ISO 20022 XML – An Opportunity to Accelerate and Elevate Receivables Reconciliation

The adoption of ISO 20022 XML standards significantly enhances invoice reconciliation and operational efficiency, improving working capital management and Days Sales Outstanding (DSO).
Whether a corporate operates through a decentralized model, shared service center or even global business services model, identifying which invoices a customer has paid and in some cases, a more basic "who has actually paid me" creates a drag on operational efficiency. Given the increased focus on working capital efficiencies, accelerating cash application will improve DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) which is a key contributor to working capital. As the industry adoption of ISO 20022 XML continues to build momentum, Zanders experts Eliane Eysackers and Mark Sutton provide some valuable insights around why the latest industry adopted version of XML from the 2019 ISO standards maintenance release presents a real opportunity to drive operational and financial efficiencies around the reconciliation domain.
A quick recap on the current A/R reconciliation challenges
Whilst the objective will always be 100% straight-through reconciliation (STR), the account reconciliation challenges fall into four distinct areas:
1. Data Quality
- Partial payment of invoices.
- Single consolidated payment covering multiple invoices.
- Truncated information during the end to end payment processing.
- Separate remittance information (typically PDF advice via email).
2. In-country Payment Practices and Payment Methods
- Available information supported through the in-country clearing systems.
- Different local clearing systems – not all countries offer a direct debit capability.
- Local market practice around preferred collection methods (for example the Boleto in Brazil).
- ‘Culture’ – some countries are less comfortable with the concept of direct debit collections and want full control to remain with the customer when it comes to making a payment.
3. Statement File Format
- Limitations associated with some statement reporting formats – for example the Swift MT940 has approximately 20 data fields compared to the ISO XML camt.053 bank statement which contains almost 1,600 xml tags.
- Partner bank capability limitations in terms of the supported statement formats and how the actual bank statements are generated. For example, some banks still create a camt.053 statement using the MT940 as the data source. This means the corporates receives an xml MT940!
- Market practice as most companies have historically used the Swift MT940 bank statement for reconciliation purposes, but this legacy Swift MT first mindset is now being challenged with the broader industry migration to ISO 20022 XML messaging.
4. Technology & Operations
- Systems limitations on the corporate side which prevent the ERP or TMS consuming a camt.053 bank statement.
- Limited system level capabilities around auto-matching rules based logic.
- Dependency on limited IT resources and budget pressures for customization.
- No global standardized system landscape and operational processes.
How can ISO20022 XML bank statements help accelerate and elevate reconciliation performance?
At a high level, the benefits of ISO 20022 XML financial statement messaging can be boiled down into the richness of data that can be supported through the ISO 20022 XML messages. You have a very rich data structure, so each data point should have its own unique xml field. This covers not only more structured information around the actual payment remittance details, but also enhanced data which enables a higher degree of STR, in addition to the opportunity for improved reporting, analysis and importantly, risk management.
Enhanced Data
- Structured remittance information covering invoice numbers, amounts and dates provides the opportunity to automate and accelerate the cash application process, removing the friction around manual reconciliations and reducing exceptions through improved end to end data quality.
- Additionally, the latest camt.053 bank statement includes a series of key references that can be supported from the originator generated end to end reference, to the Swift GPI reference and partner bank reference.
- Richer FX related data covering source and target currencies as well as applied FX rates and associated contract IDs. These values can be mapped into the ERP/TMS system to automatically calculate any realised gain/loss on the transaction which removes the need for manual reconciliation.
- Fees and charges are reported separately, combined a rich and very granular BTC (Bank Transaction Code) code list which allows for automated posting to the correct internal G/L account.
- Enhanced related party information which is essential when dealing with organizations that operate an OBO (on-behalf-of) model. This additional transparency ensures the ultimate party is visible which allows for the acceleration through auto-matching.
- The intraday (camt.052) provides an acceleration of this enhanced data that will enable both the automation and acceleration of reconciliation processes, thereby reducing manual effort. Treasury will witness a reduction in credit risk exposure through the accelerated clearance of payments, allowing the company to release goods from warehouses sooner. This improves customer satisfaction and also optimizes inventory management. Furthermore, the intraday updates will enable efficient management of cash positions and forecasts, leading to better overall liquidity management.
Enhanced Risk Management
- The full structured information will help support a more effective and efficient compliance, risk management and increasing regulatory process. The inclusion of the LEI helps identify the parent entity. Unique transaction IDs enable the auto-matching with the original hedging contract ID in addition to credit facilities (letters of credit/bank guarantees).
In Summary
The ISO 20022 camt.053 bank statement and camt.052 intraday statement provide a clear opportunity to redefine best in class reconciliation processes. Whilst the camt.053.001.02 has been around since 2009, corporate adoption has not matched the scale of the associated pain.001.001.03 payment message. This is down to a combination of bank and system capabilities, but it would also be relevant to point out the above benefits have not materialised due to the heavy use of unstructured data within the camt.053.001.02 message version.
The new camt.053.001.08 statement message contains enhanced structured data options, which when combined with the CGI-MP (Common Global Implementation – Market Practice) Group implementation guidelines, provide a much greater opportunity to accelerate and elevate the reconciliation process. This is linked to the recommended prescriptive approach around a structured data first model from the banking community.
Finally, linked to the current Swift MT-MX migration, there is now agreement that up to 9,000 characters can be provided as payment remittance information. These 9,000 characters must be contained within the structured remittance information block subject to bilateral agreement within the cross border messaging space. Considering the corporate digital transformation agenda – to truly harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technology – data – specifically structured data, will be the fuel that powers AI. It’s important to recognize that ISO 20022 XML will be an enabler delivering on the technologies potential to deliver both predictive and prescriptive analytics. This technology will be a real game-changer for corporate treasury not only addressing a number of existing and longstanding pain-points but also redefining what is possible.
ISO 20022 XML V09 – Is it time for Corporate Treasury to Review the Cash Management Relationship with Banks?

The adoption of ISO 20022 XML standards significantly enhances invoice reconciliation and operational efficiency, improving working capital management and Days Sales Outstanding (DSO).
The corporate treasury agenda continues to focus on cash visibility, liquidity centralization, bank/bank account rationalization, and finally digitization to enable greater operational and financial efficiencies. Digital transformation within corporate treasury is a must have, not a nice to have and with technology continuing to evolve, the potential opportunities to both accelerate and elevate performance has just been taken to the next level with ISO 20022 becoming the global language of payments. In this 6th article in the ISO 20022 XML series, Zanders experts Fernando Almansa, Eliane Eysackers and Mark Sutton provide some valuable insights around why this latest global industry move should now provide the motivation for corporate treasury to consider a cash management RFP (request for proposal) for its banking services.
Why Me and Why Now?
These are both very relevant important questions that corporate treasury should be considering in 2024, given the broader global payments industry migration to ISO 20022 XML messaging. This goes beyond the Swift MT-MX migration in the interbank space as an increasing number of in-country RTGS (real-time gross settlement) clearing systems are also adopting ISO 20022 XML messaging. Swift are currently estimating that by 2025, 80% of the domestic high value clearing RTGS volumes will be ISO 20022-based with all reserve currencies either live or having declared a live date. As more local market infrastructures migrate to XML messaging, there is the potential to provide richer and more structured information around the payment to accelerate and elevate compliance and reconciliation processes as well as achieving a more simplified and standardized strategic cash management operating model.
So to help determine if this really applies to you, the following questions should be considered around existing process friction points:
- Is your current multi-banking cash management architecture simplified and standardised?
- Is your account receivables process fully automated?
- Is your FX gain/loss calculations fully automated?
- Have you fully automated the G/L account posting?
- Do you have a standard ‘harmonized’ payments message that you send to all your banking partners?
If the answer is yes to all the above, then you are already following a best-in-class multi-banking cash management model. But if the answer is no, then it is worth reading the rest of this article as we now have a paradigm shift in the global payments landscape that presents a real opportunity to redefine best in class.
What is different about XML V09?
Whilst structurally, the XML V09 message only contains a handful of additional data points when compared with the earlier XML V03 message that was released back in 2009, the key difference is around the changing mindset from the CGI-MP (Common Global Implementation – Market Practice) Group1 which is recommending a more prescriptive approach to the banking community around adoption of its published implementation guidelines. The original objective of the CGI-MP was to remove the friction that existed in the multi-banking space as a result of the complexity, inefficiency, and cost of corporates having to support proprietary bank formats. The adoption of ISO 20022 provided the opportunity to simplify and standardize the multi-banking environment, with the added benefit of providing a more portable messaging structure. However, even with the work of the CGI-MP group, which produced and published implementation guidelines back in 2009, the corporate community has encountered a significant number of challenges as part of their adoption of this global financial messaging standard.
The key friction points are highlighted below:
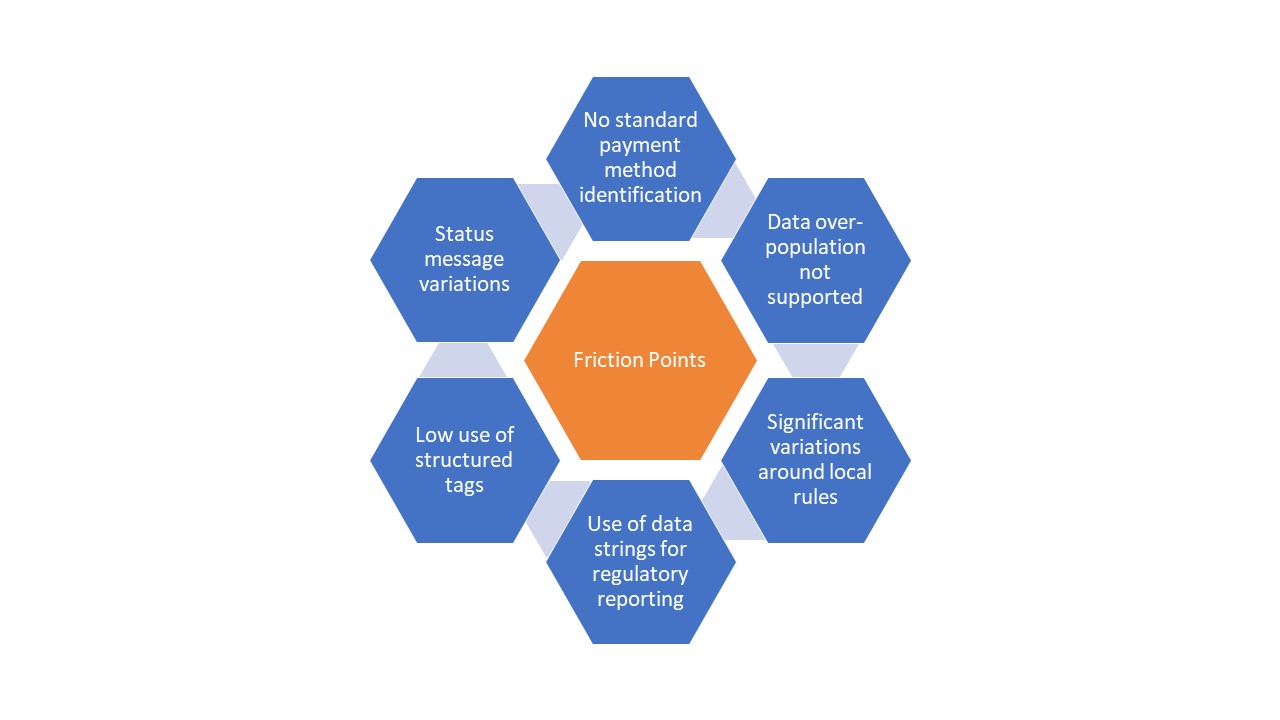
Diagram 1: Key friction points encountered by the corporate community in adopting XML V03
The highlighted friction points have resulted in the corporate community achieving a sub-optimal cash management architecture. Significant divergence in terms of the banks’ implementation of this standard covers a number of aspects, from non-standard payment method codes and payment batching logic to proprietary requirements around regulatory reporting and customer identification. All of this translated into additional complexity, inefficiency, and cost on the corporate side.
However, XML V09 offers a real opportunity to simplify, standardise, accelerate and elevate cash management performance where the banking community embraces the CGI-MP recommended ‘more prescriptive approach’ that will help deliver a win-win situation. This is more than just about a global standardised payment message, this is about the end to end cash management processes with a ‘structured data first’ mindset which will allow the corporate community to truly harness the power of technology.
What are the objectives of the RFP?
The RFP or RFI (request for information) process will provide the opportunity to understand the current mindset of your existing core cash management banking partners. Are they viewing the MT-MX migration as just a compliance exercise. Do they recognize the importance and benefits to the corporate community of embracing the recently published CGI-MP guidelines? Are they going to follow a structured data first model when it comes to statement reporting? Having a clearer view in how your current cash management banks are thinking around this important global change will help corporate treasury to make a more informed decision on potential future strategic cash management banking partners. More broadly, the RFP will provide an opportunity to ensure your core cash management banks have a strong strategic fit with your business across dimensions such as credit commitment, relationship support to your company and the industry you operate, access to senior management and ease of doing of business. Furthermore, you will be in a better position to achieve simplification and standardization of your banking providers through bank account rationalization combined with the removal of non-core partner banks from your current day to day banking operations.
In Summary
The Swift MT-MX migration and global industry adoption of ISO 20022 XML should be viewed as more than just a simple compliance change. This is about the opportunity to redefine a best in class cash management model that delivers operational and financial efficiencies and provides the foundation to truly harness the power of technology.
- Common Global Implementation–Market Practice (CGI-MP) provides a forum for financial institutions and non-financial institutions to progress various corporate-to-bank implementation topics on the use of ISO 20022 messages and to other related activities, in the payments domain. ↩︎
ISO 20022 XML version 9 – So what’s new?

The adoption of ISO 20022 XML standards significantly enhances invoice reconciliation and operational efficiency, improving working capital management and Days Sales Outstanding (DSO).
But the adoption of ISO 20022 XML messaging goes beyond SWIFT’s adoption in the interbank financial messaging space – SWIFT are currently estimating that by 2025, 80% of the RTGS (real time gross settlement) volumes will be ISO 20022 based with all reserve currencies either live or having declared a live date. What this means is that ISO 20022 XML is becoming the global language of payments. In this fourth article in the ISO 20022 series, Zanders experts Eliane Eysackers and Mark Sutton provide some valuable insights around what the version 9 payment message offers the corporate community in terms of richer functionality.
A quick recap on the ISO maintenance process?
So, XML version 9. What we are referencing is the pain.001.001.09 customer credit transfer initiation message from the ISO 2019 annual maintenance release. Now at this point, some people reading this article will be thinking they are currently using XML version 3 and now we talking about XML version 9. The logical question is whether version 9 is the latest message and actually, we expect version 12 to be released in 2024. So whilst ISO has an annual maintenance release process, the financial industry and all the associated key stakeholders will be aligning on the XML version 9 message from the ISO 2019 maintenance release. This version is expected to replace XML version 3 as the de-facto standard in the corporate to bank financial messaging space.
What new functionality is available with the version 9 payment message?
Comparing the current XML version 3 with the latest XML version 9 industry standard, there are a number of new tags/features which make the message design more relevant to the current digital transformation of the payment’s ecosystem. We look at the main changes below:
- Proxy: A new field has been introduced to support a proxy or tokenisation as its sometimes called. The relevance of this field is primarily linked to the new faster payment rails and open banking models, where consumers want to provide a mobile phone number or email address to mask the real bank account details and facilitate the payment transfer. The use of the proxy is becoming more widely used across Asia with the India (Unified Payments Interface) instant payment scheme being the first clearing system to adopt this logic. With the rise of instant clearing systems across the world, we are starting to see a much greater use of proxy, with countries like Australia (NPP), Indonesia (BI-FAST), Malaysia (DuitNow), Singapore (FAST) and Thailand (Promptpay) all adopting this feature.
- The Legal Entity Identifier (LEI): This is a 20-character, alpha-numeric code developed by the ISO. It connects to key reference information that enables clear and unique identification of legal entities participating in financial transactions. Each LEI contains information about an entity’s ownership structure and thus answers the questions of 'who is who’ and ‘who owns whom’. Simply put, the publicly available LEI data pool can be regarded as a global directory, which greatly enhances transparency in the global marketplace. The first country to require the LEI as part of the payment data is India, but the expectation is more local clearing system’s will require this identifier from a compliance perspective.
- Unique End-to-end Transaction Reference (commonly known as a UETR): This is a string of 36 unique characters featured in all payment instruction messages carried over the SWIFT network. UETRs are designed to act as a single source of truth for a payment and provide complete transparency for all parties in a payment chain, as well as enable functionality from SWIFT gpi (global payments innovation)1, such as the payment Tracker.
- Gender neutral term: This new field has been added as a name prefix.
- Requested Execution Date: The requested execution date now includes a data and time option to provide some additional flexibility.
- Structured Address Block: The structured address block has been updated to include the Building Name.
In Summary
Whilst there is no requirement for the corporate community to migrate onto the XML version 9 message, corporate treasury should now have the SWIFT ISO 20022 XML migration on their own radar in addition to understanding the broader global market infrastructure adoption of ISO 20022. This will ensure corporate treasury can make timely and informed decisions around any future migration plan.
Notes:
- SWIFT gpi is a set of standards and rules that enable banks to offer faster, more transparent, and more reliable cross-border payments to their customers.


