
Deforestation, pollution, and resource overuse are accelerating biodiversity loss, learn how to quantify your organization’s impact.

Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and resource over-extraction have caused a dramatic decline in biodiversity, with approximately 1 million species at risk of extinction, highlighting the urgent need for financial institutions to adopt biodiversity footprinting methods to measure and mitigate their environmental impact. According to the 2019 Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services by IPBES, about 1 million species are now threatened with extinction due to these human activities (Brondízio, Settele, Diaz, & Ngo, 2019). Moreover, WWF’s 2024 Living Planet Report documents a 73% decline in wildlife populations since 1970 (World Wildlife Fund, 2024). These findings underscore the urgency for action to conserve and restore natural environments.
We previously published articles exploring the importance of biodiversity risks and opportunities for financial institutions (Biodiversity risks and opportunities for financial institutions explained), and introduced a quantitative approach to scoring biodiversity risks based on sector and location (Biodiversity risks scoring: a quantitative approach). Building on those insights, this blog addresses the challenge of quantifying the biodiversity impact of a financial institution. Specifically, it explains biodiversity footprinting: a method enabling financial institutions to measure, track, and ultimately mitigate their environmental impact on biodiversity.
What is biodiversity and why it matters
A commonly used definition of biodiversity is “the variability among living organisms from all sources including, inter alia, terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems” (Convention on Biological Diversity, 1992). Hence, it represents all living organisms on earth like animals, plants, fungi and microbes, and the complex interactions that form our ecosystems. Biodiversity is the backbone of the earth's life-support systems. It directly affects the air we breathe, the food we eat and the water we drink. Additionally, healthy ecosystems help mitigate climate change by capturing carbon, safeguarding water supplies and maintaining balanced soil nutrients. Furthermore, natural habitats like wetlands, mangroves and forests protect communities from extreme weather events.
Economically, biodiversity is vital too. For example, ENCORE defines ecosystem services as the benefits that nature provides to support economic activities (ENCORE, sd). These services are categorized into provisioning services, which supply resources like food, water, and raw materials; regulating and maintenance services, which include air and water purification, climate regulation, and pest control; and cultural services, offering recreational, educational, and spiritual benefits. Biodiversity is fundamental to the proper functioning of these services.
While many global efforts and investments focus on monitoring and reducing CO2 emissions, much less attention is given to tracking and preventing biodiversity loss. This gap shows a key weakness in our environmental management strategies.
Why it matters for financial institutions
The financial sector plays a critical role in shaping the global economy by directing investments into various ventures, industries, and innovations. Biodiversity loss poses tangible risks (e.g. operational, reputational and regulatory) that financial institutions must address. Ignoring these risks could lead to stranded assets, disrupted supply chains or negative stakeholder reactions (for more about biodiversity risk for financial institutions, see this previous blog. Moreover, integrating biodiversity considerations into decision-making can lead to more resilient investment strategies and unlock new, nature-positive opportunities.
By measuring and monitoring their biodiversity impacts, banks, asset managers, insurers and other financial entities can:
- Learn about and better understand the causes and complexities of biodiversity loss;
- Identify biodiversity hotspots in their portfolios;
- Engage with clients on sustainable practices to reduce their impact;
- Align with global frameworks and evolving regulatory standards.
As awareness of biodiversity risks and opportunities grows, understanding how to measure biodiversity impacts becomes important. Biodiversity footprinting is a helpful tool for this.
What is biodiversity footprinting?
Biodiversity footprinting is a method for quantifying the impact of products, investments, or entire portfolios on natural ecosystems. Similar to measuring a carbon footprint, a biodiversity footprint measures the degree to which an activity affects habitat quality, species abundance, and overall ecological health. This is done by tracking factors like land use, water consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and pollution. The goal is to pinpoint economic activities with significant environmental impact, so that organizations can set informed targets and policies to promote biodiversity conservation.
Quantifying a biodiversity footprint is more challenging than measuring a carbon footprint, as it involves multiple local factors, diverse habitats and various impact types. The complexity and location-specific nature of biodiversity means that universal benchmarks or standardized datasets are still evolving. Today, multiple initiatives and approaches exist, each with its own methods and metrics for assessing biodiversity impacts.
Zanders’ biodiversity footprinting model
Zanders’ model for biodiversity footprinting provides financial institutions with a first scan and quantification of the impacts their financial activities have on natural ecosystems. The methodology is based on the Biodiversity Footprint for Financial Institutions (BFFI), an approach that enables calculation of biodiversity impacts across multiple asset classes.
Our model requires input data on the size of economic activities (in euros), the specific sector or asset type, and the location at a country-level granularity. It integrates this data with important environmental pressures derived from a multi-regional environmentally extended input-output database. Using life cycle assessment techniques, the biodiversity footprint is calculated by determining the Potentially Disappeared Fraction (PDF) of species. This is used to express the total biodiversity loss in square meters (m²) resulting from one year of economic activities.
By quantifying these impacts, financial institutions can identify specific biodiversity impact hotspots within their portfolios. This enables them to set informed, science-based targets aimed at effectively reducing their overall biodiversity footprint. The image below illustrates the results for a hypothetical portfolio, highlighting biodiversity impacts across various asset classes and impact categories.
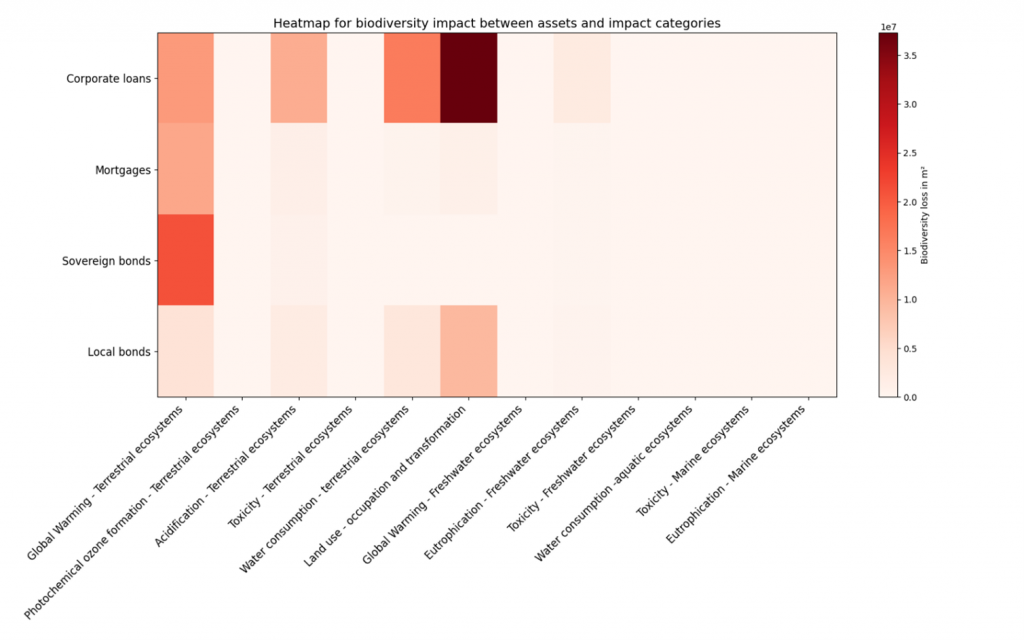
If you are interested in learning more about how Zanders can help you quantify your biodiversity impact, please contact Steyn Verhoeven, Martijn Schouten or Marije Wiersma.
Bibliography
Brondízio, E. S., Settele, J., Diaz, S., & Ngo, H. T. (2019). Global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Bonn, Germany: IPBES secretariat.
Convention on Biological Diversity. (1992). Article 2: Biodiversity definition. Retrieved from Convention on Biological Diversity: https://www.cbd.int/convention/articles?a=cbd-02
ENCORE. (n.d.). Ecosystem Services. Retrieved from ENCORE: https://www.encorenature.org/en/data-and-methodology/services
Wiersma, M., Blijlevens, S., & Manzanares, M. (2024, October). Biodiversity risks scoring: a quantitative approach. Retrieved from Zanders: https://zandersgroup.com/en/insights/blog/biodiversity-risks-scoring-a-quantitative-approach
Wiersma, M., Gerrits, J., & Fedenko, I. (2023, November). Biodiversity risks and opportunities for financial institutions explained. Retrieved from Zanders: https://zandersgroup.com/en/insights/blog/biodiversity-risks-and-opportunities-for-financial-institutions-explained
World Wildlife Fund. (2024). Living Planet Report 2024. Retrieved from https://www.worldwildlife.org/publications/2024-living-planet-report

Explore how Basel IV reforms and enhanced due diligence requirements will transform regulatory capital assessments for credit risk, fostering a more resilient and informed financial sector.

The Basel IV reforms, which are set to be implemented on 1 January 2025 via amendments to the EU Capital Requirement Regulation, have introduced changes to the Standardized Approach for credit risk (SA-CR). The Basel framework is implemented in the European Union mainly through the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3) and Capital Requirements Directive (CRD6). The CRR3 changes are designed to address shortcomings in the existing prudential standards, by among other items, introducing a framework with greater risk sensitivity and reducing the reliance on external ratings. Action by banks is required to remain compliant with the CRR. Overall, the share of RWEA derived through an external credit rating in the EU-27 remains limited, representing less than 10% of the total RWEA under the SA with the CRR.
Introduction
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) identified the excessive dependence on external credit ratings as a flaw within the Standardised Approach (SA), observing that firms frequently used these ratings to compute Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs) without adequately understanding the associated risks of their exposures. To address this issue, regulators have implemented changes aimed to reduce the mechanical reliance on external credit ratings and to encourage firms to use external credit ratings in a more informed manner. The objective is to diminish the chances of underestimating financial risks in order to further build a more resilient financial industry. Overall, the share of Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) derived through an external credit rating remains limited, and in Europe it represents less than 10% of the total RWA under the SA.
The concept of due diligence is pivotal in the regulatory framework. It refers to the rigorous process financial institutions are expected to undertake to understand and assess the risks associated with their exposures fully. Regulators promote due diligence to ensure that banks do not solely rely on external assessments, such as credit ratings, but instead conduct their own comprehensive analysis.
The due diligence is a process performed by banks with the aim of understanding the risk profile and characteristics of their counterparties at origination and thereafter on a regular basis (at least annually). This includes assessing the appropriateness of risk weights, especially when using external ratings. The level of due diligence should match the size and complexity of the bank's activities. Banks must evaluate the operating and financial performance of counterparties, using internal credit analysis or third-party analytics as necessary, and regularly access counterparty information. Climate-related financial risks should also be considered, and due diligence must be conducted both at the solo entity level and consolidated level.
Banks must establish effective internal policies, processes, systems, and controls to ensure correct risk weight assignment to counterparties. They should be able to prove to supervisors that their due diligence is appropriate. Supervisors are responsible for reviewing these analyses and taking action if due diligence is not properly performed.
Banks should have methodologies to assess credit risk for individual borrowers and at the portfolio level, considering both rated and unrated exposures. They must ensure that risk weights under the Standardised Approach reflect the inherent risk. If a bank identifies that an exposure, especially an unrated one, has higher inherent risk than implied by its assigned risk weight, it should factor this higher risk into its overall capital adequacy evaluation.
Banks need to ensure they have an adequate understanding of their counterparties’ risk profiles and characteristics. The diligent monitoring of counterparties is applicable to all exposures under the SA. Banks would need to take reasonable and adequate steps to assess the operating and financial condition of each counterparty.
Rating System
The external credit assessment institutions (ECAIs) are credit rating agencies recognised by National supervisors. The External Credit ECAIs play a significant role in the SA through the mapping of each of their credit assessments to the corresponding risk weights. Supervisors will be responsible for assigning an eligible ECAI’s credit risk assessments to the risk weights available under the SA. The mapping of credit assessments should reflect the long-term default rate.
Exposures to banks, exposures to securities firms and other financial institutions and exposures to corporates will be risk-weighted based on the following hierarchy External Credit Risk Assessment Approach (ECRA) and the Standardised Credit Risk Assessment Approach (SCRA).
ECRA: Used in jurisdictions allowing external ratings. If an external rating is from an unrecognized or non-nominated ECAI, the exposure is considered unrated. Also, banks must perform due diligence to ensure ratings reflect counterparty creditworthiness and assign higher risk weights if due diligence reveals greater risk than the rating suggests.
SCRA: Used where external ratings are not allowed. Applies to all bank exposures in these jurisdictions and unrated exposures in jurisdictions allowing external ratings. Banks classify exposures into three grades:
- Grade A: Adequate capacity to meet obligations in a timely manner.
- Grade B: Substantial credit risk, such as repayment capacities that are dependent on stable or favourable economic or business conditions.
- Grade C: Higher credit risk, where the counterparty has material default risks and limited margins of safety
The CRR Final Agreement includes a new article (Article 495e) that allows competent authorities to permit institutions to use an ECAI credit assessment assuming implicit government support until December 31, 2029, despite the provisions of Article 138, point (g).
In cases where external credit ratings are used for risk-weighting purposes, due diligence should be used to assess whether the risk weight applied is appropriate and prudent.
If the due diligence assessment suggests an exposure has higher risk characteristics than implied by the risk weight assigned to the relevant Credit Quality Step (CQS) of an exposure, the bank would assign the risk weight at least one higher than the CQS indicated by the counterparty’s external credit rating.
Criticisms to this approach are:
- Banks are mandated to use nominated ECAI ratings consistently for all exposures in an asset class, requiring banks to carry out a due diligence on each and every ECAI rating goes against the principle of consistent use of these ratings.
- When banks apply the output floor, ECAI ratings act as a backstop to internal ratings. In case the due diligence would imply the need to assign a high-risk weight, the output floor could no longer be used consistently across banks to compare capital requirements.
Implementation Challenges
The regulation requires the bank to conduct due diligence to ensure a comprehensive understanding, both at origination and on a regular basis (at least annually), of the risk profile and characteristics of their counterparties. The challenges associated with implementing this regulation can be grouped into three primary categories: governance, business processes, and systems & data.
Governance
The existing governance framework must be enhanced to reflect the new responsibilities imposed by the regulation. This involves integrating the due diligence requirements into the overall governance structure, ensuring that accountability and oversight mechanisms are clearly defined. Additionally, it is crucial to establish clear lines of communication and decision-making processes to manage the new regulatory obligations effectively.
Business Process
A new business process for conducting due diligence must be designed and implemented, tailored to the size and complexity of the exposures. This process should address gaps in existing internal thresholds, controls, and policies. It is essential to establish comprehensive procedures that cover the identification, assessment, and monitoring of counterparties' risk profiles. This includes setting clear criteria for due diligence, defining roles and responsibilities, and ensuring that all relevant staff are adequately trained.
Systems & Data
The implementation of the regulation requires access to accurate and comprehensive data necessary for the rating system. Challenges may arise from missing or unavailable data, which are critical for assessing counterparties' risk profiles. Furthermore, reliance on manual solutions may not be feasible given the complexity and volume of data required. Therefore, it is imperative to develop robust data management systems that can capture, store, and analyse the necessary information efficiently. This may involve investing in new technology and infrastructure to automate data collection and analysis processes, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
Overall, addressing these implementation challenges requires a coordinated effort across the organization, with a focus on enhancing governance frameworks, developing comprehensive business processes, and investing in advanced systems and data management solutions.
How can Zanders help?
As a trusted advisor, we built a track record of implementing CRR3 throughout a heterogeneous group of financial institutions. This provides us with an overview of how different entities in the industry deal with the different implementation challenges presented above.
Zanders has been engaged to provide project management for these Basel IV implementation projects. By leveraging the expertise of Zanders' subject matter experts, we ensure an efficient and insightful gap analysis tailored to your bank's specific needs. Based on this analysis, combined with our extensive experience, we deliver customized strategic advice to our clients, impacting multiple departments within the bank. Furthermore, as an independent advisor, we always strive to challenge the status quo and align all stakeholders effectively.
In-depth Portfolio Analysis: Our initial step involves conducting a thorough portfolio scan to identify exposures to both currently unrated institutions and those that rely solely on government ratings. This analysis will help in understanding the extent of the challenge and planning the necessary adjustments in your credit risk framework.
Development of Tailored Models: Drawing from our extensive experience and industry benchmarks, Zanders will collaborate with your project team to devise a range of potential solutions. Each solution will be detailed with a clear overview of the required time, effort, potential impact on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA), and the specific steps needed for implementation. Our approach will ensure that you have all the necessary information to make informed strategic decisions.
Robust Solutions for Achieving Compliance: Our proprietary Credit Risk Suite cloud platform offers banks robust tools to independently assess and monitor the credit quality of corporate and financial exposures (externally rated or not) as well as determine the relevant ECRA and SCRA ratings.
Strategic Decision-Making Support: Zanders will support your Management Team (MT) in the decision-making process by providing expert advice and impact analysis for each proposed solution. This support aims to equip your MT with the insights needed to choose the most appropriate strategy for your institution.
Implementation Guidance: Once a decision has been made, Zanders will guide your institution through the specific actions required to implement the chosen solution effectively. Our team will provide ongoing support and ensure that the implementation is aligned with both regulatory requirements and your institution’s strategic objectives.
Continuous Adaptation and Optimization: In response to the dynamic regulatory landscape and your bank's evolving needs, Zanders remains committed to advising and adjusting strategies as needed. Whether it's through developing an internal rating methodology, imposing new lending restrictions, or reconsidering business relations with unrated institutions, we ensure that your solutions are sustainable and compliant.
Independent and Innovative Thinking: As an independent advisor, Zanders continuously challenges the status quo, pushing for innovative solutions that not only comply with regulatory demands but also enhance your competitive edge. Our independent stance ensures that our advice is unbiased and wholly in your best interest.
By partnering with Zanders, you gain access to a team of dedicated professionals who are committed to ensuring your successful navigation through the regulatory complexities of Basel IV and CRR3. Our expertise and tailored approaches enable your institution to manage and mitigate risks efficiently while aligning with the strategic goals and operational realities of your bank. Reach out to Tim Neijs or Marco Zamboni for further comments or questions.
REFERENCE
[1] BCBS, The Basel Framework, Basel https://www.bis.org/basel_framework
[2] Regulation (EU) No 575/2013
[3] Directive 2013/36/EU
[4] EBA Roadmap on strengthening the prudential framework
[5] EBA REPORT ON RELIANCE ON EXTERNAL CREDIT RATINGS

Covid-19 exposed flaws in banks’ risk models, prompting regulatory exemptions, while new EBA guidelines aim to identify and manage future extreme market stresses.

The Covid-19 pandemic triggered unprecedented market volatility, causing widespread failures in banks' internal risk models. These backtesting failures threatened to increase capital requirements and restrict the use of advanced models. To avoid a potentially dangerous feedback loop from the lower liquidity, regulators responded by granting temporary exemptions for certain pandemic-related model exceptions. To act faster to future crises and reduce unreasonable increases to banks’ capital requirements, more recent regulation directly comments on when and how similar exemptions may be imposed.
Although FRTB regulation briefly comments on such situations of market stress, where exemptions may be imposed for backtesting and profit and loss attribution (PLA), it provides very little explanation of how banks can prove to the regulators that such a scenario has occurred. On 28th June, the EBA published its final draft technical standards on extraordinary circumstances for continuing the use of internal models for market risk. These standards discuss the EBA’s take on these exemptions and provide some guidelines on which indicators can be used to identify periods of extreme market stresses.
Background and the BCBS
In the Basel III standards, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) briefly comment on rare occasions of cross-border financial market stress or regime shifts (hereby called extreme stresses) where, due to exceptional circumstances, banks may fail backtesting and the PLA test. In addition to backtesting overages, banks often see an increasing mismatch between Front Office and Risk P&L during periods of extreme stresses, causing trading desks to fail PLA.
The BCBS comment that one potential supervisory response could be to allow the failing desks to continue using the internal models approach (IMA), however only if the banks models are updated to adequately handle the extreme stresses. The BCBS make it clear that the regulators will only consider the most extraordinary and systemic circumstances. The regulation does not, however, give any indication of what analysis banks can provide as evidence for the extreme stresses which are causing the backtesting or PLA failures.
The EBA’s standards
The EBA’s conditions for extraordinary circumstances, based on the BCBS regulation, provide some more guidance. Similar to the BCBS, the EBA’s main conditions are that a significant cross-border financial market stress has been observed or a major regime shift has taken place. They also agree that such scenarios would lead to poor outcomes of backtesting or PLA that do not relate to deficiencies in the internal model itself.
To assess whether the above conditions have been met, the EBA will consider the following criteria:
- Analysis of volatility indices (such as the VIX and the VSTOXX), and indicators of realised volatilities, which are deemed to be appropriate to capture the extreme stresses,
- Review of the above volatility analysis to check whether they are comparable to, or more extreme than, those observed during COVID-19 or the global financial crisis,
- Assessment of the speed at which the extreme stresses took place,
- Analysis of correlations and correlation indicators, which adequately capture the extreme stresses, and whether a significant and sudden change of them occurred,
- Analysis of how statistical characteristics during the period of extreme stresses differ to those during the reference period used for the calibration of the VaR model.
The granularity of the criteria
The EBA make it clear that the standards do not provide an exhaustive list of suitable indicators to automatically trigger the recognition of the extreme stresses. This is because they believe that cases of extreme stresses are very unique and would not be able to be universally captured using a small set of prescribed indicators.
They mention that defining a very specific set of indicators would potentially lead to banks developing automated or quasi-automated triggering mechanisms for the extreme stresses. When applied to many market scenarios, this may lead to a large number of unnecessary triggers due the specificity of the prescribed indicators. As such, the EBA advise that the analysis should take a more general approach, taking into consideration the uniqueness of each extreme stress scenario.
Responses to questions
The publication also summarises responses to the original Consultation Paper EBA/CP/2023/19. The responses discuss several different indicators or factors, on top of the suggested volatility indices, that could be used to identify the extreme stresses:
- The responses highlight the importance of correlation indicators. This is because stress periods are characterised by dislocations in the market, which can show increased correlations and heightened systemic risk.
- They also mention the use of liquidity indicators. This could include jumps of the risk-free rates (RFRs) or index swap (OIS) indicators. These liquidity indicators could be used to identify regime shifts by benchmarking against situations of significant cross-border market stress (for example, a liquidity crisis).
- Unusual deviations in the markets may also be strong indicators of the extreme stresses. For example, there could be a rapid widening of spreads between emerging and developed markets triggered by regional debt crisis. Unusual deviations between cash and derivatives markets or large difference between futures/forward and spot prices could also indicate extreme stresses.
- They suggest that restrictions on trading or delivery of financial instruments/commodities may be indicative of extreme stresses. For example, the restrictions faced by the Russian ruble due to the Russia-Ukraine war.
- Finally, the responses highlighted that an unusual amount of backtesting overages, for example more than 2 in a month, could also be a useful indicator.
Zanders recommends
It’s important that banks are prepared for potential extreme stress scenarios in the future. To achieve this, we recommend the following:
- Develop a holistic set of indicators and metrics that capture signs of potential extreme stresses,
- Use early warning signals to preempt potential upcoming periods of stress,
- Benchmark the indicators and metrics against what was observed during the great financial crisis and Covid-19,
- Create suitable reporting frameworks to ensure the knowledge gathered from the above points is shared with relevant teams, supporting early remediation of issues.
Conclusion
During extreme stresses such as Covid-19 and the global financial crisis, banks’ internal models can fail, not because of modeling issues but due to systemic market issues. Under FRTB, the BCBS show that they recognise this and, in these rare situations, may provide exemptions. The EBA’s recently published technical standards provide better guidance on which indicators can be used to identify these periods of extreme stresses. Although they do not lay out a prescriptive and definitive set of indicators, the technical standards provide a starting point for banks to develop suitable monitoring frameworks.
For more information on this topic, contact Dilbagh Kalsi (Partner) or Hardial Kalsi (Manager).
Explore how ridge backtesting addresses the intricate challenges of Expected Shortfall (ES) backtesting, offering a robust and insightful approach for modern risk management.

Challenges with backtesting Expected Shortfall
Recent regulations are increasingly moving toward the use of Expected Shortfall (ES) as a measure to capture risk. Although ES fixes many issues with VaR, there are challenges when it comes to backtesting.
Although VaR has been widely-used for decades, its shortcomings have prompted the switch to ES. Firstly, as a percentile measure, VaR does not adequately capture tail risk. Unlike VaR, which gives the maximum expected portfolio loss in a given time period and at a specific confidence level, ES gives the average of all potential losses greater than VaR (see figure 1). Consequently, unlike Var, ES can capture a range of tail scenarios. Secondly, VaR is not sub-additive. ES, however, is sub-additive, which makes it better at accounting for diversification and performing attribution. As such, more recent regulation, such as FRTB, is replacing the use of VaR with ES as a risk measure.
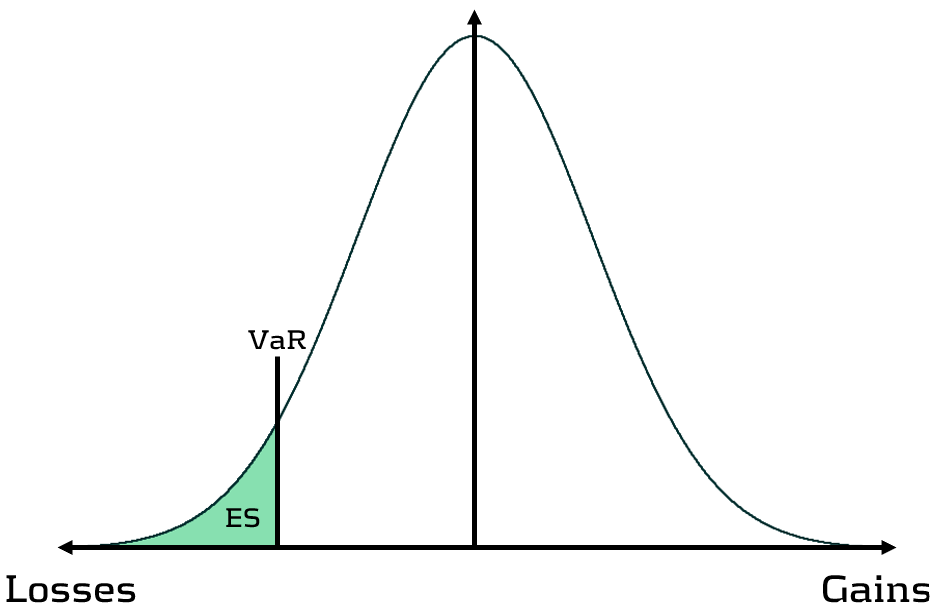
Figure 1: Comparison of VaR and ES
Elicitability is a necessary mathematical condition for backtestability. As ES is non-elicitable, unlike VaR, ES backtesting methods have been a topic of debate for over a decade. Backtesting and validating ES estimates is problematic – how can a daily ES estimate, which is a function of a probability distribution, be compared with a realised loss, which is a single loss from within that distribution? Many existing attempts at backtesting have relied on approximations of ES, which inevitably introduces error into the calculations.
The three main issues with ES backtesting can be summarised as follows:
- Transparency
- Without reliable techniques for backtesting ES, banks struggle to have transparency on the performance of their models. This is particularly problematic for regulatory compliance, such as FRTB.
- Sensitivity
- Existing VaR and ES backtesting techniques are not sensitive to the magnitude of the overages. Instead, these techniques, such as the Traffic Light Test (TLT), only consider the frequency of overages that occur.
- Stability
- As ES is conditional on VaR, any errors in VaR calculation lead to errors in ES. Many existing ES backtesting methodologies are highly sensitive to errors in the underlying VaR calculations.
Ridge Backtesting: A solution to ES backtesting
One often-cited solution to the ES backtesting problem is the ridge backtesting approach. This method allows non-elicitable functions, such as ES, to be backtested in a manner that is stable with regards to errors in the underlying VaR estimations. Unlike traditional VaR backtesting methods, it is also sensitive to the magnitude of the overages and not just their frequency.
The ridge backtesting test statistic is defined as:
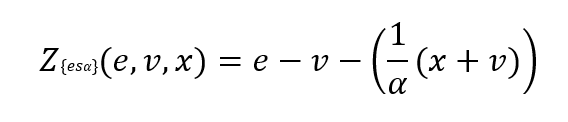
where 𝑣 is the VaR estimation, 𝑒 is the expected shortfall prediction, 𝑥 is the portfolio loss and 𝛼 is the confidence level for the VaR estimation.
The value of the ridge backtesting test statistic provides information on whether the model is over or underpredicting the ES. The technique also allows for two types of backtesting; absolute and relative. Absolute backtesting is denominated in monetary terms and describes the absolute error between predicted and realised ES. Relative backtesting is dimensionless and describes the relative error between predicted and realised ES. This can be particularly useful when comparing the ES of multiple portfolios. The ridge backtesting result can be mapped to the existing Basel TLT RAG zones, enabling efficient integration into existing risk frameworks.
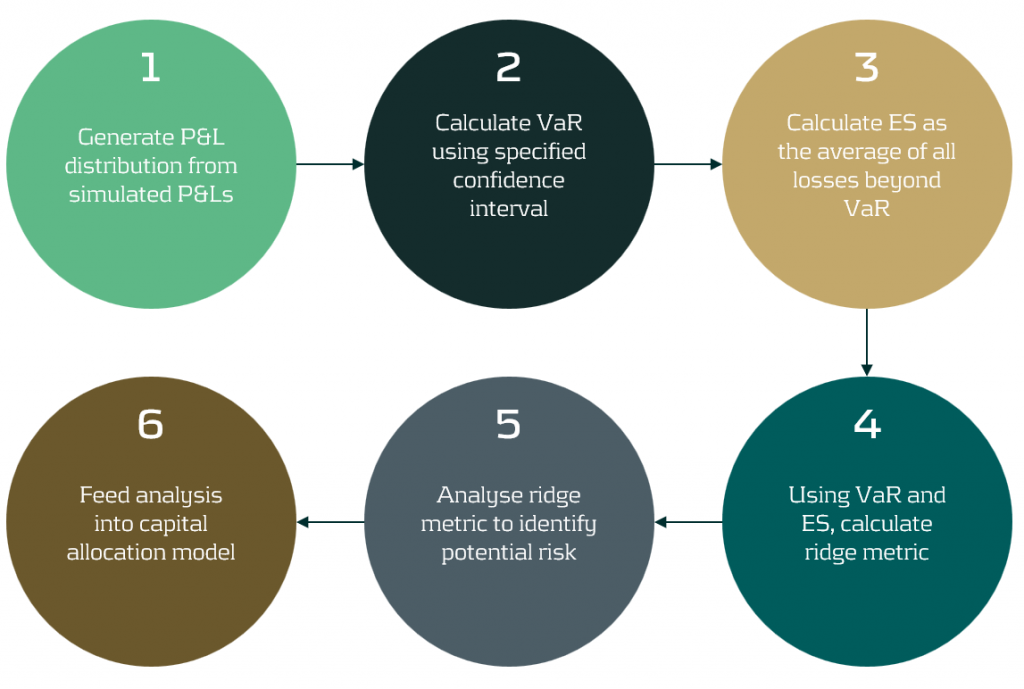
Figure 2: The ridge backtesting methodology
Sensitivity to Overage Magnitude
Unlike VaR backtesting, which does not distinguish between overages of different magnitudes, a major advantage of ES ridge backtesting is that it is sensitive to the size of each overage. This allows for better risk management as it identifies periods with large overages and also periods with high frequency of overages.
Below, in figure 3, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the ridge backtest by comparing it against a traditional VaR backtest. A scenario was constructed with P&Ls sampled from a Normal distribution, from which a 1-year 99% VaR and ES were computed. The sensitivity of ridge backtesting to overage magnitude is demonstrated by applying a range of scaling factors, increasing the size of overages by factors of 1, 2 and 3. The results show that unlike the traditional TLT, which is sensitive only to overage frequency, the ridge backtesting technique is effective at identifying both the frequency and magnitude of tail events. This enables risk managers to react more quickly to volatile markets, regime changes and mismodeling of their risk models.
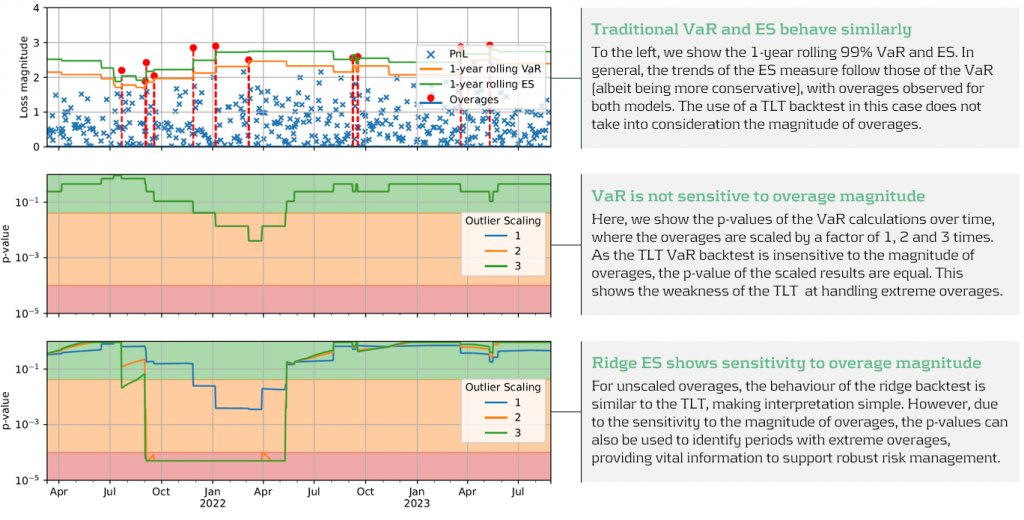
Figure 3: Demonstration of ridge backtesting’s sensitivity to overage magnitude.
The Benefits of Ridge Backtesting
Rapidly changing regulation and market regimes require banks enhance their risk management capabilities to be more reactive and robust. In addition to being a robust method for backtesting ES, ridge backtesting provides several other benefits over alternative backtesting techniques, providing banks with metrics that are sensitive and stable.
Despite the introduction of ES as a regulatory requirement for banks choosing the internal models approach (IMA), regulators currently do not require banks to backtest their ES models. This leaves a gap in banks’ risk management frameworks, highlighting the necessity for a reliable ES backtesting technique. Despite this, banks are being driven to implement ES backtesting methodologies to be compliant with future regulation and to strengthen their risk management frameworks to develop a comprehensive understanding of their risk.
Ridge backtesting gives banks transparency to the performance of their ES models and a greater reactivity to extreme events. It provides increased sensitivity over existing backtesting methodologies, providing information on both overage frequency and magnitude. The method also exhibits stability to any underlying VaR mismodeling.
In figure 4 below, we summarise the three major benefits of ridge backtesting.
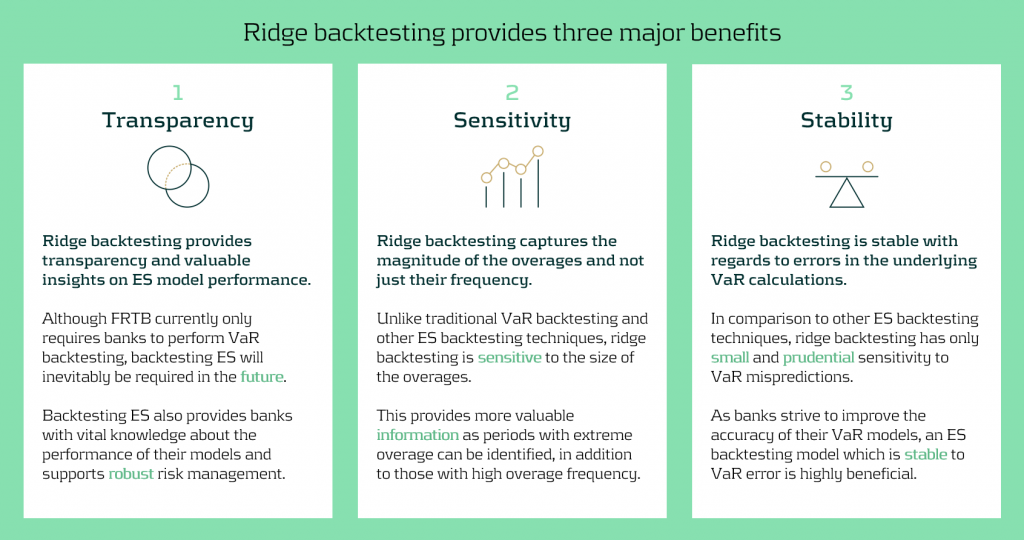
Figure 4: The three major benefits of ridge backtesting.
Conclusion
The lack of regulatory control and guidance on backtesting ES is an obvious concern for both regulators and banks. Failure to backtest their ES models means that banks are not able to accurately monitor the reliability of their ES estimates. Although the complexities of backtesting ES has been a topic of ongoing debate, we have shown in this article that ridge backtesting provides a robust and informative solution. As it is sensitive to the magnitude of overages, it provides a clear benefit in comparison to traditional VaR TLT backtests that are only sensitive to overage frequency. Although it is not a regulatory requirement, regulators are starting to discuss and recommend ES backtesting. For example, the PRA, EBA and FED have all recommended ES backtesting in some of their latest publications. However, despite the fact that regulation currently only requires banks to perform VaR backtesting, banks should strive to implement ES backtesting as it supports better risk management.
For more information on this topic, contact Dilbagh Kalsi (Partner) or Hardial Kalsi (Manager).

A comprehensive summary of a recent webinar on diverse modeling techniques and shared challenges in expected credit losses

Across the whole of Europe, banks apply different techniques to model their IFRS9 Expected Credit Losses on a best estimate basis. The diverse spectrum of modeling techniques raises the question: what can we learn from each other, such that we all can improve our own IFRS 9 frameworks? For this purpose, Zanders hosted a webinar on the topic of IFRS 9 on the 29th of May 2024. This webinar was in the form of a panel discussion which was led by Martijn de Groot and tried to discuss the differences and similarities by covering four different topics. Each topic was discussed by one panelist, who were Pieter de Boer (ABN AMRO, Netherlands), Tobia Fasciati (UBS, Switzerland), Dimitar Kiryazov (Santander, UK), and Jakob Lavröd (Handelsbanken, Sweden).
The webinar showed that there are significant differences with regards to current IFRS 9 issues between European banks. An example of this is the lingering effect of the COVID-19 pandemic, which is more prominent in some countries than others. We also saw that each bank is working on developing adaptable and resilient models to handle extreme economic scenarios, but that it remains a work in progress. Furthermore, the panel agreed on the fact that SICR remains a difficult metric to model, and, therefore, no significant changes are to be expected on SICR models.
Covid-19 and data quality
The first topic covered the COVID-19 period and data quality. The poll question revealed widespread issues with managing shifts in their IFRS 9 model resulting from the COVID-19 developments. Pieter highlighted that many banks, especially in the Netherlands, have to deal with distorted data due to (strong) government support measures. He said this resulted in large shifts of macroeconomic variables, but no significant change in the observed default rate. This caused the historical data not to be representative for the current economic environment and thereby distorting the relationship between economic drivers and credit risk. One possible solution is to exclude the COVID-19 period, but this will result in the loss of data. However, including the COVID-19 period has a significant impact on the modeling relations. He also touched on the inclusion of dummy variables, but the exact manner on how to do so remains difficult.
Dimitar echoed these concerns, which are also present in the UK. He proposed using the COVID-19 period as an out-of-sample validation to assess model performance without government interventions. He also talked about the problems with the boundaries of IFRS 9 models. Namely, he questioned whether models remain reliable when data exceeds extreme values. Furthermore, he mentioned it also has implications for stress testing, as COVID-19 is a real life stress scenario, and we might need to think about other modeling techniques, such as regime-switching models.
Jakob found the dummy variable approach interesting and also suggested the Kalman filter or a dummy variable that can change over time. He pointed out that we need to determine whether the long term trend is disturbed or if we can converge back to this trend. He also mentioned the need for a common data pipeline, which can also be used for IRB models. Pieter and Tobia agreed, but stressed that this is difficult since IFRS 9 models include macroeconomic variables and are typically more complex than IRB.
Significant Increase in Credit Risk
The second topic covered the significant increase in credit risk (SICR). Jakob discussed the complexity of assessing SICR and the lack of comprehensive guidance. He stressed the importance of looking at the origination, which could give an indication on the additional risk that can be sustained before deeming a SICR.
Tobia pointed out that it is very difficult to calibrate, and almost impossible to backtest SICR. Dimitar also touched on the subject and mentioned that the SICR remains an accounting concept that has significant implications for the P&L. The UK has very little regulations on this subject, and only requires banks to have sufficient staging criteria. Because of these reasons, he mentioned that he does not see the industry converging anytime soon. He said it is going to take regulators to incentivize banks to do so. Dimitar, Jakob, and Tobia also touched upon collective SICR, but all agreed this is difficult to do in practice.
Post Model Adjustments
The third topic covered post model adjustments (PMAs). The results from the poll question implied that most banks still have PMAs in place for their IFRS 9 provisions. Dimitar responded that the level of PMAs has mostly reverted back to the long term equilibrium in the UK. He stated that regulators are forcing banks to reevaluate PMAs by requiring them to identify the root cause. Next to this, banks are also required to have a strategy in place when these PMAs are reevaluated or retired, and how they should be integrated in the model risk management cycle. Dimitar further argued that before COVID-19, PMAs were solely used to account for idiosyncratic risk, but they stayed around for longer than anticipated. They were also used as a countercyclicality, which is unexpected since IFRS 9 estimations are considered to be procyclical. In the UK, banks are now building PMA frameworks which most likely will evolve over the coming years.
Jakob stressed that we should work with PMAs on a parameter level rather than on ECL level to ensure more precise adjustments. He also mentioned that it is important to look at what comes before the modeling, so the weights of the scenarios. At Handelsbanken, they first look at smaller portfolios with smaller modeling efforts. For the larger portfolios, PMAs tend to play less of a role. Pieter added that PMAs can be used to account for emerging risks, such as climate and environmental risks, that are not yet present in the data. He also stressed that it is difficult to find a balance between auditors, who prefer best estimate provisions, and the regulator, who prefers higher provisions.
Linking IFRS 9 with Stress Testing Models
The final topic links IFRS 9 and stress testing. The poll revealed that most participants use the same models for both. Tobia discussed that at UBS the IFRS 9 model was incorporated into their stress testing framework early on. He pointed out the flexibility when integrating forecasts of ECL in stress testing. Furthermore, he stated that IFRS 9 models could cope with stress given that the main challenge lies in the scenario definition. This is in contrast with others that have been arguing that IFRS 9 models potentially do not work well under stress. Tobia also mentioned that IFRS 9 stress testing and traditional stress testing need to have aligned assumptions before integrating both models in each other.
Jakob agreed and talked about the perfect foresight assumption, which suggests that there is no need for additional scenarios and just puts a weight of 100% on the stressed scenario. He also added that IFRS 9 requires a non-zero ECL, but a highly collateralized portfolio could result in zero ECL. Stress testing can help to obtain a loss somewhere in the portfolio, and gives valuable insights on identifying when you would take a loss.
Pieter pointed out that IFRS 9 models differ in the number of macroeconomic variables typically used. When you are stress testing variables that are not present in your IFRS 9 model, this could become very complicated. He stressed that the purpose of both models is different, and therefore integrating both can be challenging. Dimitar said that the range of macroeconomic scenarios considered for IFRS 9 is not so far off from regulatory mandated stress scenarios in terms of severity. However, he agreed with Pieter that there are different types of recessions that you can choose to simulate through your IFRS 9 scenarios versus what a regulator has identified as systemic risk for an industry. He said you need to consider whether you are comfortable relying on your impairment models for that specific scenario.
This topic concluded the webinar on differences and similarities across European countries regarding IFRS 9. We would like to thank the panelists for the interesting discussion and insights, and the more than 100 participants for joining this webinar.
Interested to learn more? Contact Kasper Wijshoff, Michiel Harmsen or Polly Wong for questions on IFRS 9.

Unlock Treasury Efficiency: Exploring SAP’s GROW and RISE Cloud Solutions

As organizations continue to adapt to the rapidly changing business landscape, one of the most pivotal shifts is the migration of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to the cloud. The evolution of treasury operations is a prime example of how cloud-based solutions are revolutionizing the way businesses manage their financial assets. This article dives into the nuances between SAP’s GROW (public cloud) and RISE (private cloud) products, particularly focusing on their impact on treasury operations.
The "GROW" product targets new clients who want to quickly leverage the public cloud's scalability and standard processes. In contrast, the "RISE" product is designed for existing SAP clients aiming to migrate their current systems efficiently into the private cloud.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
The public cloud, exemplified by SAP's "GROW" package, operates on a shared infrastructure hosted by providers such as SAP, Alibaba, or AWS. Public cloud services are scalable, reliable, and flexible, offering key business applications and storage managed by the cloud service providers. Upgrades are mandatory and occur on a six-month release cycle. All configuration is conducted through SAP Fiori, making this solution particularly appealing to upper mid-market net new customers seeking to operate using industry-standard processes and maintain scalable operations.
In contrast, the private cloud model, exemplified by the “RISE” package, is used exclusively by a single business or organization and must be hosted at SAP or an SAP-approved hyperscaler of their choice. The private cloud offers enhanced control and security, catering to specific business needs with personalized services and infrastructure according to customer preferences. It provides configuration flexibility through both SAP Fiori and the SAP GUI. This solution is mostly preferred by large enterprises, and many customers are moving from ECC to S/4HANA due to its customizability and heightened security.
Key Differences in Cloud Approaches
Distinguishing between public and private cloud methodologies involves examining factors like control, cost, security, scalability, upgrades, configuration & customization, and migration. Each factor plays a crucial role in determining which cloud strategy aligns with an organization's vision for treasury operations.
- Control: The private cloud model emphasizes control, giving organizations exclusive command over security and data configurations. The public cloud is managed by external providers, offering less control but relieving the organization from day-to-day cloud management.
- Cost: Both the public and private cloud operate on a subscription model. However, managing a private cloud infrastructure requires significant upfront investment and a dedicated IT team for ongoing maintenance, updates, and monitoring, making it a time-consuming and resource-intensive option. Making the public cloud potentially a more cost-effective option for organizations.
- Security: Both GROW and RISE are hosted by SAP or hyperscalers, offering strong security measures. There is no significant difference in security levels between the two models.
- Scalability: The public cloud offers unmatched scalability, allowing businesses to respond quickly to increased demands without the need for physical hardware changes. Private clouds can also be scaled, but this usually requires additional hardware or software and IT support, making them less dynamic.
- Upgrades: the public cloud requires mandatory upgrades every six months, whereas the private cloud allows organizations to dictate the cadence of system updates, such as opting for upgrades every five years or as needed.
- Configuration and Customization: in the public cloud configuration is more limited with fewer BAdIs and APIs available, and no modifications allowed. The private cloud allows for extensive configuration through IMG and permits SAP code modification, providing greater flexibility and control.
- Migration: the public cloud supports only greenfield implementation, which means only current positions can be migrated, not historical transactions. The private cloud offers migration programs from ECC, allowing historical data to be transferred.
Impact on Treasury Operations
The impact of SAP’s GROW (public cloud) and RISE (private cloud) solutions on treasury operations largely hinges on the degree of tailoring required by an organization’s treasury processes. If your treasury processes require minimal or no tailoring, both public and private cloud options could be suitable. However, if your treasury processes are tailored and structured around specific needs, only the private cloud remains a viable option.
In the private cloud, you can add custom code, modify SAP code, and access a wider range of configuration options, providing greater flexibility and control. In contrast, the public cloud does not allow for SAP code modification but does offer limited custom code through cloud BADI and extensibility. Additionally, the public cloud emphasizes efficiency and user accessibility through a unified interface (SAP Fiori), simplifying setup with self-service elements and expert oversight. The private cloud, on the other hand, employs a detailed system customization approach (using SAP Fiori & GUI), appealing to companies seeking granular control.
Another important consideration is the mandatory upgrades in the public cloud every six months, requiring you to test SAP functionalities for each activated scope item where an update has occurred, which could be strenuous. The advantage is that your system will always run on the latest functionality. This is not the case in the private cloud, where you have more control over system updates. With the private cloud, organizations can dictate the cadence of system updates (e.g., opting for yearly upgrades), the type of updates (e.g., focusing on security patches or functional upgrades), and the level of updates (e.g., maintaining the system one level below the latest is often used).
To accurately assess the impact on your treasury activities, consider the current stage of your company's lifecycle and identify where and when customization is needed for your treasury operations. For example, legacy companies with entrenched processes may find the rigidity of public cloud functionality challenging. In contrast, new companies without established processes can greatly benefit from the pre-delivered set of best practices in the public cloud, providing an excellent starting point to accelerate implementation.
Factors Influencing Choices
Organizations choose between public and private cloud options based on factors like size, compliance, operational complexity, and the degree of entrenched processes. Larger companies may prefer private clouds for enhanced security and customization capabilities. Startups to mid-size enterprises may favor the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of public clouds during rapid growth. Additionally, companies might opt for a hybrid approach, incorporating elements of both cloud models. For instance, a Treasury Sidecar might be deployed on the public cloud to leverage scalability and innovation while maintaining the main ERP system on-premise or on the private cloud for greater control and customization. This hybrid strategy allows organizations to tailor their infrastructure to meet specific operational needs while maximizing the advantages of both cloud environments.
Conclusion
Migrating ERP systems to the cloud can significantly enhance treasury operations with distinct options through SAP's public and private cloud solutions. Public clouds offer scalable, cost-effective solutions ideal for medium-to upper-medium-market enterprises with standard processes or without pre-existing processes. They emphasize efficiency, user accessibility, and mandatory upgrades every six months. In contrast, private clouds provide enhanced control, security, and customization, catering to larger enterprises with specific regulatory needs and the ability to modify SAP code.
Choosing the right cloud model for treasury operations depends on an organization's current and future customization needs. If minimal customization is required, either option could be suitable. However, for customized treasury processes, the private cloud is preferable. The decision should consider the company's lifecycle stage, with public clouds favoring rapid growth and cost efficiency and private clouds offering long-term control and security.
It is also important to note that SAP continues to offer on-premise solutions for organizations that require or prefer traditional deployment methods. This article focuses on cloud solutions, but on-premises remains a viable option for businesses that prioritize complete control over their infrastructure and have the necessary resources to manage it independently.
If you need help thinking through your decision, we at Zanders would be happy to assist you.

Are you leveraging the SAP Credit Risk Analyzer to its full potential?

While many business and SAP users are familiar with its core functionalities, such as limit management applying different limit types and the core functionality of attributable amount determination, several less known SAP standard features can enhance your credit risk management processes.
In this article, we will explore these hidden gems, such as Group Business Partners and the ways to manage the limit utilizations using manual reservations and collateral.
Group Business Partner Use
One of the powerful yet often overlooked features of the SAP Credit Risk Analyzer is the ability to use Group Business Partners (BP). This functionality allows you to manage credit and settlement risk at a bank group level rather than at an individual transactional BP level. By consolidating credit and settlement exposure for related entities under a single group business partner, you can gain a holistic view of the risks associated with an entire banking group. This is particularly beneficial for organizations dealing with banking corporations globally and allocating a certain amount of credit/settlement exposure to banking groups. It is important to note that credit ratings are often reflected at the group bank level. Therefore, the use of Group BPs can be extended even further with the inclusion of credit ratings, such as S&P, Fitch, etc.
Configuration: Define the business partner relationship by selecting the proper relationship category (e.g., Subsidiary of) and setting the Attribute Direction to "Also count transactions from Partner 1 towards Partner 2," where Partner 2 is the group BP.
Master Data: Group BPs can be defined in the SAP Business Partner master data (t-code BP). Ensure that all related local transactional BPs are added in the relationship to the appropriate group business partner. Make sure the validity period of the BP relationship is valid. Risk limits are created using the group BP instead of the transactional BP.
Reporting: Limit utilization (t-code TBLB) is consolidated at the group BP level. Detailed utilization lines show the transactional BP, which can be used to build multiple report variants to break down the limit utilization by transactional BP (per country, region, etc.).
Having explored the benefits of using Group Business Partners, another feature that offers significant flexibility in managing credit risk is the use of manual reservations and collateral contracts.
Use of Manual Reservations
Manual reservations in the SAP Credit Risk Analyzer provide an additional layer of flexibility in managing limit utilization. This feature allows risk managers to manually add a portion of the credit/settlement utilization for specific purposes or transactions, ensuring that critical operations are not hindered by unexpected credit or settlement exposure. It is often used as a workaround for issues such as market data problems, when SAP is not able to calculate the NPV, or for complex financial instruments not yet supported in the Treasury Risk Management (TRM) or Credit Risk Analyzer (CRA) settings.
Configuration: Apart from basic settings in the limit management, no extra settings are required in SAP standard, making the use of reservations simpler.
Master data: Use transaction codes such as TLR1 to TLR3 to create, change, and display the reservations, and TLR4 to collectively process them. Define the reservation amount, specify the validity period, and assign it to the relevant business partner, transaction, limit product group, portfolio, etc. Prior to saving the reservation, check in which limits your reservation will be reflected to avoid having any idle or misused reservations in SAP.
While manual reservations provide a significant boost to flexibility in limit management, another critical aspect of credit risk management is the handling of collateral.
Collateral
Collateral agreements are a fundamental aspect of credit risk management, providing security against potential defaults. The SAP Credit Risk Analyzer offers functionality for managing collateral agreements, enabling corporates to track and value collateral effectively. This ensures that the collateral provided is sufficient to cover the exposure, thus reducing the risk of loss.
SAP TRM supports two levels of collateral agreements:
- Single-transaction-related collateral
- Collateral agreements.
Both levels are used to reduce the risk at the level of attributable amounts, thereby reducing the utilization of limits.
Single-transaction-related collateral: SAP distinguishes three types of collateral value categories:
- Percentual collateralization
- Collateralization using a collateral amount
- Collateralization using securities
Configuration: configure collateral types and collateral priorities, define collateral valuation rules, and set up the netting group.
Master Data: Use t-code KLSI01_CFM to create collateral provisions at the appropriate level and value. Then, this provision ID can be added to the financial object.
Reporting: both manual reservations and collateral agreements are visible in the limit utilization report as stand- alone utilization items.
By leveraging these advanced features, businesses can significantly enhance their risk management processes.
Conclusion
The SAP Credit Risk Analyzer is a comprehensive tool that offers much more than meets the eye. By leveraging its hidden functionalities, such as Group Business Partner use, manual reservations, and collateral agreements, businesses can significantly enhance their credit risk management processes. These features not only provide greater flexibility and control but also ensure a more holistic and robust approach to managing credit risk. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape, unlocking the full potential of the SAP Credit Risk Analyzer can be a game-changer in achieving effective risk management.
If you have questions or are keen to see the functionality in our Zanders SAP Demo system, please feel free to contact Aleksei Abakumov or any Zanders SAP consultant.

We explore how the Bayesian Gaussian Process Classifier (GPC) injects much needed agility and interpretability into default modeling.

In brief:
- Prevailing uncertainty in geopolitical, economic and regulatory environments demands a more dynamic approach to default modeling.
- Traditional methods such as logistic regression fail to address the non-linear characteristics of credit risk.
- Score-based models can be cumbersome to calibrate with expertise and can lack the insight of human wisdom.
- Machine learning lacks the interpretability expected in a world where transparency is paramount.
- Using the Bayesian Gaussian Process Classifier defines lending parameters in a more holistic way, sharpening a bank’s ability to approve creditworthy borrowers and reject proposals from counterparties that are at a high risk of default.
Historically high levels of economic volatility, persistent geopolitical unrest, a fast-evolving regulatory environment – a perpetual stream of disruption is highlighting the limitations and vulnerabilities in many credit risk approaches. In an era where uncertainty persists, predicting risk of default is becoming increasingly complex, and banks are increasingly seeking a modeling approach that incorporates more flexibility, interpretability, and efficiency.
While logistic regression remains the market standard, the evolution of the digital treasury is arming risk managers with a more varied toolkit of methodologies, including those powered by machine learning. This article focuses on the Bayesian Gaussian Process Classifier (GPC) and the merits it offers compared to machine learning, score-based models, and logistic regression.
A non-parametric alternative to logistic regression
The days of approaching credit risk in a linear, one-dimensional fashion are numbered. In today’s fast paced and uncertain world, to remain resilient to rising credit risk, banks have no choice other than to consider all directions at once. With the GPC approach, the linear combination of explanatory variables is replaced by a function, which is iteratively updated by applying Bayes’ rule (see Bayesian Classification With Gaussian Processes for further detail).
For default modeling, a multivariate Gaussian distribution is used, hence forsaking linearity. This allows the GPC to parallel machine learning (ML) methodologies, specifically in terms of flexibility to incorporate a variety of data types and variables and capability to capture complex patterns hidden within financial datasets.
A model enriched by expert wisdom
Another way GPC shows similar characteristics to machine learning is in how it loosens the rigid assumptions that are characteristic of many traditional approaches, including logistic regression and score-based models. To explain, one example is the score-based Corporate Rating Model (CRM) developed by Zanders. This is the go-to model of Zanders to assess the creditworthiness of corporate counterparties. However, calibrating this model and embedding the opinion of Zanders’ corporate rating experts is a time-consuming task. The GPC approach streamlines this process significantly, delivering both greater cost- and time-efficiencies. The incorporation of prior beliefs via Bayesian inference permits the integration of expert knowledge into the model, allowing it to reflect predetermined views on the importance of certain variables. As a result, the efficiency gains achieved through the GPC approach don’t come at the cost of expert wisdom.
Enabling explainable lending decisions
As well as our go-to CRM, Zanders also houses machine learning approaches to default modeling. Although this generates successful outcomes, with machine learning, the rationale behind a credit decision is not explicitly explained. In today’s volatile environment, an unexplainable solution can fall short of stakeholder and regulator expectations – they increasingly want to understand the reasoning behind lending decisions at a forensic level.
Unlike the often ‘black-box’ nature of ML models, with GPC, the path to a decision or solution is both transparent and explainable. Firstly, the GPC model’s hyperparameters provide insights into the relevance and interplay of explanatory variables with the predicted outcome. In addition, the Bayesian framework sheds light on the uncertainty surrounding each hyperparameter. This offers a posterior distribution that quantifies confidence in these parameter estimates. This aspect adds substantial risk assessment value, contrary to the typical point estimate outputs from score-based models or deterministic ML predictions. In short, an essential advantage of the GPC over other approaches is its ability to generate outcomes that withstand the scrutiny of stakeholders and regulators.
A more holistic approach to probability of default modeling
In summary, if risk managers are to tackle the mounting complexity of evaluating probability of default, they need to approach it non-linearly and in a way that’s explainable at every level of the process. This is throwing the spotlight onto more holistic approaches, such as the Gaussian Process Classifier. Using this methodology allows for the incorporation of expert intuition as an additional layer to empirical evidence. It is transparent and accelerates calibration without forsaking performance. This presents an approach that not only incorporates the full complexity of credit risk but also adheres to the demands for model interpretability within the financial sector.
Are you interested in how you could use GPC to enhance your approach to default modeling? Contact Kyle Gartner for more information.

Commodity risk management has become a top CFO priority in some companies recently. Mastering commodity risk requires an integrated approach across business functions. SAP’s comprehensive solution can make a difference.

The recent periods of commodity price volatility have brought commodity risk management to the spotlight in numerous companies, where commodities constitute a substantial component of the final product, but pricing arrangements prevented a substantial hit of the bottom line in the past calm periods.
Understanding Commodity Risk Management is ingrained in the individual steps of the whole value chain, encompassing various business functions with different responsibilities. Purchasing is responsible for negotiating with the suppliers: the sales or pricing department negotiates the conditions with the customers; and Treasury is responsible for negotiating with the banks to secure financing and eventually hedge the commodity risk on the derivatives market. Controlling should have clarity about the complete value chain flow and make sure the margin is protected. Commodity risk management should be a top item on the CFO's list nowadays.
SAP's Solution: A Comprehensive Overview

Each of these functions need to be supported with adequate information system functionality and integrated well together, bridging the physical supply chain flows with financial risk management.
SAP, as the leading provider of both ERP and Treasury and risk management systems, offers numerous functionalities to cover the individual parts of the process. The current solution is the result of almost two decades of functional evolution. The first functionalities were released in 2008 on the ECC 6.04 version to support commodity price risk in the metal business. The current portfolio supports industry solutions for agriculture, oil, and gas, as well as the metal business. Support for power trading is considered for the future. In the recent releases of S/4HANA, many components have been redeveloped to reflect the experience from the existing client implementations, to better cover the trading and hedging workflow, and to leverage the most recent SAP technological innovations, like HANA database and the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP).
Functionalities of SAP Commodity Management
Let us take you on a quick journey through the available functionalities.
The SAP Commodity Management solution covers commodity procurement and commodity sales in an end-to-end process, feeding the data for commodity risk positions to support commodity risk management as a dedicated function. In the logistics process, it offers both contracts and orders with commodity pricing components, which can directly be captured through the integrated Commodity Price Engine (CPE). In some commodity markets, products need to be invoiced before the final price is determined based on market prices. For this scenario, provisional and differential invoicing are available in the solution.
The CPE allows users to define complex formulas based on various commodity market prices (futures or spot prices from various quotation sources), currency exchange translation rules, quality and delivery condition surcharges, and rounding rules. The CPE conditions control how the formula results are calculated from term results, e.g., sum, the highest value, provisional versus final term. Compound pricing conditions can be replicated using routines: Splitting routines define how the formula quantity will be split into multiple terms, while Combination routines define how multiple terms will be combined together to get the final values.
Pricing conditions from active contracts and orders for physical delivery of commodities constitute the physical exposure position. Whether in procurement, in a dedicated commodity risk management department, or in the treasury department, real-time recognition and management of the company’s commodity risk positions rely on accurate and reliable data sources and evaluation functionalities. This is provided by the SAP Commodity Risk Management solution. Leveraging the mature functionalities and components of the Treasury and Risk Management module, it allows for managing paper trades to hedge the determined physical commodity risk position. Namely, listed and OTC commodity derivatives are supported. In the OTC area, swaps, forwards, and options, including the Asian variants with average pricing periods, are well covered. These instruments fully integrate into the front office, back office, and accounting functionalities of the existing mature treasury module, allowing for integrated and seamless processing. The positions in the paper deals can be included within the existing Credit Risk Analyser for counterparty risk limit evaluation as well as in the Market Risk Analyser for complex market risk calculations and simulations.
Managing Commodity Exposures
Physical commodity exposure and paper deals are bundled together via the harmonized commodity master data Derivative Contract Specification (DCS), representing individual commodities traded on specific exchanges or spot markets. It allows for translating the volume information of the physical commodity to traded paper contracts and price quotation sources.
In companies with extensive derivative positions, broker statement reconciliation can be automated via the recent product SAP Broker Reconciliation for Commodity Derivatives. This cloud-based solution is natively integrated into the SAP backend to retrieve the derivative positions. It allows for the automatic import of electronic brokers' statements and automates the reconciliation process to investigate and resolve deviations with less human intervention.
To support centralized hedging with listed derivatives, the Derivative Order and Trade execution component has been introduced. It supports a workflow in which an internal organizational unit raises a Commodity Order request, which in turn is reviewed and then fully or partially fulfilled by the trader in the external market.
Innovations in SAP Commodity Management
Significant innovations were released in the S/4HANA 2022 version.
The Commodity Hedge Cockpit supports the trader view and hedging workflow.
In the area of OTC derivatives (namely commodity swaps and commodity forwards), the internal trading and hedging workflow can be supported by Commodity Price Risk Hedge Accounting. It allows for separating various hedging programs through Commodity Hedging areas and defining various Commodity Hedge books. Within the Hedge books, Hedge specifications allow for the definition of rules for concluding financial trades to hedge commodity price exposures, e.g., by defining delivery period rules, hedge quotas, and rules for order utilization sequence. Individual trade orders are defined within the Hedge specification. Intercompany (on behalf of) trading is supported by the automatic creation of intercompany mirror deals, if applicable.
Settings under the hedge book allow for automatically designating cash flow hedge relationships in accordance with IFRS 9 principles, documenting the hedge relationships, running effectiveness checks, using valuation functions, and generating hedge accounting entries. All these functions are integrated into the existing hedge accounting functionalities for FX risk available in SAP Treasury and Risk Management.
The underlying physical commodity exposure can be uploaded as planned data reflecting the planned demand or supply from supply chain functions. The resulting commodity exposure can be further managed (revised, rejected, released), or additional commodity exposure data can be manually entered. If the physical commodity exposure leads to FX exposure, it can be handed over to the Treasury team via the automated creation of Raw exposures in Exposure Management 2.0.
Modelled deals allow for capturing hypothetical deals with no impact on financial accounting. They allow for evaluating commodity price risk for use cases like exposure impact from production forecasts, mark-to-intent for an inventory position (time, location, product), and capturing inter-strategy or late/backdated deals.
Even though a separate team can be responsible for commodity risk management (front office) - and it usually is - bundling together the back office and accounting operations under an integrated middle and back office team can help to substantially streamline the daily operations.
Last but not least, the physical commodity business is usually financed by trade finance instruments. SAP has integrated Letters-of-Credit, as well as Guarantees into the Treasury module and enhanced the functionality greatly in 2016.
All-in-all, every commodity-driven business, upstream or downstream, consumer or producer, works under different setups and business arrangements. The wide variety of available functionalities allows us to define the right solution for every constellation. Especially with commodity management functionalities active in the supply chain modules of the ERP system, SAP commodity risk management can offer a lot of efficiencies in an integrated and streamlined solution. We are happy to accompany you on the journey of defining the best solution for your enterprise.

Mergers, divestments, and other M&A activities reshape Treasury management, posing strategic challenges for Treasurers as they navigate disentanglement and build Treasury functions for stand-alone companies.

The corporate landscape is continuously reshaped by strategic realignments such as mergers, divestments, and other M&A activities, wherein a company divests a portion of its business or acquires other businesses to refocus its operations or unlock shareholder value. These transactions greatly affect Treasury management, influencing cash flow, banking structures, financial risk management, financing, and technology. This article explores the challenges Treasurers face during the disentanglement or carve-out process, emphasizing the need for strategic realignment of Treasury activities and focusing on the Treasury perspective of a divesting company. It acknowledges the transitional complexities that arise and the demand for agile response strategies to safeguard against financial instability. We will have a look at the special carve-out situation of building a Treasury function for a stand-alone company in a second part of this article.
Treasury Challenges in Carve-Out Situations
In the dynamic world of corporate restructuring, carve-outs present both a new frontier of opportunity and a multifaceted challenge for Treasurers. While divesting a part of an organization can streamline focus and potentially increase shareholder value, it can place unique pressures on treasury management to reassess and realign financial strategies.
When a corporation decides to execute a carve-out, the Treasury immediately takes on the critical task of separating financial operations and managing transitional service agreements. From the perspective of the divesting company, preserving liquidity and ensuring compliance with financial covenants is a key priority. This intricate division process demands the disentanglement of complex cash flows, re-evaluation and unwinding of cash pooling and internal as well as external debt structures, as well as a review of financial risk and investment policies. Such an endeavour requires rigorous planning and flawless execution to ensure that operational continuity is maintained. Additionally, it requires going into the details, such as the allocation of planning objects (e.g., vendor contracts, machines, vehicles) to the right business for purposes of liquidity forecasting.
Our experience shows that factors like company revenue, industry complexity, and operating countries affect the volume and frequency of treasury transactions. This can increase complexity and workload, especially for intricate transactions. An interesting remark is that carve-out transactions also impact the remaining group. Potentially, the geographic footprint is smaller, or the number of individual business models within the group is less than before – with a significant impact on Treasury.
The Role of Technology in Carve-Outs
A key component in the disentanglement process is represented by Treasury technology. In evaluating treasury technology during a carve-out, scrutiny of the landscape and meticulous planning are paramount to ensuring a smooth transition. The systems must not only handle specific needs such as segmenting data, independent entity reporting, and tracking discrete cash flows and risks, but they must also facilitate a seamless detachment and swift reconfiguration for the newly autonomous entities in the course of the disentanglement of a business. It is essential that these systems support operational independence and continuity with minimal disruptions during the restructuring process.
Implementing the right technology for the new entity, e.g., to cover stand-alone requirements, is crucial. It must meet current transaction needs and be robust enough to handle future demands. Given our breadth of experience across various technological domains and in various M&A scenarios, we have enriched many discussions on which solutions possess the adaptability and scalability necessary to accommodate the evolving needs of a redefined business. 'Right-sizing' the systems, structures, and processes, tailored specifically to the unique contours of the carved-out entity, is a decisive factor for laying the groundwork for sustainable success post-divestiture.
Strategic Realignment for Treasury
Any M&A transaction significantly changes the Treasury Process Map for both the remaining group and the carved-out entity. It has inherited risk and different risk types. We think that Treasury should deal with operational risks first, such as filling resource needs and/or stabilizing business operations. The resource issue requires an analysis of the available employees and their specific skill sets. Onboarding interim resources and back-filling resource gaps until the onboarding of dedicated new staff are alternative options to cover shortfalls.
The operational issue focuses on the impact on cash management and payment operations. Treasury needs to assess the impact on the existing banking and cash management structure and on liquidity as funds received by one entity are required by another. Bank relationships are foundational to Treasury operations and must be revisited and sometimes reinvented. Treasuries must work diligently to maintain trust and communication with old and new banking partners, articulating changes in the company's profile, needs, objectives, and strategies. Beyond negotiation and administration, the process often entails renegotiating terms and ensuring that the newly formed entity's financial needs will continue to be met effectively. The technical and operational ability to execute and receive payments through the company’s (new) bank accounts is a core requirement, which needs to be at the top of the list of priorities. Next, centralization of liquidity and cash structures is essential to avoid cash drag if inflows cannot be invested and/or concentrated in a relatively short time.
Treasury may also deal with different types of financial risk, such as interest rate or foreign exchange exposures. The financial risk management perspective is a crucial one for companies, but in the context of carve-out activities, it is often a second-order priority (depending on the financial risk profile of a company). However, proper identification and assessment of financial risk shall always be a top priority in a disentanglement process. Process implementation can be approached following the establishment of sound business and treasury processes if there is no significant financial risk.
If your organization is contemplating or in the midst of a carve-out, contact Zanders for support. Our consultative expertise in Treasury is your asset in ensuring financial stability and strategic advantage during and post-carve-out. Let Zanders be your partner in transforming challenges into successes.


