
The 2025 Swiss Climate Scenarios provide updated estimates of consequences for Switzerland of various global warming scenarios. They cover the likelihood and severity of extreme heat, heavy precipitation, droughts, forest fires, flash floods and thawing permafrost. We summarize the main estimates, highlight the potential economic consequences and discuss ways in which financial institutions can make use of the updated scenarios.

On November 4, MeteoSwiss published updated climate scenarios for Switzerland. The scenarios describe the expected changes in the climate in Switzerland under an increase in global warming by 1.5, 2 and 3 degrees respectively (Global Warming Level (GWL)) compared to the reference period 1991-2020. The timing if and when these GWLs are reached depends on the specific climate scenario considered.
The climate scenarios for Switzerland are anchored in the global climate scenarios that have been included in the sixth and last assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) from 2022. The three main global scenarios considered are a combination of a Shared Socio-Economic Pathway (SSP) and a Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP):
- “SSP1-2.6” represents a combination of SSP1 and RCP2.6 ("2-degree path with net-zero target achieved by 2050")
- “SSP2-4.5” represents a combination of SSP2 and RCP4.5 (“’Middle ground’ scenario following current and planned measures“)
- “SSP5-8.5” represents a combination of SSP5 and RCP8.5 (“Fossil fuel path without climate protection“)
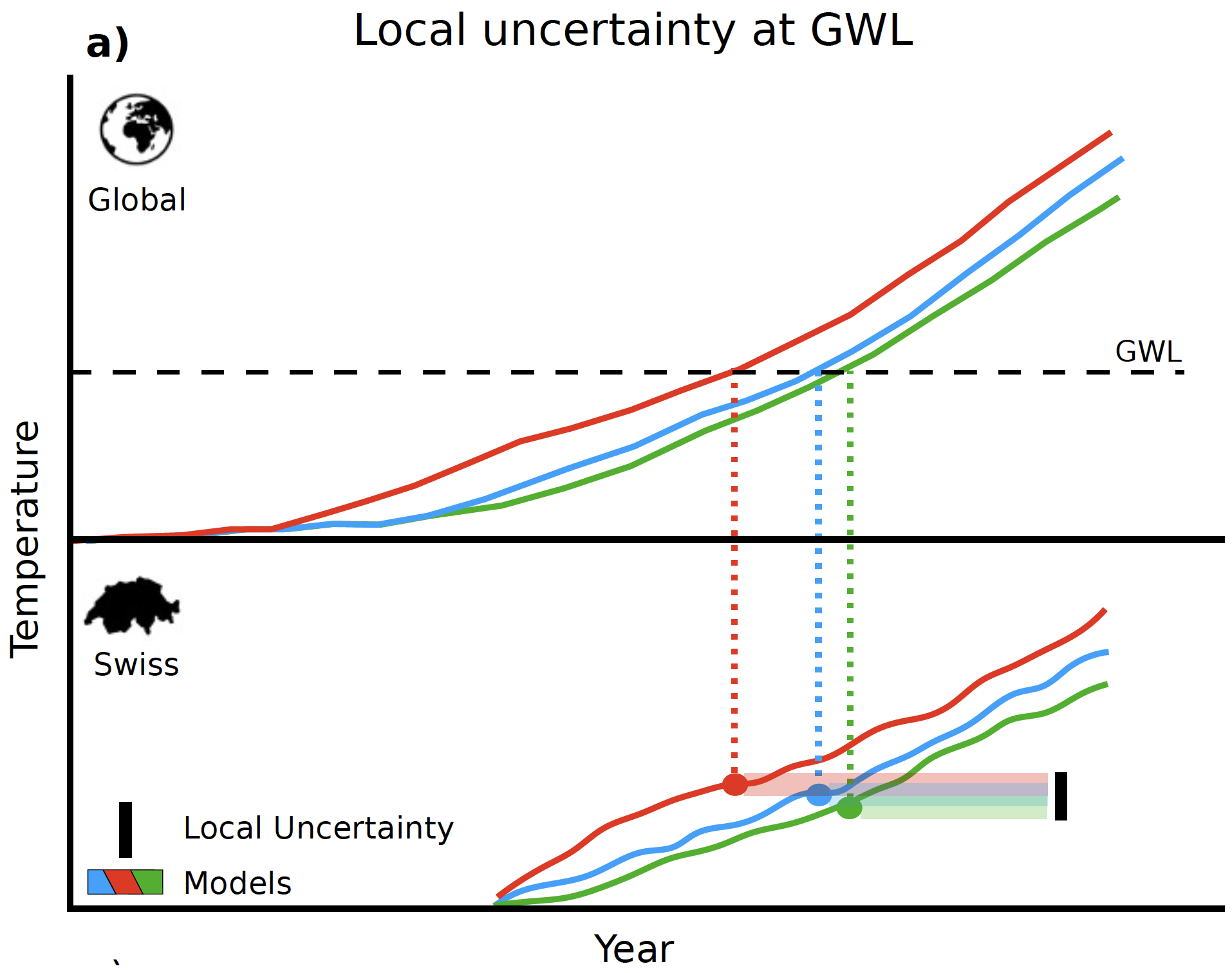
The Figure above depicts the approach taken by MeteoSwiss to assess the consequences for Switzerland at specific GWLs:
- The top part of the Figure (“Global”) shows three global climate scenarios, each of which achieves the depicted GWL at a different point in time.
- MeteoSwiss has translated each of the global scenarios to specific scenarios for Switzerland (more than three in fact, but the picture only shows three). These scenarios are shown in the bottom part of the Figure (“Swiss”). It can be seen that the same GWL in the global scenarios corresponds to different warming levels for Switzerland. This leads to a range of possible warming levels in Switzerland for each GWL.
In the next sections, the main expected changes in temperature and precipitation in Switzerland under the different GWLs are considered. Subsequently, the steps needed to use the information about the climate scenarios for a materiality assessment of climate risk are outlined. In addition, an overview is provided of the data that has been made available for the Swiss climate scenarios by MeteoSwiss, which can be used for such a materiality assessment.
1. Changes in temperature
MeteoSwiss estimates that by 2024, the average temperature in Switzerland already increased by 2.9°C compared to pre-industrial times (1871-1900). This is more than double the rise of 1.4°C in average global temperature. The larger rise in Switzerland is partially due to the fact that the temperature above land increases more quickly than above sea.
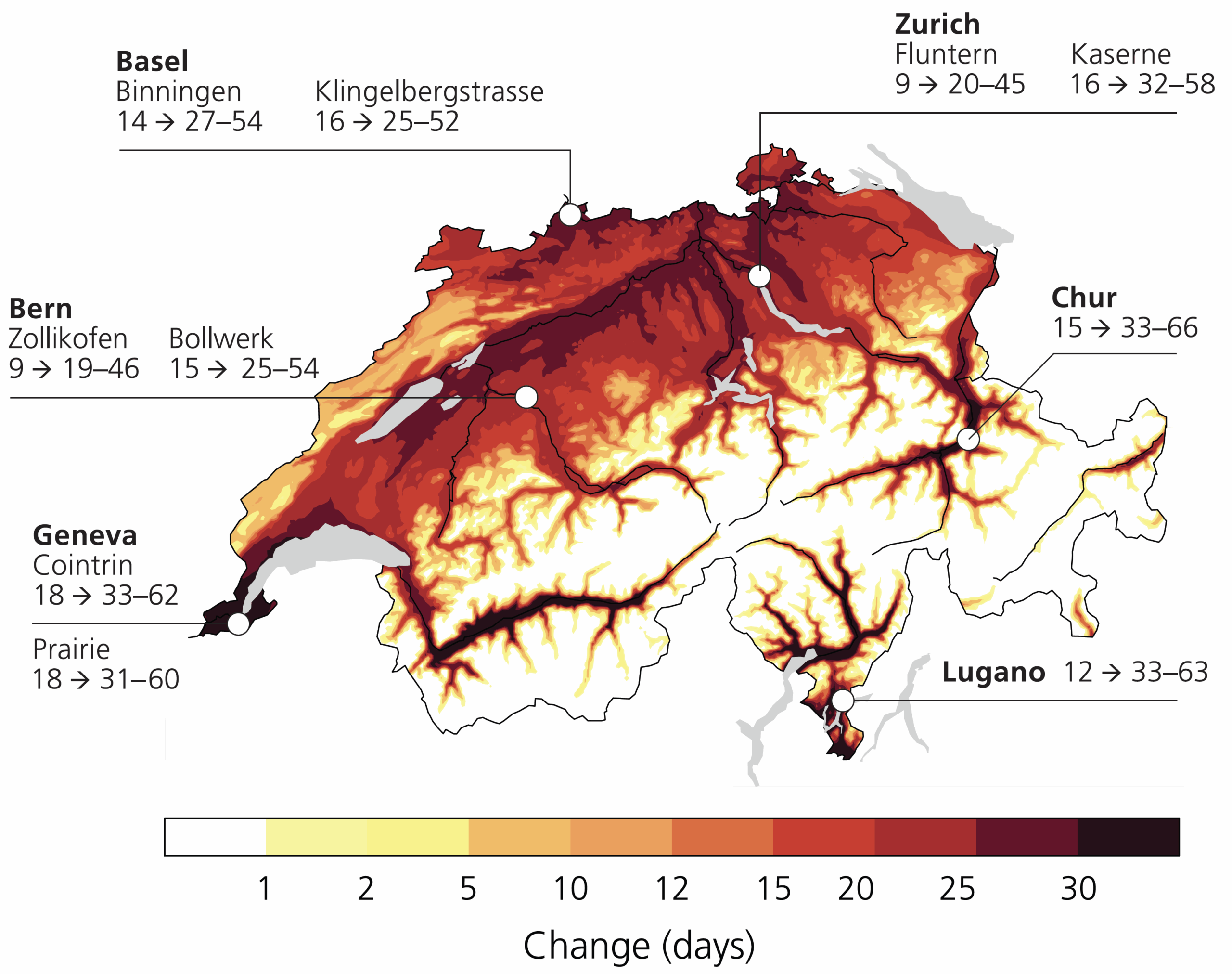
With rising global warming, the number of hot days (>30°C) in Switzerland is expected to roughly triple in a 3-degree world (GWL3.0). The largest impact will be in urban areas, as depicted in the Figure on the right.
In line with this, the average summer temperature as well as extreme temperatures (warmest day and night) will increase.
Potential economic consequences:
- Extreme heat during the day and a lack of cooling at night put strain on the body and affect health. In addition, physical and mental work is made more difficult during heatwaves, with dense urban development exacerbating this. This will affect productivity, lower economic output and may increase costs for cooling work environments.
2. Changes in precipitation
Yearly precipitation is not expected to change in Switzerland with global warming, but summers are expected to get drier and winters are expected to get wetter. Moreover, extreme precipitation (heavy rainfall, hail) is expected to increase in both frequency and intensity, as depicted in the Figure below.
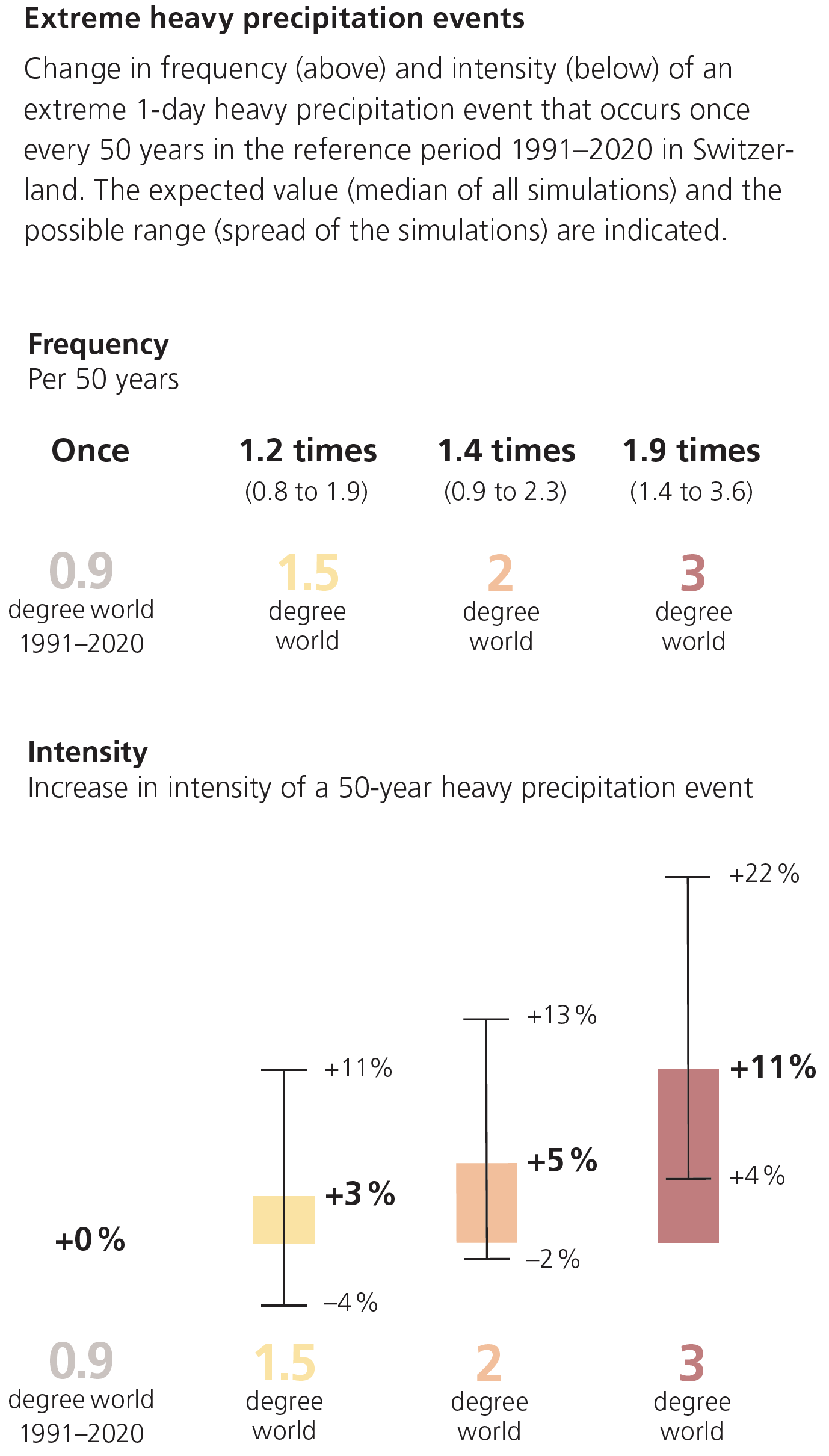
Source: Climate CH2025 – Brochure, MeteoSwiss (link)
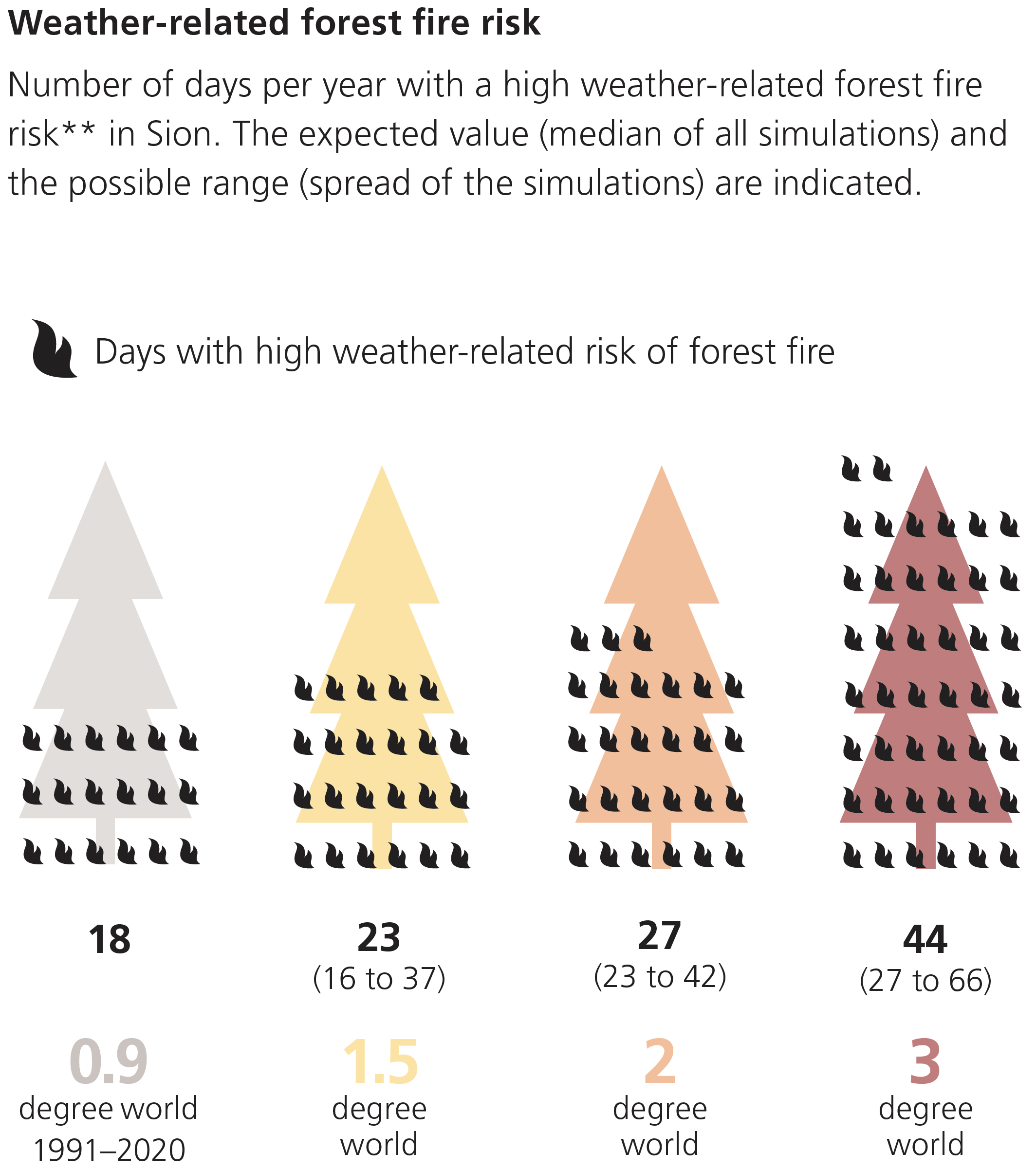
Drier summers lead to an increased risk of forest fires as well as increasing frequency and intensity of droughts, as depicted in the Figures below.

Precipitation in winter will increasingly fall in the form of rain instead of snow as the zero-degree line increases.
Potential economic consequences:
- Sudden flash floods and hail can cause property damage and business interruptions. In addition, they can destroy agricultural crops. This will negatively affect economic output and decrease the value of properties in areas at risk.
- Drought leads to yield losses in agriculture and increased risk of forest fires, causes water shortages in reservoirs and restricts water supply. In addition, drought can intensify and prolong heatwaves. This will negatively affect economic output
- Thawing permafrost and melting glaciers can lead to unstable slopes, and the water cycle may be disrupted. This will affect industries that depend on water (e.g., for cooling). Decreasing snow will also affect winter tourism and associated industry sectors.
3. Estimating financial impacts
For the potential future changes in temperature and precipitation in Switzerland because of global warming, the possible economic consequences have been explored in the sections above. To what extent these are relevant for risk management of a financial institution will depend on the sectors and physical locations of their clients, counterparties and issuers of securities in which they invest.
The general steps taken to perform a materiality assessment for individual clients, counterparties and issuers are:
1. Identify transmission channels through which the impacts of global warming can negatively impact their business.
2. Estimate the financial impact of individual transmission channels.
- As historical data is not representative of what is likely to happen in the future under global warming, a common approach is to use scenario analysis.
- FINMA explicitly expects financial institutions to employ scenario analysis when performing the materiality assessment for nature-related financial risks in its recent circular (link, see our Zanders blog for a summary).
- The Swiss climate scenarios can form a basis for the scenario analysis. However, the climate impacts that have been made available by MeteoSwiss (see Section 4) need to be translated to a financial impact for clients, counterparties and issuers. The impact on both revenues (e.g., lower sales due to business disruptions or lower demand) and costs (e.g., higher costs due to damages or required additional investments) need to considered.
- Mitigating measures such as insurance can be taken into account if they are deemed effective in the scenarios considered.
3. Reflect the estimated financial impact in internal risk metrics, such as credit ratings, collateral values and the value-at-risk of investments.
For companies that are active internationally, or which depend on international supply chains, the exposure of their supply chains and international markets to the impact of global warming also needs to be considered.
4. Swiss climate scenario data
With the publication of the Swiss climate scenarios, MeteoSwiss also makes available detailed scenario data. This data can be viewed through an interactive WebAtlas (link) for combinations of:
- Various temperature and precipitation indicators (listed in the document “Overview of CH2025 climate indicators” (link))
- Reference period (1991-2020) and three future Global Warming Levels (GWL1.5, GWL2.0 and GWL3.0)
- Annual changes as well as seasonal changes (Winter, Spring, Sommer and Autumn)
- Switzerland as a whole, each of five ‘biogeographic’ regions (Jura, Swiss Plateau, Pre-Alps, Alps, and South side of the Alps) as well as individual weather stations
- Three climate scenarios (SSP1-2.6, SSP2-4.5 and SSP5-8.5) over time (2040-2060) (for mean temperature and precipitation only)
The following detailed data can also be accessed directly:
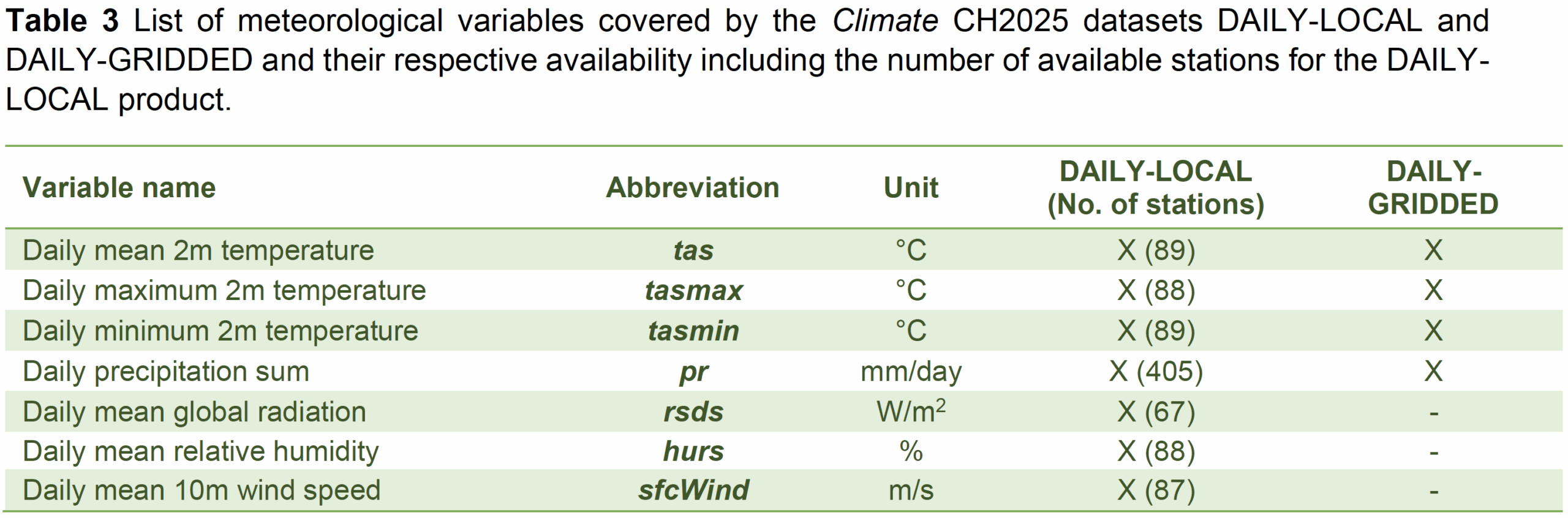
- Historical climate data (daily) at individual Swiss measurement stations since measurement started, covering 169 indicators related to temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind, sunshine, snow, air pressure, evaporation and radiation. (link)
- These data have been ‘homogenized’ for changes in measurement methods over time.
- Scenario forecast data (daily) for different Global Warming Levels (GWL) under different Regional Climate Models (RMC) (link)(link) at
- Individual weather stations (DAILY_LOCAL)
- 1km×1km gridpoints in Switzerland (DAILY-GRIDDED)
Climate variables included in the daily scenario forecasts are shown in the table below.
How Zanders can help
We have supported various banks with the assessment of the materiality of climate risks for their clients, counterparties and investment issuers. With our focus on risk and technology and our strength in applying quantitative approaches, we are particularly well equipped to substantiate a materiality assessment with scenario analysis and the use of data. If you want to learn more, do not hesitate to contact us.

Get climate risk support
Speak to an expert
In March 2021, the European Banking Authority (EBA) was mandated through Article 501c of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR) to “assess […] whether a dedicated prudential treatment of exposures related to assets or activities associated substantially with environmental and/or social objectives would be justified”.

More simply put, the EBA was asked to investigate whether the current prudential framework properly captures environmental and social risks. In response, the EBA published a Discussion Paper (DP) [1] in May 2022 to collect input from stakeholders such as academia and banking professionals.
After briefly presenting the DP, this article reviews the current Pillar 1 Capital (P1C) requirements. We limit ourselves to the P1C requirements for credit risk as this is by far the largest risk type for banks. Furthermore, we only discuss the interaction of the P1C with climate change risks (as opposed to broader environmental and/or social risk types). After establishing the extent to which the prudential framework takes climate change risks into account, possible amendments to the framework will be considered.
Key take-aways of this article:
- The current prudential framework includes several mechanisms that allow the reflection of climate change risks into the P1C.
- The interaction between P1C and climate change risks is limited to specific parts of the portfolio, and in those cases, it remains to be seen to what extent this is properly accounted for at the moment.
- Amendments to the prudential framework can be considered, but it is important to avoid double counting issues and to take into account differences in time horizons.
- The EBA is expected to publish a final report on the prudential treatment of environmental risks in the first half of this year.
- Financial institutions that are using the internal ratings-based approach are advised to start with the incorporation of climate change risks into PD and LGD models.
EBA’s Discussion Paper

In the introduction of the DP, the EBA mentions the increasing environmental risks – and their interaction with the traditional risk types – as the trigger for the review of the prudential framework. One of the main concerns is whether the current framework is sufficiently capturing the impact of transition risks and the more frequent and severe physical risks expected in the coming decades. In this context, they stress the special characteristics of environmental risks: compared to the traditional risk types, environmental risks tend to have a “multidimensional, non-linear, uncertain and forward-looking nature.”
The EBA also explains that the P1C requirements are not intended to cover all risks a financial institution is exposed to. The P1C represents a baseline capital requirement that is complemented by the Pillar 2 Capital requirement, which is more reflective of a financial institution’s specific business model and risks. Still, it is warranted to assess whether environmental risks are appropriately reflected in the P1C requirements, especially if these lead to systemic risks.
Even though the DP raises more questions than it provides answers, some starting points for the discussion are introduced. One is that the EBA takes a risk-based approach. Their standpoint is that changes to the prudential framework should reflect actual risk differentials compared to other risk types and that it should not be a tool to (unjustly) incentivize the transition to a sustainable economy. The latter lies “in the remit of political authorities.”
The DP also discusses some challenges related to environmental risks. One example is the lack of high-quality, granular historical data, which is needed to support the calibration of the prudential framework. The EBA also mentions the mismatch in the time horizon for the prudential framework (i.e., a business cycle) and the time horizon over which the environmental risks will unfold (i.e., several decades). They wonder whether “the business cycle concepts and assumptions that are used in estimating risk weights and capital requirements are sufficient to capture the emergence of these risks.”
Finally, the EBA does not favor supporting and/or penalizing factors, i.e., the introduction of adjustments to the existing risk weights based on a (green) taxonomy-based classification of the exposures1. They are right to argue that there is no direct relationship between an exposure’s sustainability profile and its credit risk. In addition, there is a risk of double counting if environmental risk drivers have already been reflected in the current prudential framework. Consequently, the EBA concludes that targeted amendments to the framework may be more appropriate. An example would be to ensure that environmental risks are properly included in external credit ratings and the credit risk models of financial institutions. We explain this in more detail in the following paragraphs.
Pillar 1 Capital requirements
The assessment to what extent climate change risks are properly captured in the current prudential framework requires at least a high-level understanding of the framework. Figure 1 presents a schematic overview of the P1C requirements.
The P1C (at the top of Figure 1) depends on the total amount of Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs; on the row below)2. RWAs are determined separately for each (traditional) risk type. As mentioned, we only focus on credit risk in this article. The RWAs for credit risk are approximately 80% of the average bank’s total RWAs3. Financial institutions can choose between two methodologies for determining their credit risk RWAs: the Standardized Approach (SA)4 and the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach5 . In Europe, on average 40% of the total RWAs for credit risk are based on the SA, while the rest is based on the IRB approach6 :
Figure 1 – Schematic overview of the P1C requirements and the interaction with climate change risks
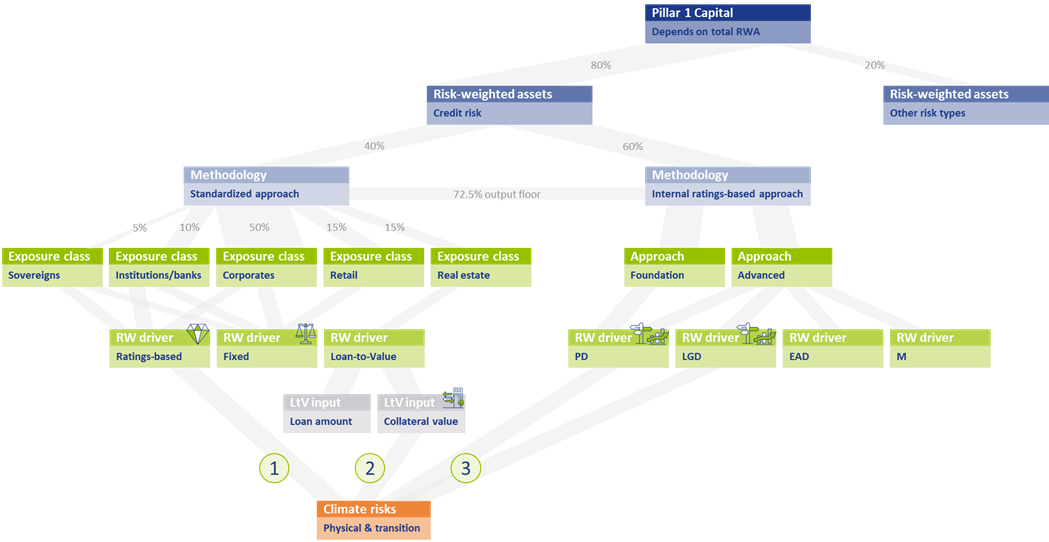
Standardized Approach
In the SA, risk weights (RWs) are assigned to individual exposures, depending on their exposure class. About 50% of the RWAs for credit risk in the SA stem from the Corporates exposure class7. Generally speaking, there are three possible RW drivers: the RWAs depend on the external credit rating for the exposure, a fixed RW applies, or the RW depends on the Loan-to-Value8 (LtV) of the (real estate) exposure. The RW for an exposure to a sovereign bond for example, is either equal to 100% if no external credit rating is available (a fixed RW) or it ranges between 0% (for an AAA to AA-rated bond) and 150% (for a below B-rated bond).
Internal Ratings-Based Approach
Within the IRB approach, a distinction is made between Foundation IRB (F-IRB) and Advanced IRB (A-IRB). In both cases, a financial institution is allowed to use its internal models to determine the Probability of Default (PD) for the exposure. In the A-IRB approach, the financial institution in addition is allowed to use internal models to determine the Loss Given Default (LGD), Exposure at Default (EAD), and the Effective Maturity (M).
Interaction with climate change risks
The overview of the P1C requirements introduced in the previous section allows us to investigate the interaction between climate change risks and the P1C requirement. This is done separately for the SA and the IRB approach.
Standardized Approach
In the SA, there are two elements that allow for interaction between climate change risks and the resulting P1C. Climate change risks could be reflected in the P1C if the RW depends on an external credit rating, and this rating in turn properly accounts for climate change risks in the assessment of the counterparty’s creditworthiness (see 1 in Figure 1). The same holds if the RW depends on the LtV and in turn, the collateral valuation properly accounts for climate change risks (see 2 in Figure 1). This raises several concerns:

First, it can be questioned whether external credit ratings are properly capturing all climate change risks. In a report from the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) [3], which was published at the same time as EBA’s DP, it is stated that credit rating agencies (CRAs) have so far not attempted to determine the credit impact of environmental risk factors (through back-testing for example). Also, the lack of high-quality historical data is mentioned as an explanation that statistical relationships between environmental risks and credit ratings have not been quantified. Further, a paper published by the ECB [4] concludes that, given the current level of disclosures, it is impossible for users of credit ratings to establish the magnitude of adjustments to the credit rating stemming from ESG-related risks. Nevertheless, they state that credit rating agencies “have made significant progress with their disclosures and methodologies around ESG in recent years.” The need for this is supported by academic research. An example is a study [5] from 2021 in which a correlation between credit default swap (CDS) spreads and ESG performance was demonstrated, and a study from 2020 [6] which demonstrated that high emitting companies have a shorter distance-to-default.

Secondly, the EBA has reported in the DP that less than 10% of the SA’s total RWAs is derived based on external credit ratings. This implies that a large share of the total RWAs is assigned a fixed RW. Obviously, in those cases there is no link between the P1C and the climate change risks involved in those exposures.

Finally, climate change risks only impact the P1C maintained for real estate exposures to the extent that these risks have been reflected in collateral valuations. Although climate change risks are priced in financial markets according to academic literature, many papers and institutions indicate that these risks are not (yet) fully reflected. In a survey held by Stroebel and Wurgler in 2021 [7], it is shown that a large majority of the respondents (consisting of finance academics, professionals and public sector regulators, among others) is of the opinion that climate change risks have insufficiently been priced in financial markets. A nice overview of this and related literature is presented in a publication from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) [8]. The EBA DP itself lists some research papers in chapter 5.1 that indicate a relationship between a home’s sales price and its energy efficiency, or with the occurrence of physical risk events. It is unclear though if climate change risks are fully captured in the collateral valuations. For example, research is presented that information on flood risk is not priced into residential property prices. Recent research by ABN AMRO [9] also shows this.
Internal Ratings-Based Approach
In the IRB approach, financial institutions have more flexibility to include climate change risks in their internal models (see 3 in Figure 1). In the F-IRB approach this is limited to PD models, but in the A-IRB approach also LGD models can be adjusted.

A complicating factor is the forward-looking nature of climate change risks. In recent years, the competent authorities have pressured financial institutions to use historical data as much as possible in their model calibration and to back-test the performance of their models. As climate change risks will unfold over the next couple of decades, these are not (yet) reflected in historical data. To incorporate climate change risk, expert judgement would therefore be required. This has been discouraged over the past years (e.g., through the ECB’s Targeted Review of Internal Models (TRIM)) and it will probably trigger a discussion with the competent authorities. A possible deterioration of model performance (due to higher estimated risks compared to historically observations) is just one example that may attract attention.

Another complicating factor is that under the IRB approach, the PD of an obligor is estimated based on long-run average one-year default rates. While this may be an appropriate approach if there are no clear indications that the overall risk level will change, this does not hold if climate change risks increase in the future, and possibly increase systemic risks. By continuing to base a PD model on historical data only, especially for exposures with a time to maturity beyond a couple of years, the credit risk may be understated.
Are amendments to the prudential framework needed?
We have explained that there are several mechanisms in the prudential framework that allow environmental risks to be included in the P1C: the use of external credit ratings, the valuation of collateral, and the PD and LGD models used in the IRB approach. We have also seen, however, that it is questionable whether these mechanisms are fully effective. External credit ratings may not properly reflect all environmental risks and these risks may not be fully priced in on capital markets, leading to incorrect collateral values. Finally, a large share of the RWAs for credit risk depends on fixed RWs that are not (environmentally) risk-sensitive.
Consequently, it can be argued that amendments or enhancements to the prudential framework are needed. One must be careful, however, as the risk of double counting is just around the corner. Therefore, the following amendments or actions should be considered:
- Further research should be undertaken to investigate the relationship between climate change risk and the creditworthiness of counterparties. If there is more clarity on this relationship, it should also be assessed to what extent this relationship is sufficiently reflected in external ratings. Requiring more advanced disclosures from credit rating agencies could help to understand whether these risks are sufficiently captured in the prudential framework. One should be cautious to amend the ratings-based RWs in the SA, since credit rating agencies are continuously working on the inclusion of environmental risks into their credit assessments; there would be a real risk of double counting.
- The potential negative impact of climate change risks on collateral value should be further investigated. Financial institutions are already required by the ECB9 to consider environmental risks in their collateral valuations but this is not at a sufficient level yet. It will be important to consider the possibility of sudden value changes due to transition risks like shifting consumer sentiment or awareness.
- To improve the risk-sensitivity of the framework, a dependency on the carbon emissions of the counterparty could be introduced in the fixed RWs, possibly only for the most carbon-intensive sectors. It could be argued that there are other factors that have a more significant relationship with the default risk of a certain counterparty that could be included in the SA. Climate change risks, however, differ in the sense that they can lead to a systemic risk (as opposed to an idiosyncratic risk) that is currently not captured in the overall level of the RWs.
- In the SA, a distinction could be introduced based on the exposure’s time to maturity. For relatively short-term exposures, the current calibrations are probably fine. For longer-term exposures, however, the risks stemming from climate change may be underestimated as these are expected to increase over time.
- In the IRB approach, a reflection of climate change risk would require the regulator to allow for forward-looking expert judgment in the (re)calibration of PD and LGD models. Further guidance from the competent authorities on the potentially negative impact on model performance based on historical data would also be useful.
Conclusion
Based on the schematic overview of the P1C requirements and the (potential) interaction with climate change risks, we conclude that several mechanisms in the prudential framework allow for climate change risks to be incorporated into the P1C. At the same time, we conclude that this interaction is limited to specific parts of the portfolio, and that in those cases it remains to be seen to what extent this is properly accounted for. To remedy this, amendments to the prudential framework could be considered. It is important, however, to avoid double counting issues and to be mindful of time horizon differences.
It is expected that the EBA will publish a final report on the prudential treatment of environmental risks in the first half of this year. However, especially financial institutions that are using the IRB approach should not take a wait-and-see approach. Given the complexity of modeling climate change risks, it is prudent to start incorporating climate change risks into PD and LGD models sooner rather than later.
With Zanders’ extensive experience covering both credit risk modeling and climate change risk, we are well suited to support with this process. If you are looking for support, please reach out to us.
1 Supporting factors are currently in place for SMEs and infrastructure projects, but the EBA advocated their removal.
2 See RBC20.1 in the Basel Framework.
3 See for example the results from the EBA’s EU-wide transparency exercise. This is reflected in Figure 1 by the percentage in the grey link between P1C and RWAs for credit risk.
4 See CRE20 to CRE22 in the Basel Framework.
5 See CRE30 to CRE36 in the Basel Framework.
6 In the Netherlands, less than 20% of the total RWAs is based on the SA. See the EBA’s EU-wide transparency exercise for more information. The percentages in the grey link between ‘Risk-weighted assets’ and ‘Methodology’ in Figure 1 are based on the European average.
7 See the EBA’s Risk assessment of the European banking system [2]. The percentages in the grey link between ‘Standardized Approach’ and the ‘Exposure class’ in Figure 1 reflect the share of RWAs in the SA for each of the different exposure classes.
8 The LtV is defined as the ratio between the loan amount and the value of the property that serves as collateral.
9 See expectation 8.3 in the ECB’s Guide on climate-related and environmental risks.
References
- The role of environmental risks in the prudential framework, European Banking Authority, Discussion Paper, 2 May 2022
- Risk assessment of the European banking system, European Banking Authority, December 2022
- Capturing risk differentials from climate-related risks, Network for Greening the Financial System, Progress Report, May 2022
- Disclosure of climate change risk in credit ratings, European Central Bank, Occasional Paper Series, No. 303, September 2022
- Pricing ESG risk in credit markets, Federated Hermes, March 2021
- Climate change and credit risk, Capasso, Gianfrate, and Spinelli, Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 266, September 2020
- What do you think about climate finance?, Stroebel and Wurgler, Journal of Financial Economics, vol 142, no 2, November 2021
- Pricing of climate risks in financial markets, Bank for International Settlements, Monetary and Economic Department, December 2022
- Is flood risk already affecting house prices?, ABN AMRO, 11 February 2022
- Guide on climate-related and environmental risks, European Central Bank, November 2020

On Thursday 9 June, we hosted a roundtable in our head office in Utrecht titled ’Integrating ESG risks into a bank’s credit risk framework’. The roundtable was attended by credit and climate risk managers, as well as model validators, working for Dutch banks of different sizes. In this article we briefly describe Zanders’ view on this topic and share the key insights of the roundtable.

The last three to four years have seen a rapid increase in the number of publications and guidance from regulators and industry bodies. Environmental risk is currently receiving the most attention, triggered by the alarming reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). These reports show that it is a formidable, global challenge to shift to a sustainable economy in order to reduce environmental impact.
Zanders’ view
Zanders believes that banks have an important role to play in this transition. Banks can provide financing to corporates and households to help them mitigate or adapt to climate change, and they can support the development of new products such as sustainability-linked derivatives. At the same time, banks need to integrate ESG risk factors into their existing risk processes to prepare for the new risks that may arise in the future. Banks and regulators so far have mostly focused on credit risk.
We believe that the nature and materiality of ESG risks for the bank and its counterparties should be fully understood, before making appropriate adjustments to risk models such as rating, pricing, and capital models. This assessment allows ESG risks to be appropriately integrated into the credit risk framework. To perform this assessment, banks may consider the following four steps:
- Step 1: Identification. A bank can identify the possible transmission channels via which ESG risk factors can impact the credit risk profile of the bank. This can be through direct exposures, or indirectly via the credit risk profile of the bank’s counterparties. This can for example be done on portfolio or sector level.
- Step 2: Materiality. The materiality of the identified ESG risk factors can be assessed by assigning them scores on impact and likelihood. This process can be supported by identifying (quantitative) internal and external sources from the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS), governmental bodies, or ESG data providers.
- Step 3: Metrics. For the material ESG risk factors, relevant and feasible metrics may be identified. By setting limits in line with the Risk Appetite Statement (RAS) of the bank, or in line with external benchmarks (e.g., a climate science-based emission path that follows the Paris Agreement), the exposure can be managed.
- Step 4: Verification. Because of the many qualitative aspects of the aforementioned steps, it is important to verify the outcomes of the assessment with portfolio and credit risk experts.
Key insights
Prior to the roundtable, Zanders performed a survey to understand the progress that Dutch banks are marking with the integration of ESG risks into their credit risk framework, and the challenges they are facing.
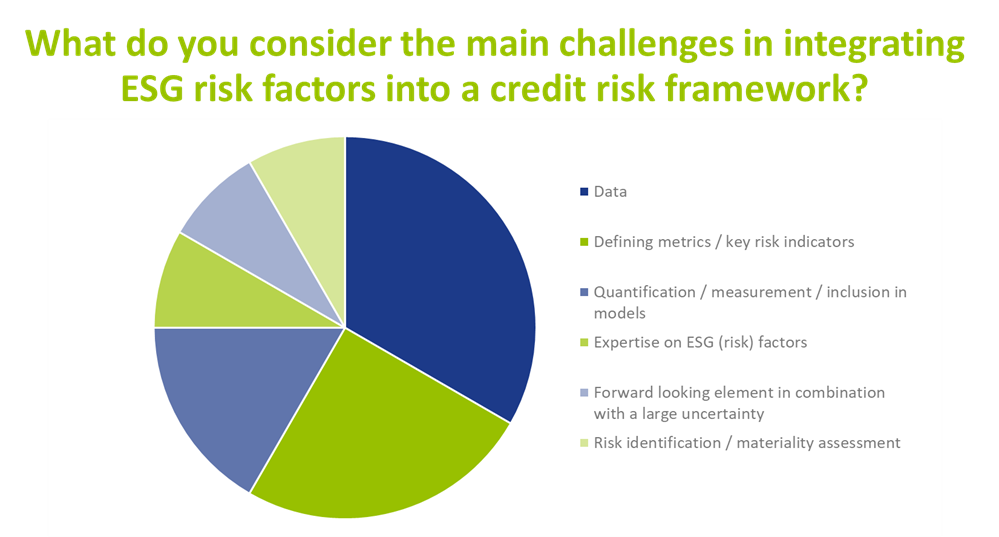
Currently, when it comes to incorporating ESG risks in the credit risk framework, banks are mainly focusing their attention on risk identification, the materiality assessment, risk metric definition and disclosures. The survey also reveals that the level of maturity with respect to ESG risk mitigation and risk limits differs significantly per bank. Nevertheless, the participating banks agreed that within one to three years, ESG risk factors are expected to be integrated in the key credit risk management processes, such as risk appetite setting, loan origination, pricing, and credit risk modeling. Data availability, defining metrics and the quantification of ESG risks were identified by banks as key challenges when integrating ESG in credit risk processes, as illustrated in the graph below.
In addition to the challenges mentioned above, discussion between participating banks revealed the following insights:
- Insight 1: Focus of ESG initiatives is on environmental factors. Most banks have started integrating environmental factors into their credit risk management processes. In contrast, efforts for integrating social and governance factors are far less advanced. Participants in the roundtable agreed that progress still has to be made in the area of data, definitions, and guidelines, before social and governance factors can be incorporated in a way that is similar to the approach for environmental factors.
- Insight 2: ESG adjustments to risk models may lead to double counting. The financial market still needs to gain more understanding to what extent ESG risk factor will manifest itself via existing risk drivers. For example, ESG factors such as energy label or flood risk may already be reflected in market prices for residential real estate. In that case, these ESG factors will automatically manifest itself via the existing LGD models and separate model adjustments for ESG may lead to double counting of ESG impact. Research so far shows mixed signals on this. For example, an analysis of housing prices by researchers from Tilburg University in 2021 has shown that there is indeed a price difference between similar houses with different energy labels. On the other hand, no unambiguous pricing differentiation was found as part of a historical house price analysis by economists from ABN AMRO in 2022 between similar houses with different flood risks. Participating banks agreed that further research and guidance from banks and the regulators is necessary on this topic.
- Insight 3: ESG factors may be incorporated in pricing. An outcome of incorporating ESG in a credit risk framework could be that price differentiation is introduced between loans that face high versus low climate risk. For example, consideration could be given to charging higher rates to corporates in polluting sectors or ones without an adequate plan to deal with the effects of climate change. Or to charge higher rates for residential mortgages with a low energy label or for the ones that are located in a flood-prone area. Participating banks agreed that in theory, price differentiation makes sense and most of them are investigating this option as a risk mitigating strategy. Nevertheless, some participants noted that, even if they would be able to perfectly quantify these risks in terms of price add-ons, they were not sure if and how (e.g., for which risk drivers and which portfolios) they would implement this. Other mitigating measures are also available, such as providing construction deposits to clients for making their homes more sustainable.
Conclusion
Most participating banks have made efforts to include ESG risk factors in their credit risk management processes. Nevertheless, many efforts are still required to comply with all regulatory expectations regarding this topic. Not only efforts by the banks themselves but also from researchers, regulators, and the financial market in general.
Zanders has already supported several banks and asset managers with the challenges related to integrating ESG risks into the risk organization. If you are interested in discussing how we can help your organization, please reach out to Sjoerd Blijlevens or Marije Wiersma.

On 24 January 2022, the European Banking Authority (EBA) published its final draft Implementing Technical Standards (ITS) on Pillar 3 (P3) disclosures on Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) risks.

This publication fits nicely into the ‘horizon priority’ of the EBA1 to provide tools to banks to measure and manage ESG-related risks. In this article we present a brief overview of the way the ITS have been developed, what qualitative and quantitative disclosures are required, what timelines and transitional measures apply – and where the largest challenges arise. By requiring banks to disclose information on their exposure to ESG-related risks and the actions they take to mitigate those risks – for example by supporting their clients and counterparties in the adaptation process – the EBA wants to contribute to a transition to a more sustainable economy. The Pillar 3 disclosure requirements apply to large institutions with securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state.
In an earlier report2, the EBA defined ESG-related risks as “the risks of any negative financial impact on the institution stemming from the current or prospective impacts of ESG factors on its counterparties or invested assets”. Hence, the focus is not on the direct impact of ESG factors on the institution, but on the indirect impact through the exposure of counterparties and invested assets to ESG-related risks. The EBA report also provides examples for typical ESG-related factors.
While the ITS have been streamlined and simplified compared to the consultation paper published in March 2021, there are plenty of challenges remaining for banks to implement these standards.
Development of the ITS
The EBA has been mandated to develop the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks in Article 434a of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The EBA has opted for a sequential approach, with an initial focus on climate change-related risks. This is further narrowed down by only considering the banking book. The short maturity and fast revolving positions in the trading book are out of scope for now. The scope of the ITS will be extended to included other environmental risks (like loss of biodiversity), and social and governance risks, in later stages.
In the development of the ITS, the EBA has strived for alignment with several other regulations and initiatives on climate-related disclosures that apply to banks. The most notable ones are listed below (and in Figure 1):
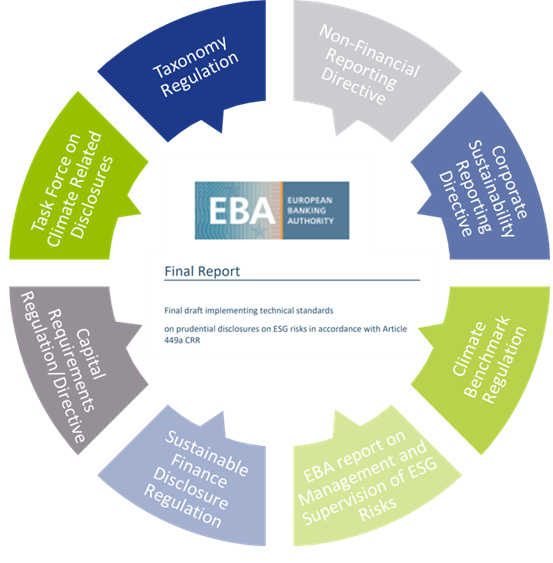
Figure 1 – Overview of related regulations and initiatives considered in the development of the ITS
- Capital Requirements Directive and Regulation (CRD and CRR): article 98(8) of the CRD3 mandated the EBA to publish the EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks, which includes the split of climate change-related risks in physical and transition risks. Article 434a of the CRR4 mandated the EBA to develop the draft ITS to specify the ESG disclosure requirements described in article 449a.
- EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks2: the report provides common definitions of ESG risks and contains proposals on how to include ESG risks in the risk frameworks of banks, covering its identification, assessment, and management. It also discusses the way to include ESG risks in the supervisory review process.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)5: the Financial Stability Board’s TFCD has published recommendations on climate-related disclosures. The metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) included in the ITS have been aligned with the TCFD recommendations.
- Taxonomy Regulation6: the European Union’s common classification system of environmentally sustainable economic activities is underpinning the main KPIs introduced in the ITS.
- Climate Benchmark Regulation (CBR)7: In the CBR, two types of climate benchmarks were introduced (‘EU Climate Transition’ and ‘EU Paris-aligned’ benchmarks) and ESG disclosures for all other benchmarks (excluding interest rate and currency benchmarks) were required.
- Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD)8: the NFRD introduces ESG disclosure obligations for large companies, which include climate-related information.
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)9: a proposal by the European Commission to extend the scope of the NFRD to also include all companies listed on regulated markets (except listed micro-enterprises). One of the ITS’s KPIs, the Green Asset Ratio (GAR) is directly linked to the scope of the NFRD/CSRD.
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)10: the SFDR lays down sustainability disclosure obligations for manufacturers of financial products and financial advisers towards end-investors. It applies to banks that provide portfolio management investment advice services.
Compared to the consultation paper for the ITS, several changes have been made to the required templates. Some templates have been combined (e.g., templates #1 and #2 from the consultation paper have been combined into template #1 of the final draft ITS) and several templates have been reorganized and trimmed down (e.g., the requirement to report exposures to top EU or top national polluters has been removed).
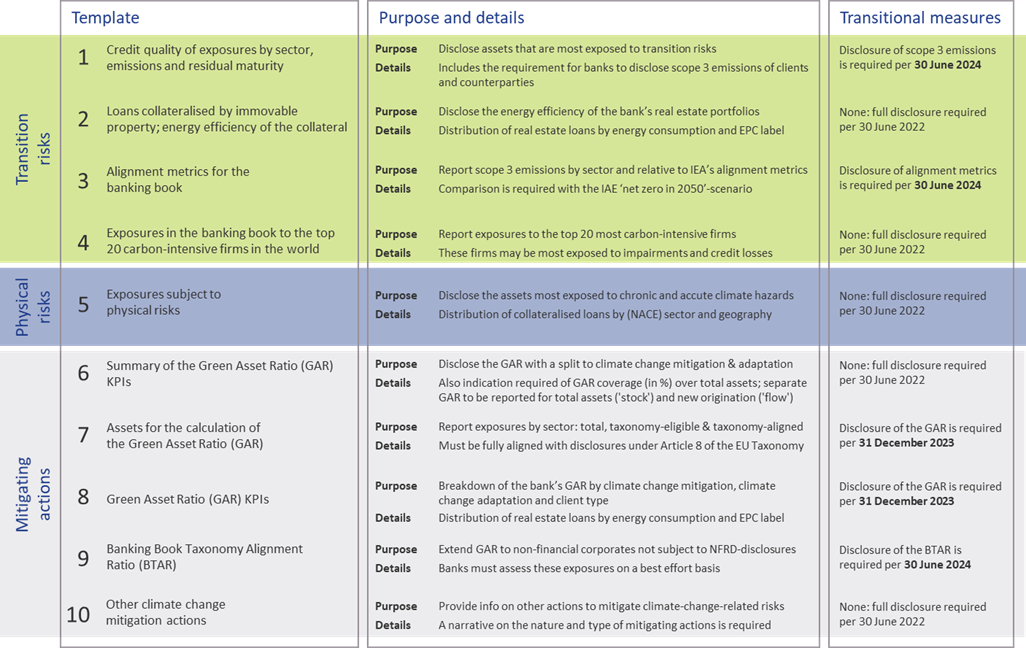
Quantitative disclosures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks introduce ten templates on quantitative disclosures. These can be grouped in four templates on transition risks, one on physical risks, and five on mitigating actions:
- Transition risks
Two of the required templates are relatively straightforward. Banks need to report the energy efficiency of real estate collateral in the loan portfolio (#2) and report their aggregate exposure to the top 20 of the most carbon-intensive firms in the world (#4).
The main challenge for banks though will be in completing the other two templates:- Template #1 requires banks to disclose the gross carrying amount of loans and advances provided to non-financial corporates, classified by NACE sector codes and residual maturities. It is also required to report on the counterparties’ scope 1, 2, and 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Reflecting the challenge in reporting on scope 3 emissions, a transitional measure is in place. Full reporting needs to be in place by June 2024. Until then, banks need to report their available estimates (if any) and explain the methodologies and data sources they intend to use.
- In the last template (#3), banks also need to report scope 3 emissions, but relate these to the alignment metrics defined by the International Energy Agency (IEA) for the ‘net zero by 2050’ scenario. For this scenario, a target for a CO2 intensity metric is defined for 2030. By calculating the distance to this target, it becomes clear how banks are progressing (over time) towards supporting a sustainable economy. A similar transitional measure applies as for template #1.
- Physical risks
In template #5, banks are required to disclose how their banking book positions are exposed to physical risks, i.e., “chronic and acute climate-related hazards”. The exposures need to be reported by residual maturity and by NACE sector codes and should reflect exposure to risks like heat waves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. Specialized databases need to be consulted to compile a detailed understanding of these exposures. To support their submissions, banks further need to compile a narrative that explains the methodologies they used. - Mitigating actions
The final set of templates covers quantitative information on the actions a bank takes to mitigate or adapt to climate change risks.- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
- In template #7, banks need to report the outstanding banking book exposures to different types of clients/issuers, as well as the amount of these exposures that are taxonomy-eligible (that is, to sectors included in the EU Taxonomy) and taxonomy-aligned (that is, taxonomy-eligible exposures financing activities that contribute to climate change mitigation or adaptation). Based on this information, the bank’s GAR can be determined.
- In template #8, a GAR needs to be reported for the exposures to each type of client/issuer distinguished in template #7, with a distinction between a GAR for the full outstanding stock of exposures per client/issuer type, and a GAR for newly originated (‘flow’) exposures.
- Template #6 contains a summary of the GARs from templates #7 and #8.
In these templates, the numerator of the GAR only includes exposures to non-financial corporations that are required to publish non-financial information under the NFRD. Any exposures to other corporate counterparties therefore are considered 0% Taxonomy-aligned.
- The main challenge in this group of templates is in template #9. To incentivize banks to support all of their counterparties to transition to a more sustainable business model, and to collect ESG data on these counterparties, the EBA introduces the Banking Book Taxonomy Alignment Ratio (BTAR). In this metric, the numerator does include the exposures to counterparties that are not subject to NFRD disclosure obligations. The BTAR ratios obtained from the information in template #9 therefore complement the GAR ratios obtained in templates #7 and #8.
- In the final template (#10), banks have the opportunity to include any other climate change mitigating actions that are not covered by the EU Taxonomy. They can for example report on their use of green or sustainable bonds and loans.
- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
An overview of the templates for quantitative disclosures in presented in Figure 2.
Qualitative disclosures
In the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks, three tables are included for qualitative disclosures. The EBA has aligned these tables with their Report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks11. The three tables are set up for qualitative information on environmental, social, and governance risks, respectively. For each of these topics, banks need to address three aspects: on business strategy and processes, governance, and risk management. An overview of the required disclosures is presented in Figure 3.
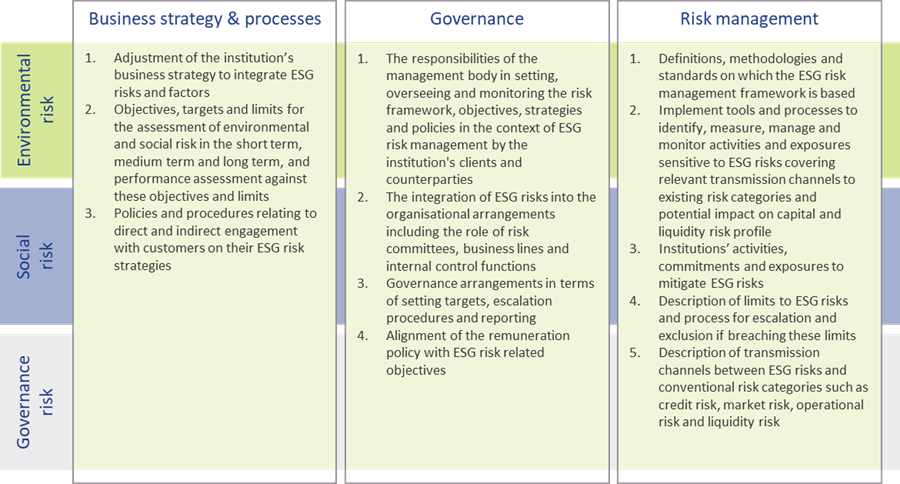
Figure 3 – Overview of qualitative ESG disclosures (based on templates & section 2.3.2 of the EBA ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks)
Timelines and transitional measures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks become effective per 30 June 2022 for large institutions that have securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state. A semi-annual disclosure is required, but the first disclosure is annual. Consequently, based on 31 December 2022 data, the first reporting will take place in the first quarter of 2023.
The EBA has introduced a number of transitional measures. These can be summarized as follows:
- The reporting of information on the GAR is only required as of 31 December 2023.
- The reporting of information on the BTAR, the bank’s financed scope 3 emissions, and the alignment metrics is only required as of June 2024.
The EBA has further indicated in the ITS that they will conduct a review of the ITS’s requirements during 2024. They may then also extend the ITS with other environmental risks (other than the climate change-related risks in the current version). The EU Taxonomy is expected to cover a broader range of environmental risks by the end of 2022. Sometime after 2024, it is expected that the EBA will further extend the ITS by including disclosure requirements on social and governance risks.
An overview of the main timelines and transitional measures is presented in Figure 4.
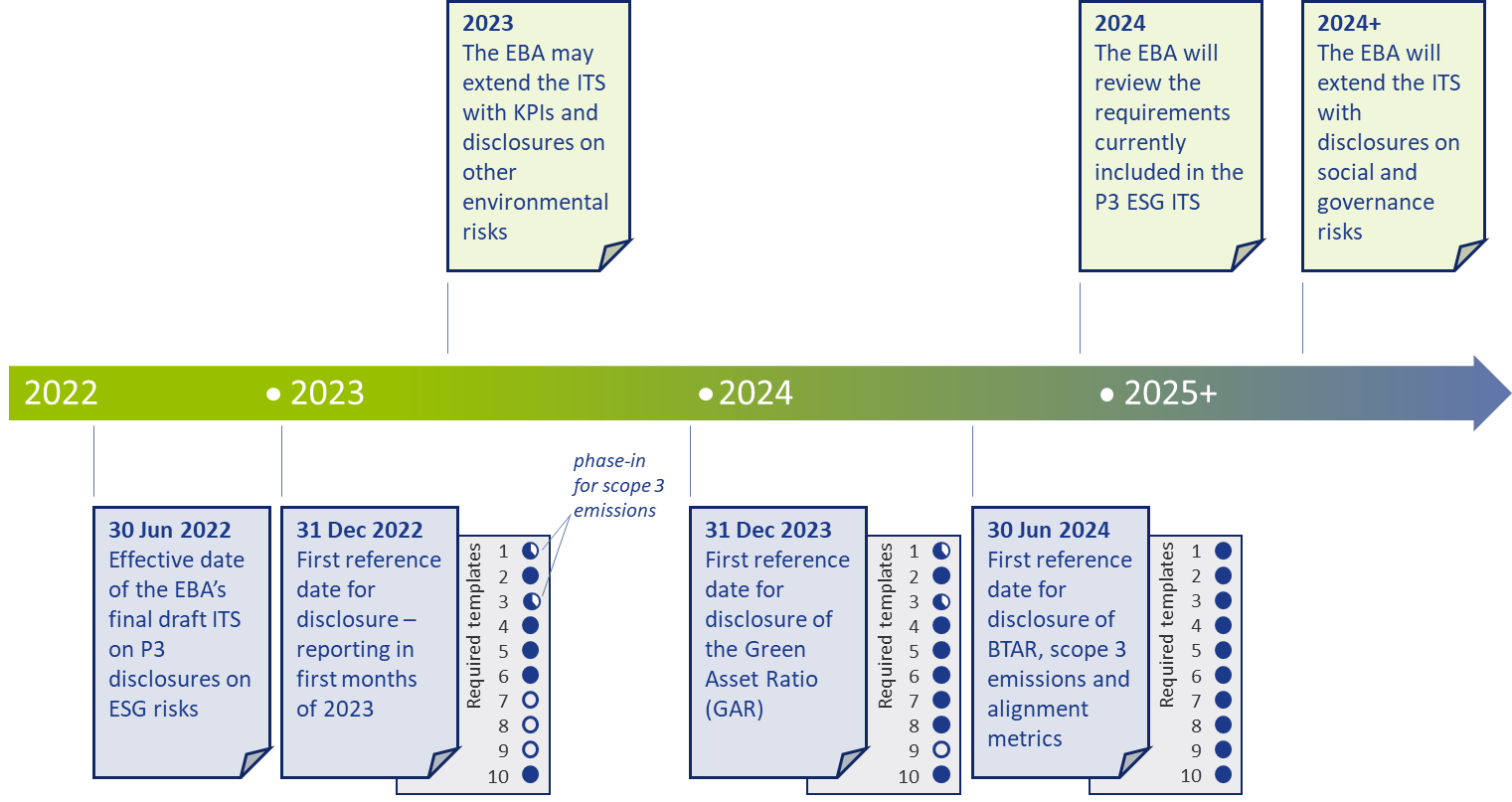
Figure 4 – Overview of the main timelines and transitional measures for the ESG disclosures
Conclusion
Society, and consequently banks too, are increasingly facing risks stemming from changes in our climate. In recent years, supervisory authorities have stepped up by introducing more and more guidance and regulation to create transparency about climate change risk, and more broadly ESG risks. The publication of the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks by the EBA marks an important milestone. It offers banks the opportunity to disseminate a constructive and positive role in the transition to a sustainable economy.
Nonetheless, implementing the disclosure requirements will be a challenge. Developing detailed assessments of the physical risks to which their asset portfolio is exposed and to estimate the scope 3 emissions of their clients and counterparties (‘financed emissions’) will not be straightforward. For their largest counterparties, banks will be able to profit from the NFRD disclosure obligations, but especially in Europe a bank’s portfolio typically has many exposures to small- and medium-sized enterprises. Meeting the disclosure requirements introduced by the EBA will require timely and intensive discussions with a substantial part of the bank’s counterparties.
Banks also need to provide detailed information on how ESG risks are reflected in the bank’s strategy and governance and incorporated in the risk management framework. With our extensive knowledge on market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and business risk, Zanders is well equipped to support banks with integrating the identification, measurement, and management of climate change-related risks into existing risk frameworks. For more information, please contact Pieter Klaassen or Sjoerd Blijlevens via +31 88 991 02 00.
References
- See the EBA 2022 Work Programme.
- The EBA’s Report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks for credit institutions and investment firms, published in June 2021.
- See the EBA’s interactive Single Rulebook.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/876.
- See the TCFD’s Final Report on Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures published in June 2017.
- See the EBA’s response to EC Call for Advice on Article 8 Taxonomy Regulation.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/2089.
- See Directive 2014/95/EU.
- See the European Commission’s Proposal for a Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/2088.
- The EBA report can be found here.



