risks, which, in turn, introduces requirements for real-time monitoring and enhanced data capabilities to capture both the credit and liquidity dimensions of CCR. Ultimately, this introduces additional risks and modelling challenges with respect to wrong way risk and clearing counterparty risk.
As banks continue to invest in advanced XVA models and supporting technologies, senior executives must ensure that systems are equipped to adapt to these new risk characteristics, as well as to meet growing regulatory scrutiny around collateral management and liquidity resilience.
The Internal Model Method (IMM) vs. SA-CCR
In terms of calculating CCR, approaches based on IMM and SA-CCR provide divergent paths. On one hand, IMM allows banks to tailor models to specific risks, potentially leading to capital efficiencies. SA-CCR, on the other hand, offers a standardised approach that’s straightforward yet conservative. Regulatory trends indicate a shift toward SA-CCR, especially in the U.S., where reliance on IMM is diminishing.
As banks shift towards SA-CCR for Regulatory capital and IMM is used increasingly for internal purposes, senior leaders might need to re-evaluate whether separate calibrations for CVA and IMM are warranted or if CVA data can inform IMM processes as well.
Regulatory focus on CCR: Real-time monitoring, stress testing, and resilience
Real-time monitoring and stress testing are taking centre stage following increased regulatory focus on resilience. Evolving guidelines, such as those from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), emphasise a need for efficiency and convergence between trading and risk management systems. This means that banks must incorporate real-time risk data and dynamic monitoring to proactively manage CCR exposures and respond to changes in a timely manner.
CVA hedging and regulatory treatment under IMM
CVA hedging aims to mitigate counterparty credit spread volatility, which affects portfolio credit risk. However, current regulations limit offsetting CVA hedges against CCR exposures under IMM. This regulatory separation of capital for CVA and CCR leads to some inefficiencies, as institutions can’t fully leverage hedges to reduce overall exposure.
Ongoing BIS discussions suggest potential reforms for recognising CVA hedges within CCR frameworks, offering a chance for more dynamic risk management. Additionally, banks are exploring CCR capital management through LGD reductions using third-party financial guarantees, potentially allowing for more efficient capital use. For executives, tracking these regulatory developments could reveal opportunities for more comprehensive and capital-efficient approaches to CCR.
Leveraging advanced analytics and data integration for CCR
Emerging technologies in data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and scenario analysis are revolutionising CCR. Real-time data analytics provide insights into counterparty exposures but typically come at significant computational costs: high-performance computing can help mitigate this, and, if coupled with AI, enable predictive modelling and early warning systems. For senior leaders, integrating data from risk, finance, and treasury can optimise CCR insights and streamline decision-making, making risk management more responsive and aligned with compliance.
By leveraging advanced analytics, banks can respond proactively to potential CCR threats, particularly in scenarios where early intervention is critical. These technologies equip executives with the tools to not only mitigate CCR but also enhance overall risk and capital management strategies.
Strategic considerations for senior executives: Capital efficiency and resilience
Balancing capital efficiency with resilience requires careful alignment of CCR and XVA frameworks with governance and strategy. To meet both regulatory requirements and competitive pressures, executives should foster collaboration across risk, finance, and treasury functions. This alignment will enhance capital allocation, pricing strategies, and overall governance structures.
For banks facing capital constraints, third-party optimisation can be a viable strategy to manage the demands of SA-CCR. Executives should also consider refining data integration and analytics capabilities to support efficient, resilient risk management that is adaptable to regulatory shifts.
Conclusion
As counterparty credit risk re-emerges as a focal point for financial institutions, its integration with XVA, and the shifting emphasis from IMM to SA-CCR, underscore the need for proactive CCR management. For senior risk executives, adapting to this complex landscape requires striking a balance between resilience and efficiency. Embracing real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and strategic cross-functional collaboration is crucial to building CCR frameworks that withstand regulatory scrutiny and position banks competitively.
In a financial landscape that is increasingly interconnected and volatile, an agile and resilient approach to CCR will serve as a foundation for long-term stability. At Zanders, we have significant experience implementing advanced analytics for CCR. By investing in robust CCR frameworks and staying attuned to evolving regulatory expectations, senior executives can prepare their institutions for the future of CCR and beyond thereby avoiding being left behind.
Confirmed Methodology for Credit Risk in EBA 2025 Stress Test

On November 12 2024, the confirmed methodology for the EBA 2025 stress testing exercise was published on the EBA website. This is the final version of the draft for initial consultation that was published earlier.
| The timelines for the entire exercise have been extended to accommodate the changes in scope: | |
| Launch of exercise (macro scenarios) | Second half of January 2025 |
| First submission of results to the EBA | End of April 2025 |
| Second submission to the EBA | Early June 2025 |
| Final submission to the EBA | Early July 2025 |
| Publication of results | Beginning of August 2025 |
Below we share the most significant aspects for Credit Risk and related challenges. In the coming weeks we will share separate articles to cover areas related to Market Risk, Net Interest Income & Expenses and Operational Risk.
The final methodology, along with the requirements introduced by the CRR3 poses significant challenges on the execution of the Credit Risk stress testing. Earlier we provided details on this topic and possible impacts on stress testing results, see our article: “Implications of CRR3 for the 2025 EU-wide stress test” Regarding the EBA 2025 stress test we view the following 5 points as key areas of concern:
1- The EBA stress test requires different starting points; actual and restated CRR3 figures. This raises requirements in data management, reporting and implementation of related processes.
2- The EBA stress test requires banks to report both transitional and fully loaded results under CRR3; this requires the execution of additional calculations and implementation of supporting data processes.
3- The changes in classification of assets require targeted effort on the modelling side, stress test approach and related data structures.
4- Implementation of the Standardized Approach output floor as part of the stress test logic.
5- Additional effort is needed to correctly align Pillar 1 and Pillar 2 models, in terms of development, implementation and validation.
At Zanders, we specialize in risk advisory and our consultants have participated in every single EU wide stress testing exercise, as well as a few others going back to the initial stress tests in 2009 following the Great Financial Crisis. We can support you throughout all key stages of the stress testing exercise across all areas to ensure a successful submission of the final templates.
Based on the expertise in Stress Testing we have gained over the last 15 years, our clients benefit the most from our services in these areas:
- Full gap analysis against latest set of requirements
- Review, design and implementation of data processes & relevant data quality controls
- Alignment of Pillar 2 models to Pillar 1 (including CCR3 requirements)
- Design, implementation and execution of stress testing models
- Full automation of populating EBA templates including reconciliation and data quality checks.
Contact us for more information about how we can help make this your most successful run yet. Reach out to Martijn de Groot, Partner at Zanders.
Implications of CRR3 for the 2025 EU-wide stress test

An overview of how the new CRR3 regulation impacts banks’ capital requirements for credit risk and its implications for the 2025 EU-wide stress test, based on EBA’s findings.
With the introduction of the updated Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3), which has entered into force on 9 July 2024, the European Union's financial landscape is poised for significant changes. The 2025 EU-wide stress test will be a major assessment to measure the resilience of banks under these new regulations. This article summarizes the estimated impact of CRR3 on banks’ capital requirements for credit risk based on the results of a monitoring exercise executed by the EBA in 2022. Furthermore, this article comments on the potential impact of CRR3 to the upcoming stress test, specifically from a credit risk perspective, and describes the potential implications for the banking sector.
The CRR3 regulation, which is the implementation of the Basel III reforms (also known as Basel IV) into European law, introduces substantial updates to the existing framework [1], including increased capital requirements, enhanced risk assessment procedures and stricter reporting standards. Focusing on credit risk, the most significant changes include:
- The phased increase of the existing output floor to internally modelled capital requirements, limiting the benefit of internal models in 2028 to 72.5% of the Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) calculated under the Standardised Approach (SA), see Table 1. This floor is applied on consolidated level, i.e. on the combined RWA of all credit, market and operational risk.

- A revised SA to enhance robustness and risk sensitivity, via more granular risk weights and the introduction of new asset classes.1
- Limiting the application of the Advanced Internal Ratings Based (A-IRB) approach to specific asset classes. Additionally, new asset classes have been introduced.2
After the launch of CRR3 in January 2025, 68 banks from the EU and Norway, including 54 from the Euro area, will participate in the 2025 EU-wide stress test, thus covering 75% of the EU banking sector [2]. In light of this exercise, the EBA recently published their consultative draft of the 2025 EU-wide Stress Test Methodological Note [3], which reflects the regulatory landscape shaped by CRR3. During this forward-looking exercise the resilience of EU banks in the face of adverse economic conditions will be tested within the adjusted regulatory framework, providing essential data for the 2025 Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP).
The consequences of the updated regulatory framework are an important topic for banks. The changes in the final framework aim to restore credibility in the calculation of RWAs and improve the comparability of banks' capital ratios by aligning definitions and taxonomies between the SA and IRB approaches. To assess the impact of CRR3 on the capital requirements and whether this results in the achievement of this aim, the EBA executed a monitoring exercise in 2022 to quantify the impact of the new regulations, and published the results (refer to the report in [4]).
For this monitoring exercise the EBA used a sample of 157 banks, including 58 Group 1 banks (large and internationally active banks), of which 8 are classified as a Global Systemically Important Institution (G-SII), and 99 Group 2 banks. Group 1 banks are defined as banks that have Tier 1 capital in excess of EUR 3 billion and are internationally active. All other banks are labelled as Group 2 banks. In the report the results are separated per group and per risk type.
Looking at the impact on the credit risk capital requirements specifically caused by the revised SA and the limitations on the application of IRB, the EBA found that the median increase of current Tier 1 Minimum Required Capital3 (hereafter “MRC”) is approximately 3.2% over all portfolios, i.e. SA and IRB approach portfolios. Furthermore, the median impact on current Tier 1 MRC for SA portfolios is approximately 2.1% and for IRB portfolios is 0.5% (see [4], page 31). This impact can be mainly attributed to the introduction of new (sub) asset classes with higher risk weights on average. The largest increases are expected for ‘equities’, ‘equity investment in funds’ and ‘subordinated debt and capital instruments other than equity’. Under adverse scenarios the impact of more granular risk weights may be magnified due to a larger share of exposures having lower credit ratings. This may result in additional impact on RWA.
The revised SA results in more risk-sensitive capital requirements predictions over the forecast horizon due to the more granular risk weights and newly introduced asset classes. This in turn allows banks to more clearly identify their risk profile and provides the EBA with a better overview of the performance of the banking sector as a whole under adverse economic conditions. Additionally, the impact on RWA caused by the gradual increase of the output floor, as shown in Table 1, was estimated. As shown in Table 2, it was found that the gradual elevation of the output floor increasingly affects the MRC throughout the phase-in period (2023-2028).
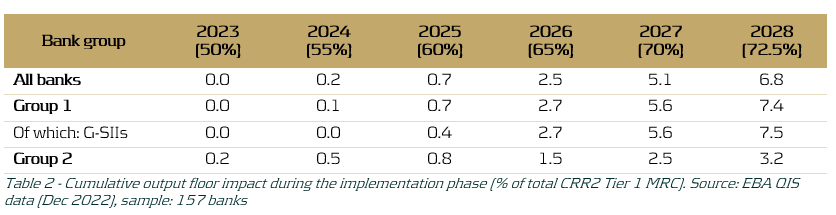
Table 2 demonstrates that the impact is minimal in the first three years of the phase-in period, but grows significantly in the last three years of the phase-in period, with an average estimated 7.5% increase in Tier 1 MRC for G-SIIs in 2028. The larger increase in Tier 1 MRC for Group 1 banks, and G-SIIs in particular, as compared to Group 2 banks may be explained by the fact that larger banks more often employ an IRB approach and are thus more heavily impacted by an increased IRB floor, relative to their smaller counterparts. The expected impact on Group 1 banks is especially interesting in the context of the EU-wide stress test, since for the regulatory stress test only the 68 largest banks in Europe participate. Assuming that banks need to employ an increasing version of the output floor for their projections during the 2025 EU-wide stress test, this could lead to significant increases in capital requirements in the last years of the forecast horizon of the RWA projections. These increases may not be fully attributed to the adverse effects of the provided macroeconomic scenarios.
Conversely, it is good to note that a transition cap has been introduced by the Basel III reforms and adopted in CRR3. This cap puts a limit on the incremental increase of the output floor impact on total RWAs. The transitional period cap is set at 25% of a bank’s year-to-year increase in RWAs and may be exercised at the discretion of supervisors on a national level (see [5]). As a consequence, this may limit the observed increase in RWA during the execution of the 2025 EU-wide stress test.
In conclusion, the implementation of CRR3 and its adoption into the 2025 EU-wide stress test methodology may have a significant impact on the stress test results, mainly due to the gradual increase in the IRB output floor but also because of changes in the SA and IRB approaches. However, this effect may be partly mitigated by the transitional 25% cap on year-on-year incremental RWA due to the output floor increase. Additionally, the 2025 EU-wide stress test will provide a comprehensive view of the impact of CRR3, including the closer alignment between the SA and the IRB approaches, on the development of capital requirements in the banking sector under adverse conditions.
References:
- final_report_on_amendments_to_the_its_on_supervisory_reporting-crr3_crd6.pdf (europa.eu)
- The EBA starts dialogue with the banking industry on 2025 EU-Wide stress test methodology | European Banking Authority (europa.eu)
- 2025 EU-wide stress test - Methodological Note.pdf (europa.eu)
- Basel III monitoring report as of December 2022.pdf (europa.eu)
- Basel III: Finalising post-crisis reforms (bis.org)
- This includes the addition of the ‘Subordinated debt exposures’ asset class, as well as an additional branch of specialized lending exposures within the corporates asset class. Furthermore, a more detailed breakdown of exposures secured by mortgages on immovable property and acquisition, development and construction financing? has been introduced. ↩︎
- For in detailed information on the added asset classes and limited application of IRB refer to paragraph 25 of the report in [1]. ↩︎
- Tier 1 capital refers to the core capital held in a bank's reserves. It includes high-quality capital, predominantly in the form of shares and retained earnings that can absorb losses. The Tier 1 MRC is the minimum capital required to satisfy the regulatory Tier 1 capital ratio (ratio of a bank's core capital to its total RWA) determined by Basel and is an important metric the EBA uses to measure a bank’s health. ↩︎
ECB – Cyber Resilience Stress Test: Scope, Methodology and Scenario.
The European Central Bank (ECB) is charting new territories in the realm of financial security with a groundbreaking thematic stress test slated for 2024
In the stress test methodology, participating banks are required to evaluate the impact of a cyber attack. They must communicate their response and recovery efforts by completing a questionnaire and submitting pertinent documentation. Banks undergoing enhanced assessment are further mandated to conduct and report the results of IT recovery tests specific to the scenario. The reporting of the cyber incident is to be done using the template outlined in the SSM Cyber-incident reporting framework.
Assessing Digital Fortitude: Scope and Objectives
The ECB's decision to conduct a thematic stress test on cyber resilience in 2024 holds profound significance. The primary objective is to assess the digital operational resilience of 109 Significant Institutions, contemplating the impact of a severe but plausible cybersecurity event. This initiative seeks to uncover potential weaknesses within the systems and derive strategic remediation actions. Notably, 28 banks will undergo an enhanced assessment, heightening the scrutiny on their cyber resilience capabilities. The outcomes are poised to reverberate across the financial landscape, influencing the 2024 SREP OpRisk Score and shaping qualitative requirements.
General Overview and Scope
- Supervisory Board of ECB has decided to conduct a thematic stress test on „cyber resilience“ in 2024.
- Main objective is to assess the digital operational resilience in case of a severe but plausible cybersecurity event, to identify potential weaknesses and derive remediation actions.
- Participants will be 109 Significant Institutions (28 banks will be in scope of an enhanced assessment).
- The outcome will have an impact on the 2024 SREP OpRisk Score and qualitative requirements.
Navigating the Evaluation: Stress Test Methodology
Participating banks find themselves at the epicenter of this evaluative process. They are tasked with assessing the impact of a simulated cyber attack and meticulously reporting their response and recovery efforts. This involves answering a comprehensive questionnaire and providing relevant documentation as evidence. For those under enhanced assessment, an additional layer of complexity is introduced – the execution and reporting of IT recovery tests tailored to the specific scenario. The cyber incident reporting follows a structured template outlined in the SSM Cyber-incident reporting framework.
Stress Test Methodology
- Participating banks have to assess the impact of the cyber-attack and report their response and recovery by answering the questionnaire and providing relevant documentation as evidence.
- Banks under the enhanced assessment are additionally requested to execute and provide results of IT recovery tests tailored to the specific scenario.
- The cyber incident has to be reported by using the template of the SSM Cyber-incident reporting framework.
Setting the Stage: Scenario Unveiled
The stress test unfolds with a meticulously crafted hypothetical scenario. Envision a landscape where all preventive measures against a cyber attack have either been bypassed or failed. The core of this simulation involves a cyber-attack causing a loss of integrity in the databases supporting a bank's main core banking system. Validation of the affected core banking system is a crucial step, overseen by the Joint Supervisory Team (JST). The final scenario details will be communicated on January 2, 2024, adding a real-time element to this strategic evaluation.
Scenario
- The stress test will consist of a hypothetical scenario that assumes that all preventive measures have been bypassed or have failed.
- The cyber-attack will cause a loss of integrity of the database(s) that support the bank’s main core banking system.
- The banks have to validate the selection of the affected core banking system with the JST.
- The final scenario will be communicated on 2 January 2024.
Partnering for Success: Zanders' Service Offering
In the complex terrain of the Cyber Resilience Stress Test, Zanders stands as a reliable partner. Armed with deep knowledge in Non-Financial Risk, we navigate the intricacies of the upcoming stress test seamlessly. Our support spans the entire exercise, from administrative aspects to performing assessments that determine the impact of the cyber attack on key financial ratios as requested by supervisory authorities. This service offering underscores our commitment to fortifying financial institutions against evolving cyber threats.
Zanders Service Offering
- Our deep knowledge in Non-Financial Risk enables us to navigate smoothly through the complexity of the upcoming Cyber Resilience Stress Test.
- We support participating banks during the whole exercise of the upcoming Stress Test.
- Our Services cover the whole bandwidth of required activities starting from administrative aspects and ending up at performing assessments to determine the impact of the cyber-attack in regard of key financial ratios requested by the supervisory authority.
Performance of Dutch banks in the 2023 EBA stress test
The European Central Bank (ECB) is charting new territories in the realm of financial security with a groundbreaking thematic stress test slated for 2024
Seventy banks have been considered, which is an increase of twenty banks compared to the previous exercise. The portfolios of the participating banks contain around three quarters of all EU banking assets (Euro and non-Euro).
Interested in how the four Dutch banks participating in this EBA stress test exercise performed? In this short note we compare them with the EU average as represented in the results published [1].
General comments
The general conclusion from the EU wide stress test results is that EU banks seem sufficiently capitalized. We quote the main 5 points as highlighted in the EBA press release [1]:
- The results of the 2023 EU-wide stress test show that European banks remain resilient under an adverse scenario which combines a severe EU and global recession, increasing interest rates and higher credit spreads.
- This resilience of EU banks partly reflects a solid capital position at the start of the exercise, with an average fully-loaded CET1 ratio of 15% which allows banks to withstand the capital depletion under the adverse scenario.
- The capital depletion under the adverse stress test scenario is 459 bps, resulting in a fully loaded CET1 ratio at the end of the scenario of 10.4%. Higher earnings and better asset quality at the beginning of the 2023 both help moderate capital depletion under the adverse scenario.
- Despite combined losses of EUR 496bn, EU banks remain sufficiently apitalized to continue to support the economy also in times of severe stress.
- The high current level of macroeconomic uncertainty shows however the importance of remaining vigilant and that both supervisors and banks should be prepared for a possible worsening of economic conditions.
For further details we refer to the full EBA report [1].
Dutch banks
Making the case for transparency across the banking sector, the EBA has released a detailed breakdown of relevant figures for each individual bank. We use some of this data to gain further insight into the performance of the main Dutch banks versus the EU average.
CET1 ratios
Using the data presented by EBA [2], we display the evolution of the fully loaded CET1 ratio for the four banks versus the average over all EU banks in the figure below. The four Dutch banks are: ING, Rabobank, ABN AMRO and de Volksbank, ordered by size.
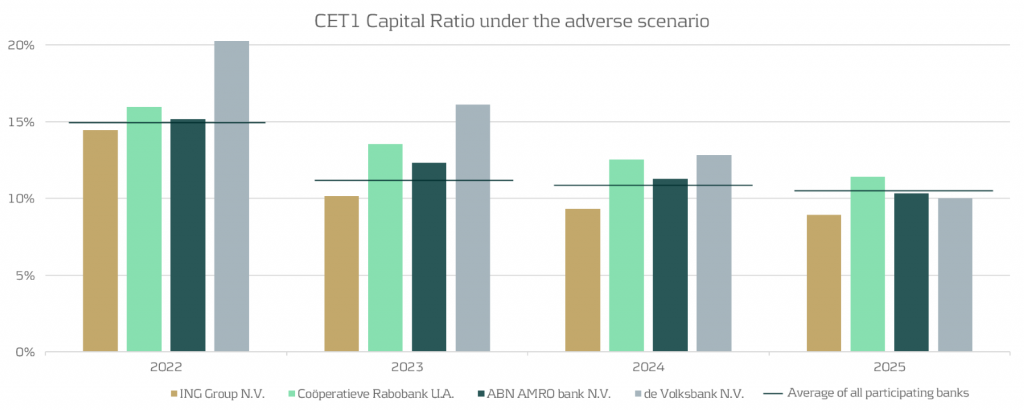
From the figure, we observe the following:
- Compared to the average EU-wide CET1 ratio (indicated by the horizontal lines in the graph above), it can be observed that three out of four of the banks are very close to the EU average.
- For the average EU wide CET1 ratio we observe a significant drop from year 1 to year 2, while for the Dutch banks the impact of the stress is more spread out over the full scenario horizon.
- The impact after year 4 of the stress horizon is more severe than the EU average for three out of four of the Dutch banks.
Evolution of retail mortgages during adverse scenario
The most important product the four Dutch banks have in common are the retail mortgages. We look at the evolution of the retail mortgage portfolios of the Dutch banks compared to the EU average. Using EBA data provided [2], we summarize this in the following chart:
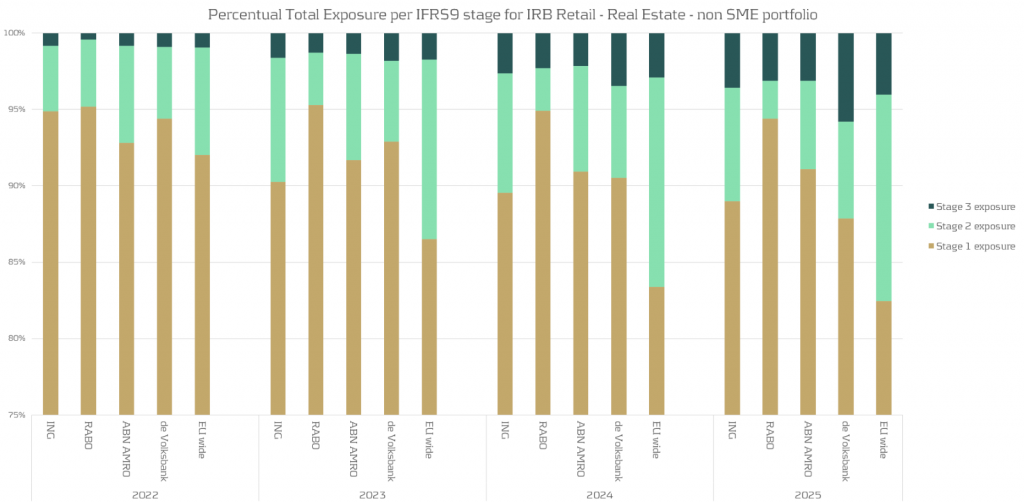
Based on the analysis above , we observe:
- There is a noticeable variation between the banks regarding the migrations between the IFRS stages.
- Compared to the EU average there are much less mortgages with a significant increase in credit risk (migrations to IFRS stage 2) for the Dutch banks. For some banks the percentage of loans in stage 2 is stable or even decreases.
Conclusion
This short note gives some indication of specifics of the 2023 EBA stress applied to the four main Dutch banks.
Should you wish to go deeper into this subject, Zanders has both the expertise and track record to assist financial organisations with all aspects of stress testing. Please get in touch.


