Digital transformation through a corporate treasury lens

The corporate landscape is being redefined by a plethora of factors, from new business models and changing regulations to increased competition from digital natives and the acceleration of the consumer digital-first mindset.
The new landscape is all about a digital real-time experience which is creating the need for change in order to stay relevant and ideally thrive. If we reflect on the various messages from the numerous industry surveys, it’s becoming crystal clear that a digital transformation is now an imperative.
We are seeing an increasing trend that recognizes technological progress will fundamentally change an organization and this pressure to move faster is now becoming unrelenting. However, to some corporates, there is still a lack of clarity on what a digital transformation actually means. In this article we aim to demystify both the terminology and relevance to corporate treasury as well as considering the latest trends including what’s on the horizon.
What is digital transformation?
There is no one-size-fits-all view of a digital transformation because each corporate is different and therefore each digital transformation will look slightly different. However, a simple definition is the adoption of the new and emerging technologies into the business which deliver operational and financial efficiencies, elevate the overall customer experience and increase shareholder value.
Whilst these benefits are attractive, to achieve them it’s important to recognize that a digital transformation is not a destination – it’s a journey that extends beyond the pure adoption of technology. Whilst technology is the enabler, in order to achieve the full benefits of this digital transformation journey, a more holistic view is required.
Figure 1 provides a more holistic view of a digital transformation, which embraces the importance of cultural change like the adoption of the ‘fail fast’ philosophy that is based on extensive testing and incremental development to determine whether an idea has value.
In terms of the drivers, we see four core pillars providing the motivation:
- Elevate the customer experience
- Operational agility and resilience
- Data driven real time vision
- Workforce enablement
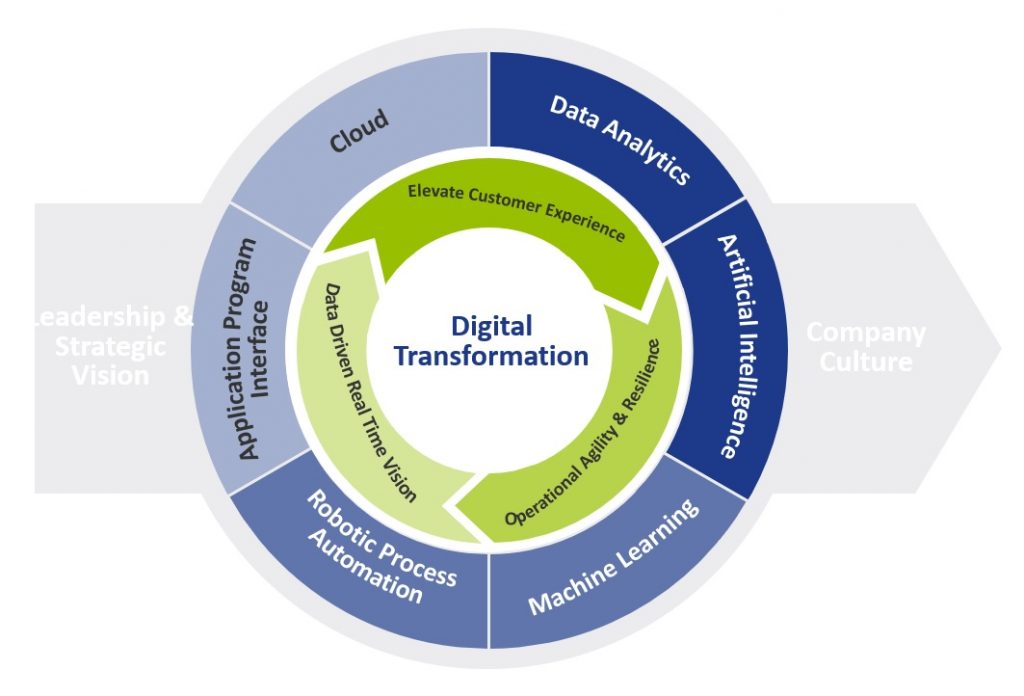
Figure 1: Digital Transformation View
What is the relevance to corporate treasury?
Considering the digital transformation journey, it’s important to understand the relevance of the technologies available.
Whilst figure 2 highlights the foundational technologies, it’s important to note that these technologies are all at a different stage of evolution and maturity. However, they all offer the opportunity to re-define what is possible, helping to digitize and accelerate existing processes and elevate overall treasury performance.
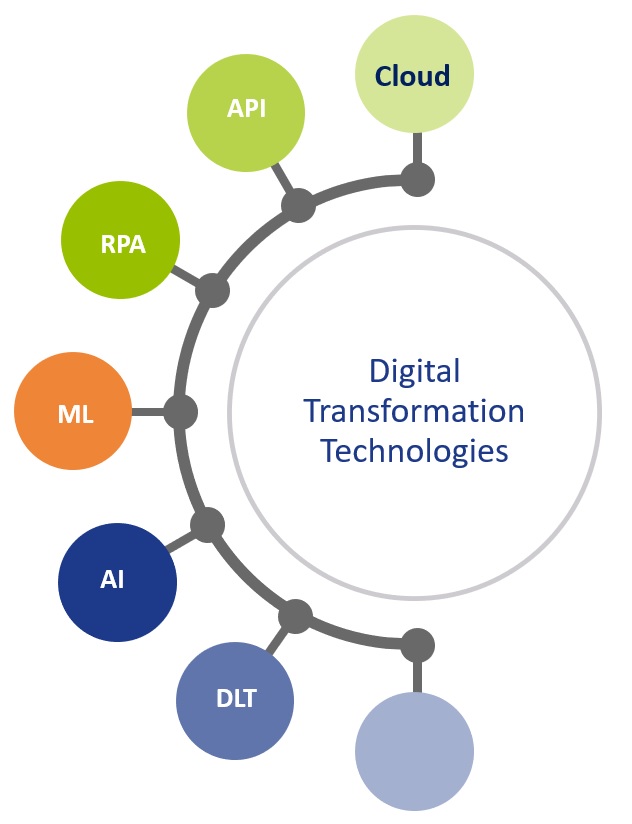
Figure 2: Core Digital Transformation Technologies
To help polarize the potential application and value of these technologies, we need to look through two lenses.
Firstly, what are some of today’s mainstream challenges that currently impact the performance of the treasury function, and secondly, how these technologies provide the opportunity to both optimize and elevate the treasury function.
The challenges and opportunities to optimize
Considering some of the major challenges that still exist within corporate treasury, the new and emerging technologies will provide the foundation for the digital transformation within corporate treasury as they will deliver the core capabilities to elevate overall performance. Figure 3 below provides some insights into why these technologies are more than just ‘buzzwords’, providing a clear opportunity to elevate current performance.
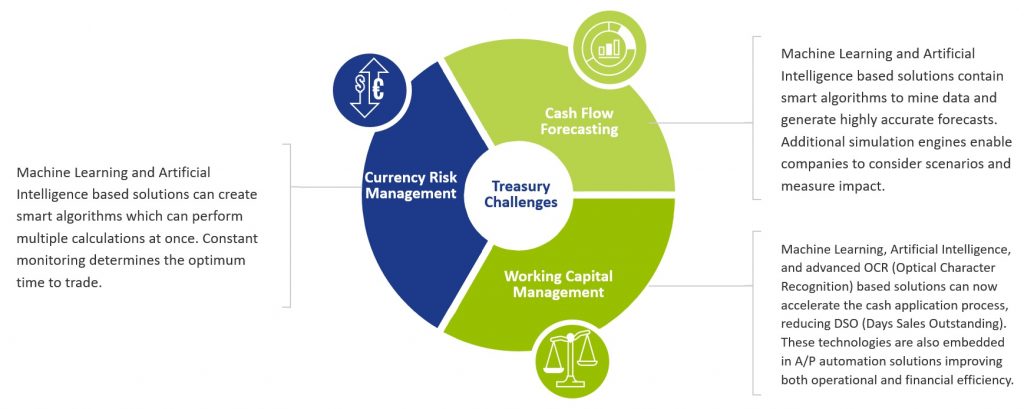
Figure 3: Common challenges within corporate treasury
Cognitive cash flow forecasting systems can learn and adapt from the source data, enabling automatic and continuous improvements in the accuracy and timeliness of the forecasts. Additionally, scenario analysis accelerates the informed decision-making process. Focusing on currency risk, the cognitive technology is on a continuous learning loop and therefore continues to update its decision-making process which helps improve future predictions.
Moving onto working capital, these new cognitive technologies combined with advanced optical character recognition/intelligent character recognition can automate and accelerate key processes within both the accounts payables (A/P) and account receivables (A/R) functions to contribute to overall working capital management. On the A/R side, these technologies can read PDF and email remittance information as well as screen scrape data from customer portals. This data helps automate and accelerate the cash application process with levels exceeding 95% straight through reconciliation now being achieved. Applying cash one day earlier has a direct positive impact on days sales outstanding (DSO) and working capital. On the A/P side, the technology enables greater compliance, visibility and control providing the opportunity for ‘autonomous A/P’. With invoice approval times now down to just 10.4 business hours*, it provides a clear opportunity to maximize early payment discounts (EPDs).
Whilst artificial intelligence/machine learning technologies will play a significant role within the corporate treasury digital transformation, the increased focus on real-time treasury also points to the power of financial application program interfaces (APIs). API technology will play an integral part of an overall blended solution architecture. Whilst API technology is not new, the relevance to finance really started with Europe’s PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2) Open Banking initiative, with API technology underpinning this. There are already several use cases for both Treasury and the SSC (shared service center) to help both digitize and importantly accelerate existing processes where friction currently exists. This includes real time balances, credit notifications and payments.
The latest trends
Whilst a number of these new and emerging technologies are expected to have a profound impact on corporate treasury, when we consider the broader enterprise-wide adoption of these technologies, we are generally seeing corporate treasury below these levels. However, in terms of general market trends we see the following:
- Artificial intelligence/machine learning is being recognized as a key enabler of strategic priorities, with the potential to deliver both predictive and prescriptive analytics. This technology will be a real game-changer for corporate treasury not only addressing a number of existing and longstanding pain-points but also redefining what is possible.
- Whilst robotic process automation (RPA) is becoming mainstream in other business areas, this technology is generally viewed as less relevant to corporate treasury due to more complex and skilled activities. That said, Treasury does have a number of typically manually intensive activities, like manual cash pooling, financial closings and data consolidations. So, broader adoption could be down to relative priorities.
- Adoption of API technology now appears to be building momentum, given the increased focus around real time treasury. This technology will provide the opportunity to automate and accelerate processes, but a lack of industry standardization across financial messaging, combined with the relatively slow adoption and limited API banking service proposition across the global banking community, will continue to provide a drag on adoption levels.
What is on the horizon?
Over the past decade, we have seen a tsunami of new technologies that will play an integral part in the digital transformation journey within corporate treasury. Given that, it has taken approximately ten years for cloud technology to become mainstream from the initial ‘what is cloud?’ to the current thinking ‘why not cloud?’ We are currently seeing the early adoption of some of these foundational transformational technologies, with more corporates embarking on a digital first strategy. This is effectively re-defining the partnership between man and machine, and treasury now has the opportunity to transform its technology, approach and people which will push the boundaries on what is possible to create a more integrated, informed and importantly real-time strategic function.
However, whilst these technologies will be supporting critical tasks, assisting with real-time decision-making process and reducing risk, to truly harness the power of technology a data strategy will also be foundational. Data is the fuel that powers AI, however most organizations remain heavily siloed, from a system, data, and process perspective. Probably the biggest challenge to delivering on the AI promise is access to the right data and format at the right time.
So, over the next 5-10 years, we expect the solutions underpinned by these new foundational technologies to evolve, leveraging better quality structured data to deliver real time data visualization which embraces both predictive and prescriptive analytics. What is very clear is that this ecosystem of modern technologies will effectively redefine what is possible within corporate treasury.
*) Coupa 2021 Business Spend Management Benchmark Report
Climate change risk

Amidst the aftermath of the corona pandemic and the unfolding tragedy in Ukraine, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published its latest report1 on climate change on 28 February 2022, containing a more alarming message than ever before.
The Working Group II contribution to the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report states that “climate change is a grave and mounting threat to our wellbeing and a healthy planet”. It is a formidable, global challenge to transition to a sustainable economy before time is running out. Banks have an important role to play in this transition. By stepping up to this role now, banks will be better prepared for the future, and reap the benefits along the way.
In the Paris Agreement (or COP21), adopted in December 2015, 196 parties agreed to limit global warming to well below 2.0°C, and preferably to no more than 1.5°C. To prevent irreversible impacts to our climate, the IPCC stresses that the increase in global temperature (relative to the pre-industrial era) needs to remain below 1.5°C. To achieve this target, a rapid and unprecedented decrease in the emission of greenhouse gasses (GHG) is required. With CO2 emissions still on the rise, as depicted in Figure 1, the challenge at hand has increased considerably in the past decade.
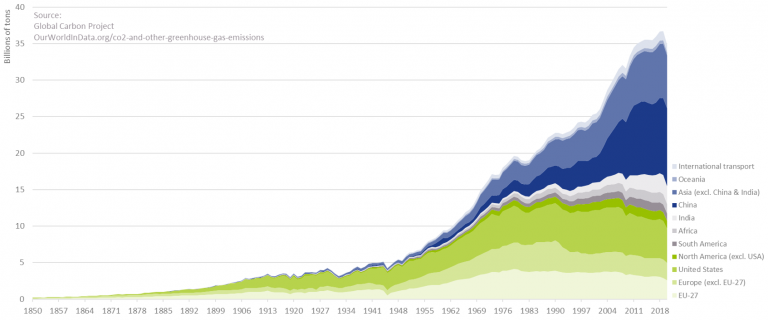
Figure 1 – Annual CO2 emissions from fossil fuels.
To further illustrate this, Figure 2 depicts for several starting years a possible pathway in CO2 reductions to ensure global warming does not exceed 2.0°C. Even under the assumption that CO2 emissions have already peaked, it becomes clear that the required speed of CO2 reductions is rapidly increasing with every year of inaction. We are a long way from limiting global warming to 2.0°C. This even holds under the assumption that all countries’ pledges to reduce GHG emissions will be achieved, as can be observed in Figure 3.
To quote the IPCC Working Group II co-chair Hans-Otto Pörtner: “Any further delay in concerted anticipatory global action on adaptation and mitigation will miss a brief and rapidly closing window of opportunity to secure a livable and sustainable future for all.”
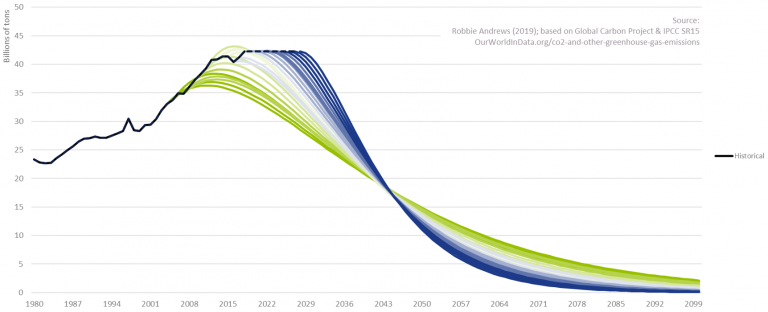
Figure 2 – CO2 reduction need to limit global warming.
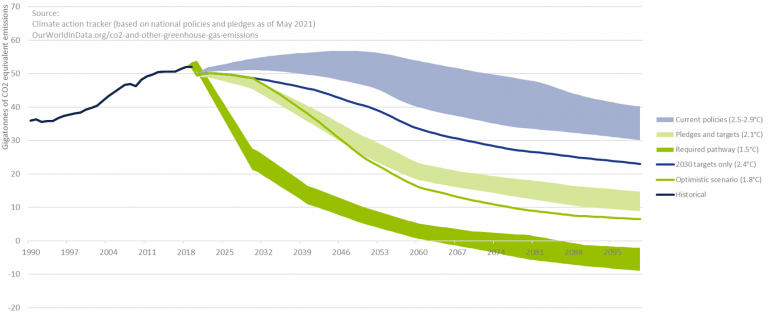
Figure 3 – Global GHG emissions and warming scenario’s.
The role of banks in the transition – and the opportunities it offers
Historically, banks have been instrumental to the proper functioning of the economy. In their role as financial intermediaries, they bring together savers and borrowers, support investment, and play an important role in facilitating payments and transactions. Now, banks have the opportunity to become instrumental to the proper functioning of the planet. By allocating their available capital to ‘green’ loans and investments at the expense of their ‘brown’ counterparts, banks can play a pivotal role in the transition to a sustainable economy. Banks are in the extraordinary position to make a fundamentally positive contribution to society. And even better, it comes with new opportunities.
The transition to a sustainable economy requires huge investments. It ranges from investments in climate change adaption to investments in GHG emission reductions: this covers for example investments in flood risk warning systems and financing a radical change in our energy mix from fossil-fuel based sources (like coal and natural gas) to clean energy sources (like solar and wind power). According to the Net Zero by 2050 Report from the International Energy Agency (IEA)2, the annual investments in the energy sector alone will increase from the current USD 2.3 trillion to USD 5.0 trillion by 2030. Hence, across sectors, the increase in annual investments could easily be USD 3.0 to 4.0 trillion. As much as 70% of this investment may need to be financed by the private sector (including banks and other financial institutions)3. To put this in perspective, the total outstanding credit to non-financial corporates currently stands at USD 86.3 trillion4. Assuming an average loan maturity of 5 years, this would translate to a 12-16% increase in loans and investments by banks on a global level. Hence, the transition to a sustainable economy will open up a large market for banks through direct investments and financing provided to corporates and households.
The transition to a sustainable economy is also triggering product development. The Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI) for example reports that the combined issuance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) bonds, sustainability-linked bonds and transition debt reached almost USD 500 billion in 2021H1, representing a 59% year-on-year growth rate. Other initiatives include the introduction of ‘green’ exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and sustainability-linked derivatives. The latter first appeared in 2019 and they provide an incentive for companies to achieve sustainable performance targets. If targets are met, a company is for example eligible for a more attractive interest coupon. Again, this is creating an interesting market for banks.
By embracing the transition, with all the opportunities that it offers, banks are also bracing themselves for the future. Banks that adopt climate change-resilient business models and integrate climate risk management into their risk frameworks will be much better positioned than banks that do not. They will be less exposed to climate-related risks, ranging from physical and transition risks to risks stemming from a reputational perspective or litigation, also justifying lower capital requirements. The early adaptors of today will be the leaders of tomorrow.
A roadmap supporting the transition
How should a bank approach this transition? As depicted in Figure 4, we identify four important steps: target setting, measurement and reporting, strategy and risk framework, and engaging with clients.

Figure 4 – The roadmap supporting the transition to a sustainable economy.
Target setting
The starting point for each transition is to set GHG emission targets in alignment with emission pathways that have been established by climate science. One important initiative that can support banks in setting these targets is the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). This organization supports companies to set targets in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement. Unlike many other companies, the majority of a bank’s GHG emissions are outside their direct control. They can influence, however, their so-called financed emissions, which are the GHG emissions coming from their lending and investment portfolios. The SBTi has developed a framework for banks that reflects this. It encourages banks to use the Absolute Contraction approach that requires a 2.5% (for a well-below 2.0°C target) or 4.2% (for a 1.5°C target) annual reduction in GHG emissions. A clear emission pathway guides banks in the subsequent steps of the transition process.
Measurement and reporting
With targets in place, the next important step for a bank is to determine their level of GHG emissions: both for scope 1 and 2 (the GHG emissions they control) and for scope 3 (the financed emissions). Important initiatives for the quantification of the financed emissions are the Paris Agreement Capital Transition Assessment (PACTA) and the Platform Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF). PCAF is a Dutch initiative to deliver a global, standardized GHG accounting and reporting approach for financial institutions (building on the GHG Protocol). PACTA enables banks to measure the alignment of financial portfolios with climate scenarios.
By keeping track of the level of GHG emissions on an annual basis, banks can assess whether they are following their selected emission pathway. Reporting, in line with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), will contribute to a greater understanding of climate risks with their investors and other stakeholders.
Strategy and risk framework
Setting targets and measuring the current level of GHG emissions are necessary but not sufficient conditions to achieve a successful transition. Climate change risk needs to be fully integrated into a bank’s strategy and its risk framework. To assess the climate change-resilience of a bank’s strategy, a logical first step is to understand which climate change risks are material to the organization (e.g., by composing a materiality matrix). Subsequently, studying the transmission channels of these risks using scenario analysis and/or stress testing creates an understanding of what parts of the business model and lending portfolio are most exposed. This could lead to general changes in a bank’s positioning, but these risks should also be factored into the bank’s existing risk framework. Examples are the loan origination process, capital calculations, and risk reporting.
Engaging with clients
A fourth step in the game plan to successfully support the transition is for a bank to actively engage with its clients. A dialogue is required to align the bank’s GHG emission targets with those of its clients. This extends to discussing changes in the operations and/or business model of a client to align with a sustainable economy. This also may include timely announcing that certain economic activities will no longer be financed, and by financing client’s initiatives to mitigate or adapt to climate change: e.g., financing wind turbines for clients with energy- or carbon-intensive production processes (like cement or aluminium) or financing the move of production locations to less flood-prone areas.
Conclusion
Banks are uniquely positioned to play a pivotal role in the transition to a sustainable economy. The transition is already providing a wide range of opportunities for banks, from large financing needs to the introduction of green bonds and sustainability-linked derivatives. At the same time, it is of paramount importance for banks to adopt a climate change-resilient strategy and to integrate climate change risk into their risk frameworks. With our extensive track record in financial and non-financial risk management at financial institutions, Zanders stands ready to support you with this ambitious, yet rewarding challenge.
ESG risk management and Zanders
Zanders is currently supporting several clients with the identification, measurement, and management of ESG risks. For a start, we are supporting a large Dutch bank with the identification of ESG risk factors that have a material impact on the credit risk profile of its portfolio of corporate loans. The material risk factors are then integrated in the bank’s existing credit risk framework to ensure a proper management of this new risk type.
We are supporting other banking clients with the quantification of climate change risk. In one case, we are determining climate change risk-adjusted Probabilities of Default (PDs). Using expected future emissions and carbon prices based on the climate change scenarios of the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS), company specific shocks based on carbon prices and country specific shocks on GDP level are determined. These shocked levels are then used to determine the impact on the forecasted PDs. In another case, we are investigating the potential impact of floods and droughts on the collateral value of a portfolio of residential mortgage loans.
We also gained experience with the data challenges involved in the typical ESG project: e.g., we are supporting an asset manager with integrating and harmonizing ESG data from a range of vendors, which is underlying their internally developed ESG scores. We also support them with embedding these scores in the investment process.
With our extensive track record in financial and non-financial risk management at financial institutions in general, and our more recent ESG experience, Zanders stands ready to support you with the ambitious, yet rewarding challenge to adopt a climate change-resilient strategy and to integrate climate change risk in your existing risk frameworks.
Foot notes:
1 The IPCC Working Group II contribution: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability.
2 The IEA report, Net Zero by 2050.
3 See the Net Zero Financing roadmaps from the UN, ‘Race to Zero’ and the ‘Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero’ (GFANZ).
4 Based on the statistics of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) per 2021-Q3.
5 The Climate Bonds Initiative’s Sustainable Debt Highlights H1 2021.
Payment flow security at Royal FloraHolland

The corporate landscape is being redefined by a plethora of factors, from new business models and changing regulations to increased competition from digital natives and the acceleration of the consumer digital-first mindset.
With a complex landscape consisting of two SAP systems and several banks, the choice was made to implement SWIFT’s Alliance Lite 2 functionality.
This new standardized approach to bank connectivity has enabled Royal FloraHolland to connect with new banks, and in addition, the embedded payment approval workflow within AL2 provides the opportunity for Royal FloraHolland to carry out a final control before releasing payment and collection files to their partner banks. Unfortunately, this final control process was highly dependent on manual activities, where files were retrieved from folders within SAP environments and subsequently uploaded into AL2. Despite these payment and collection files being authorized after being uploaded into AL2, the fact that they are downloaded to a user’s personal desktop has always been a risk from an audit and control perspective. Royal FloraHolland wanted to mitigate the risk of human error and remove the vulnerability of the files in transit.
Considerations
After carrying out a short assessment of available solutions on the market, ranging from payment hub providers to full blown SWIFT Service Bureaus, Royal FloraHolland decided to explore options towards developing a solution in house. This was motivated by the fact that Royal FloraHolland had already invested in a generic bank connectivity solution. Their requirements were simple; namely that payment and collection files must be transferred to AL2 in a secure manner without any human intervention. In this context, the minimum security requirements must not allow following:
- Files to be manipulated in the transit between SAP and AL2
- The injection of files from sources other than the (production) SAP system
Solution
SWIFT Autoclient is a SWIFT solution that allows clients to automatically upload/download files to/from AL2. Royal FloraHolland was already using Autoclient to automatically download their bank statements from AL2, however they were not currently leveraging on the automatic file upload capabilities offered by Autoclient. When using the upload functionality, there are a few things that should be considered.
Firstly, it is important to consider the vulnerability of files in transit. Autoclient uploads files automatically to SWIFT AL2 once they are placed in the configured source directory. To avoid the risk of processing files that have either been manipulated or have originated from a non-trusted source system, Autoclient offers the option to secure files using LAU (Local Authentication). This method ensures a secure transfer of (payment) files between backend applications and Autoclient by calculating an electronic signature over the file. This signature is then transferred together with the file to Autoclient and verified. Only files that have been successfully verified will be transferred into AL2. This method requires a symmetric key infrastructure, whereby the secret key used to calculate the electronic signature is the same key used to verify the signature, meaning there is a requirement to maintain the secret key in both the source (SAP) application and in Autoclient. Since this deviates from SAP standard functionality, a bespoke development was required, alongside the additional logic to calculate the LAU signature.
Secondly, the routing of outgoing payment files needs to be managed. When uploading payment files to AL2 there is a requirement to transfer the relevant parameters for FileAct traffic. Normally, this can be achieved by using the Autoclient configuration options, however, when using LAU, SWIFT recommends its customers to provide the FileAct parameters together with a payment file. To fulfil this requirement a transaction was built in SAP to maintain these parameters. A clear advantage of this transaction is that the connection to new partner banks can now be managed fully via configuration in the SAP systems. There is no immediate requirement for further updates in Autoclient or AL2 as the parameter files supplied already contain all required routing information.
A third hurdle to overcome is the approval workflow within AL2. By default, AL2 will deliver files that are uploaded via Autoclient directly to partner banks. Any verification and authorization steps in AL2 will be bypassed. Royal FloraHolland wanted an additional authentication workflow to be active in AL2, which included files uploaded via Autoclient. As this requirement deviates from the standard functionality offered by AL2, a change request was raised to SWIFT, who developed and implemented this logic.
Implementation
The new solution was developed such that there was no impact on the existing file transfer process. This allowed Royal FloraHolland to perform a dry run in the production system using a limited number of payments, to ensure that the new solution is working as designed.
Conclusion
Royal FloraHolland is now running their payments and collections in an automated way. Not only has this reduced the workload burden for the AP department but has increased confidence that payments arriving in AL2 are from a trusted source.
Providing possible technical solutions for CLS in SAP Treasury

The corporate landscape is being redefined by a plethora of factors, from new business models and changing regulations to increased competition from digital natives and the acceleration of the consumer digital-first mindset.
The CLS system was established back in 2002 and since then, the FX market has grown significantly. Therefore, there is a high demand from corporates to leverage CLS to improve corporate treasury efficiency.
In this article we shed some light on the possible technical solutions in SAP Treasury to implement CLS in the corporate treasury operations. This includes CLS deal capture, limit utilization implications in Credit risk analyzer, and changes in the correspondence framework of SAP TRM.
Technical solution in SAP Treasury
There is no SAP standard solution for CLS as such. However, SAP standard functionality can be used to cover major parts of the CLS solution. The solution may vary depending on the existing functionality for hedge management/accounting and limit management as well as the technical landscape accounting for SAP version and SWIFT connectivity.
Below is a simplified workflow of CLS deal processing:
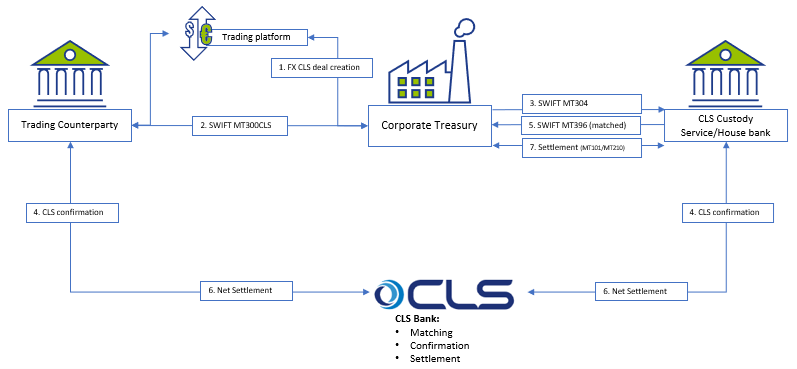
The proposed solution may be applicable for a corporate using SAP TRM (ECC to S/4HANA), having Credit risk analyzer activated and using SWIFT connection for connectivity with the banks.
Capturing CLS FX deals
There are a few options on how to register the FX deal as a CLS deal, with two described below:
Option 1: CLS Business partner – a replica of your usual business partner (BP) which would have CLS BIC code and complete settlement instructions.
Option 2: CLS FX product type/transaction type – a replica of normal FX SPOT, FX FORWARD or FX SWAP product type/transaction type.
Each option has pros and cons and may be applied as per a client technical specific.
FX deals trading and capturing may be executed via SAP Trade Platform Integration (TPI), which would improve the processing efficiency, but development may still be required depending on characteristics of the scope of FX dealing. In particular, the currency, product type, counterparty scope and volume of transactions would drive whether additional development is required, or whether standard mapping logic can be used to isolate CLS deals.
For the scenarios where a custom solution is required to convert standard FX deals into CLS FX deals during its creation, a custom program could be created that includes an additional mapping table to help SAP determine CLS eligible deals. The bespoke mapping table could help identify CLS eligibility based on the below characteristics:
- Counterparty
- Currency Pair
- Product Type (Spot, Forward, SWAP)
Correspondence framework
Once CLS deal is captured in SAP TRM, it needs to be counter-confirmed with the trading counterparty and with CLS Bank. Three new types of correspondence need to be configured:
- MT300 with CLS specifics to be used to communicate with the trading counterparty;
- MT304 to communicate with CLS Custody service;
- SWIFT MT396 to get the matching status from CLS bank.
Credit Risk Analyzer (CRA)
FX CLS deals do not bring settlement exposure, thus CLS deals need to be exempt from the settlement risk utilization. Configuration of the limit characteristics must include either business partner number (for CLS Business Partner) or transaction type (for CLS transaction type). This will help determine the limits without FX CLS deals.
No automatic limits creation should be allowed for the respective limit type; this will disable a settlement limit creation based on CLS deal capture in SAP.
CLS Business partner setting must be done with ‘parent <-> subsidiary’ relationship with the regular business partner. This is required to keep a single credit limit utilization and having FX deals being done with two business partners.
Deal execution
Accounting for CLS FX deals is normally the same as for regular FX deals, though it depends on the corporate requirements. We do not see any need for a separate FX unrealized result treatment for CLS deals.
However, settlement of CLS deals is different and standard settlement instructions of CLS deals vary from normal FX deals.
Either the bank’s virtual accounts or separate house bank accounts are opened to settle CLS FX deals.
Since CLS partner performs the net settlement on-behalf of a corporate there is no need to generate payment request for every CLS deal separately. Posting to the bank’s CLS clearing account with cash flow postings (TBB1) is sufficient at this level.
The following day the bank statement will clear the postings on the CLS settlement account on a net basis based on the total amount and posting date.
Cash Management
A liquidity manager needs to know the net result of the CLS deals in advance to replenish the CLS bank account in case the net settlement amount for CLS deal is negative. In addition, the funds would need to be transmitted between the house bank accounts either manually or automatically, with cash concentration requiring transparency on the projected cash position.
The solution may require extra settings in the cash management module with CLS bank accounts to be added to specific groupings.
Conclusion
Designing a CLS solution in SAP requires deep understanding of a client’s treasury operations, bank account structure and SAP TMS specifics. Together with a client and based on the unique business landscape, we review the pros and cons of possible solutions and help choosing the best one. Eventually we can design and implement a solution that makes treasury operations more efficient and transparent.
Our corporate clients are requesting our support with design and implementation of Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS) solutions for FX settlements in their SAP Treasury system. If you are interested, please do not hesitate to contact us.
SAP treasury reporting for the treasury executive

The corporate landscape is being redefined by a plethora of factors, from new business models and changing regulations to increased competition from digital natives and the acceleration of the consumer digital-first mindset.
Over recent years, SAP has added an array of products in the data warehousing, reporting and analytics space to assist decision-making as well as address some of the historical weaknesses in its reporting capabilities.
These more recent SAP tools focus on delivering key business drivers in the reporting space – such as agility, flexibility, independence from IT, data processing, intelligent analysis (using artificial intelligence), and data centralization – thereby addressing many of the previous frustrations that business users experienced with getting the necessary information out of their SAP systems to make sound business decisions. Previously, reporting within SAP was often limited, inflexible and required a reliance on IT to develop custom reports and/or data models. But with more options, choosing the most appropriate reporting landscape design can seem overwhelming to the treasury executive and it’s easy to get lost in the technical jargon.
The appropriate tool for your unique business design
When it comes to treasury analytics solutions offered by SAP, there are among others embedded Fiori analytical apps, SAP Analytics Cloud, BW4/HANA and the new Data Warehouse Cloud. It may be difficult to get a clear understanding of what each tool offers and for what purposes to use each. The question then is whether to invest in all tools or which one(s) to choose to meet our reporting needs. Additionally, there may be uncertainty too around what is offered to customers using SAP S/4HANA Cloud versus those customers who run SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition (and on premise deployments).
The answer about how to structure your SAP reporting architecture depends on your unique business design and reporting requirements, and more specifically what questions you need answered by your data. Here we will give a brief overview of the functionality of the main tools and what to consider when making system selection decisions. Note, the below information speaks more to customers who run the on-premise version of SAP S/4HANA, although we do mention what is offered on the cloud, where relevant.
SAP S/4HANA Fiori Analytical Apps
SAP S/4HANA Finance for treasury and risk management comes standard with analytical Fiori apps for daily reporting as well as Dashboard reporting. With your daily reporting apps, you will be able to display treasury position flows, analyze the treasury position, use the Cash Flow Analyzer as well as display the treasury posting journal. These apps assist the treasury executive to see the details and results of what has taken place over a given period within the organization. There are also currently four dashboard-type Fiori apps which give an overview of different key areas, namely Foreign Exchange Overview, Interest Rate Overview, Market Data Overview, and Bank Relationship Overview.
Without paying any additional license fees, the above apps give the treasury executive a great starting point with which to review current positions but may not be sufficient to provide the information you want to see and how you want to see it.
SAP Analytics Cloud
SAP Analytics Cloud is SAP’s solution for data visualization, offering business intelligence, planning and predictive analytics in a single solution for all modules, providing a broader, deeper and more flexible analysis of the organization’s operations than the embedded analytical Fiori apps can.
Although the SAP Analytics Cloud OEM version is delivered embedded into Treasury Management for SAP S/4HANA Cloud, customers with the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, or an on-premise version of Treasury Management will need an additional license to get access to SAP Analytics Cloud functionality. However, it is worth noting that this license is for the full-use SAP Analytics Cloud Enterprise edition, which comes with more features and functionalities than the embedded version.
In terms of Treasury Management, the Treasury Executive Dashboard is the main offering within SAP Analytics Cloud. This dashboard is based on a preconfigured data model that offers real-time insights into the treasury operations across eight tab strips. Areas that can be reported on are Liquidity, Cash management, Bank relationship, Indebtedness, Counterparty risk, Market risk, Bank guarantee and Market overview. The dashboard provides visual overviews of the underlying data and allows for drill-down to see the detail. Customizing the layout is also possible.
With the full-use Enterprise version of SAP Analytics Cloud, there is the possibility of creating more dashboards (called Stories) according to business reporting needs. Business Content is also delivered out the box with the full version which means the creation of new dashboards is accelerated as the groundwork has already been done by SAP or one of their business partners.
Another feature of SAP Analytics Cloud worth mentioning is its predictive capabilities. Historical data is analyzed to identify trends and patterns, and these are then used to predict a potential future outcome, further adding to the tools at the executive’s disposal.
SAP Analytics Cloud is designed to be set up and used by the business user with minimal IT intervention. Dashboards are responsive and user-friendly, with a large degree of flexibility in terms of layout and design.
SAP BW/4HANA
SAP BW/4HANA is SAP’s next generation data warehousing solution designed to run exclusively on the SAP HANA database. The key areas of focus for SAP BW∕4HANA are data modelling, data procurement, analysis and planning. An SAP customer needs to license this product and it runs on a separate instance.
SAP BW/4HANA is not an upgrade of SAP BW but a widely rewritten solution designed to reduce complexity and effort around data warehousing as well as increasing speed and agility, offering advanced UIs.
Data from multiple sources across the enterprise can be imported and stored centrally in the SAP BW∕4HANA Enterprise Data Warehouse. This data can be transformed and cleaned up, ready for analysis. SAP BW/4HANA provides a single source of truth, handling large data volumes at speed for complex organizations. SAP BW/4HANA has been designed to create reports on current, historical, and external data from multiple SAP and non-SAP sources. The data modeling capabilities are also much more powerful than SAP Analytics Cloud offers as a standalone solution.
A note here that SAP has recently released the Data Warehouse Cloud. This is intended as a data warehousing solution for SAP S/4HANA Cloud customers and is not seen as a direct replacement for BW/4HANA. However, the approaches for supporting Self-Service BI, the “SAP BW Bridge capabilities”, or the inclusion of CDS views from SAP S/4HANA make it a good candidate for a hybrid approach at least.
Selecting the right solution
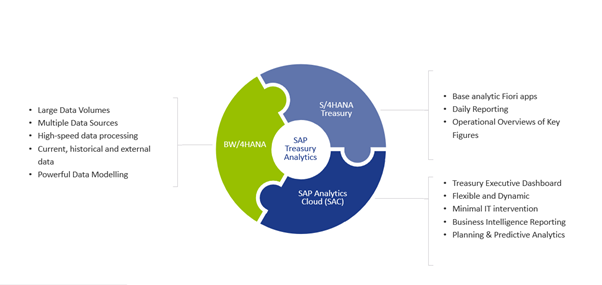
SAP believes that there are four main drivers of the value of data – Span (data from anywhere), Volume (data of any size), Quality (data of any kind) and Usage (data for anyone). They have focused on ensuring that value is maximized for organizations by offering solutions for each driver. The SAP HANA database ensures that a vast volume of data can be handled at high speed, SAP BW/4HANA has been designed so that high volumes of data of any kind can be consolidated for analysis and SAP Analytics Cloud delivers a single solution for visual, easy-to-use analytics across the business.
Customers that have SAP S/4HANA Treasury in their on-premise deployment with minimal data sources could supplement their SAP S/4HANA Treasury system with SAP Analytics Cloud alone. This is ideal when the main reporting needs are operational and real-time and would allow treasury executives to easily access the information they need to optimize their portfolios for liquidity and risk, giving them the additional flexibility and ability to design required reports.
Where the data volumes are large and from a diverse range of sources, a combination of SAP BW4/HANA and SAP Analytics Cloud could be better. The latter has been optimized to work with SAP BW/4HANA as a source and this allows customers to get the powerful, interactive visualizations of SAP Analytics Cloud using the immense data volume capabilities of SAP BW/4HANA. Together, these two products, alongside your SAP S/4HANA Treasury system, give up-to-date, broad, easy-to-read information at a glance to ensure the treasury executive can be proactive and responsive, making the best possible decisions around liquidity, funding and risk management across the entire enterprise. SAP BW4/HANA can of course be implemented without SAP Analytics Cloud, as other BI tools can be used, but the advantages of SAP Analytics Cloud are the highly visual design, flexibility and most importantly not needing to rely on IT to design reports.
To conclude
Knowing what your options are and which would suit your current and future system landscapes is where Zanders can come in, providing sound guidance and ensuring you are able to make the most of any investment to analyze data and make decisions. We can assist treasury executives by ensuring the customer has the right mix of reporting solutions, weighing up total cost of ownership against the data reporting requirements of the organization.
Providing possible technical solutions for CLS in SAP Treasury

Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS) is an established global system to mitigate settlement risks for FX trades, improving corporate cash and liquidity management among other benefits. The CLS system was established back in 2002 and since then, the FX market has grown significantly. Therefore, there is a high demand from corporates to leverage CLS to improve corporate treasury efficiency.
In this article we shed some light on the possible technical solutions in SAP Treasury to implement CLS in the corporate treasury operations. This includes CLS deal capture, limit utilization implications in Credit risk analyzer, and changes in the correspondence framework of SAP TRM.
Technical solution in SAP Treasury
There is no SAP standard solution for CLS as such. However, SAP standard functionality can be used to cover major parts of the CLS solution. The solution may vary depending on the existing functionality for hedge management/accounting and limit management as well as the technical landscape accounting for SAP version and SWIFT connectivity.
Below is a simplified workflow of CLS deal processing:
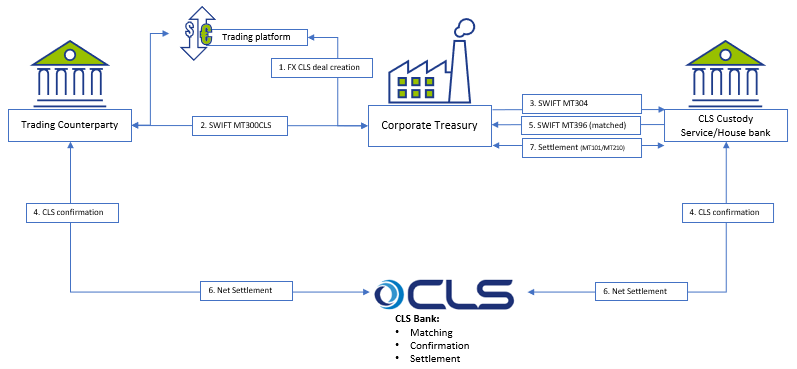
The proposed solution may be applicable for a corporate using SAP TRM (ECC to S/4HANA), having Credit risk analyzer activated and using SWIFT connection for connectivity with the banks.
Capturing CLS FX deals
There are a few options on how to register the FX deal as a CLS deal, with two described below:
Option 1: CLS Business partner – a replica of your usual business partner (BP) which would have CLS BIC code and complete settlement instructions.
Option 2: CLS FX product type/transaction type – a replica of normal FX SPOT, FX FORWARD or FX SWAP product type/transaction type.
Each option has pros and cons and may be applied as per a client technical specific.
FX deals trading and capturing may be executed via SAP Trade Platform Integration (TPI), which would improve the processing efficiency, but development may still be required depending on characteristics of the scope of FX dealing. In particular, the currency, product type, counterparty scope and volume of transactions would drive whether additional development is required, or whether standard mapping logic can be used to isolate CLS deals.
For the scenarios where a custom solution is required to convert standard FX deals into CLS FX deals during its creation, a custom program could be created that includes an additional mapping table to help SAP determine CLS eligible deals. The bespoke mapping table could help identify CLS eligibility based on the below characteristics:
- Counterparty
- Currency Pair
- Product Type (Spot, Forward, SWAP)
Correspondence framework
Once CLS deal is captured in SAP TRM, it needs to be counter-confirmed with the trading counterparty and with CLS Bank. Three new types of correspondence need to be configured:
- MT300 with CLS specifics to be used to communicate with the trading counterparty;
- MT304 to communicate with CLS Custody service;
- SWIFT MT396 to get the matching status from CLS bank.
Credit Risk Analyzer (CRA)
FX CLS deals do not bring settlement exposure, thus CLS deals need to be exempt from the settlement risk utilization. Configuration of the limit characteristics must include either business partner number (for CLS Business Partner) or transaction type (for CLS transaction type). This will help determine the limits without FX CLS deals.
No automatic limits creation should be allowed for the respective limit type; this will disable a settlement limit creation based on CLS deal capture in SAP.
CLS Business partner setting must be done with ‘parent <-> subsidiary’ relationship with the regular business partner. This is required to keep a single credit limit utilization and having FX deals being done with two business partners.
Deal execution
Accounting for CLS FX deals is normally the same as for regular FX deals, though it depends on the corporate requirements. We do not see any need for a separate FX unrealized result treatment for CLS deals.
However, settlement of CLS deals is different and standard settlement instructions of CLS deals vary from normal FX deals.
Either the bank’s virtual accounts or separate house bank accounts are opened to settle CLS FX deals.
Since CLS partner performs the net settlement on-behalf of a corporate there is no need to generate payment request for every CLS deal separately. Posting to the bank’s CLS clearing account with cash flow postings (TBB1) is sufficient at this level.
The following day the bank statement will clear the postings on the CLS settlement account on a net basis based on the total amount and posting date.
Cash Management
A liquidity manager needs to know the net result of the CLS deals in advance to replenish the CLS bank account in case the net settlement amount for CLS deal is negative. In addition, the funds would need to be transmitted between the house bank accounts either manually or automatically, with cash concentration requiring transparency on the projected cash position.
The solution may require extra settings in the cash management module with CLS bank accounts to be added to specific groupings.
Conclusion
Designing a CLS solution in SAP requires deep understanding of a client’s treasury operations, bank account structure and SAP TMS specifics. Together with a client and based on the unique business landscape, we review the pros and cons of possible solutions and help choosing the best one. Eventually we can design and implement a solution that makes treasury operations more efficient and transparent.
Our corporate clients are requesting our support with design and implementation of Continuous Linked Settlement (CLS) solutions for FX settlements in their SAP Treasury system. If you are interested, please do not hesitate to contact us.
A roadmap to becoming a data-driven organization

Developing a data strategy depends on using the various types of payment, market, cashflow, bank and risk data available to a treasury, and then considering the time implications of past historical data, present and future models, to better inform decision-making. We provide a roadmap and ‘how to’ guide to becoming a data-driven organization.
Why does this aim matter? Well, in this age of digitization, almost every aspect of the business has a digital footprint. Some significantly more than the others. This presents a unique opportunity where potentially all information can be reliably processed to take tactical and strategic decisions from a position of knowledge. Good data can facilitate hedging, forecasting and other key corporate activities. Having said all that, care must also be taken to not drown in the data lake1 and become over-burdened with useless information. Take the example of Amazon in 2006 when it reported that cross-selling attributed for 35% of their revenue2. This strategy looked at data from shopping carts and recommended other items that may be of interest to the consumer. The uplift in sales was achieved only because Amazon made the best use of their data.
Treasury is no exception. It too can become data-driven thanks to its access to multiple functions and information flows. There are numerous ways to access and assess multiple sets of data (see Figure 1), thereby finding solutions to some of the perennial problems facing any organization that wants to mitigate or harness risk, study behavior, or optimize its finances and cashflow to better shape its future.
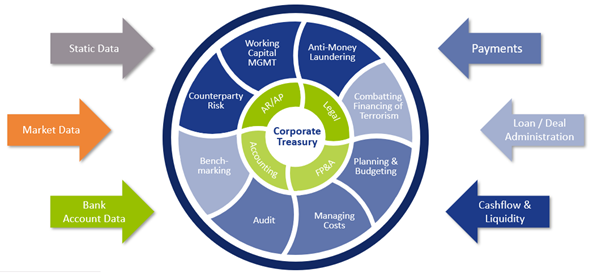
Time is money
The practical business use cases that can be realized by harnessing data in the Treasury often revolve around mastering the time function. Cash optimization, pooling for interest and so on often depend on a good understanding of time – even risk hedging strategies can depend on the seasons, for instance, if we’re talking about energy usage.
When we look at the same set of data from a time perspective, it can be used for three different purposes:
I. Understand the ‘The Past’ – to determine what transpired,
II. Ascertain ‘The Present’ situation,
III. Predict ‘The Future’ based on probable scenarios and business projections.
I – The Past
“Study the past if you would define the future”
Confucius
The data in an organization is the undeniable proof of what transpired in the past. This fact makes it ideal to perform analysis through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), perform statistical analysis on bank wallet distribution & fee costs, and it can also help to find the root cause of any irregularities in the payments arena. Harnessing historical data can also positively impact hedging strategies.
II – The Present
“The future depends on what we do in the present”
M Gandhi
Data when analyzed in real-time can keep stakeholders updated and more importantly provide a substantial basis for taking better informed tactical decisions. Things like exposure, limits & exceptions management, intra-day cash visibility or near real-time insight/access to global cash positions all benefit, as does payment statuses which are particularly important for day-to-day treasury operations.
III – The Future
“The best way to predict the future is to create it.”
Abraham Lincoln
There are various areas where an organization would like to know how it would perform under changing conditions. Simulating outcomes and running future probable scenarios can help firms prepare better for the near and long-term future.
These forecast analyses broadly fall under two categories:
Historical data: assumes that history repeats itself. Predictive analytics on forecast models therefore deliver results.
Probabilistic modelling: this creates scenarios for the future based on the best available knowledge in the present.
Some of the more standard uses of forecasting capabilities include:
- risk scenarios analysis,
- sensitivity analysis,
- stress testing,
- analysis of tax implications on cash management structures across countries,
- & collateral management based on predictive cash forecasting, adjusted for different currencies.
Working capital forecasting is also relevant, but has typically been a complex process. The predication accuracy can be improved by analyzing historical trends and business projections of variables like receivables, liabilities, payments, collections, sales, and so on. These can feed the forecasting algorithms. In conjunction with analysis of cash requirements in each business through studying the trends in key variables like balances, intercompany payments and receipts, variance between forecasts and actuals, this approach can lead to more accurate working capital management.
How to become a data-driven organization
“Data is a precious thing and will last longer than the systems themselves.”
Tim Berners-Lee
There can be many uses of data. Some may not be linked directly to the workings of the treasury or may not even have immediate tangible benefits, although they might in the future for comparative purposes. That is why data is like a gold mine that is waiting to be explored. However, accessing it and making it usable is a challenging proposition. It needs a roadmap.
The most important thing that can be done in the beginning is to perform a gap analysis of the data ecosystem in an organization and to develop a data strategy, which would embed importance of data into the organization’s culture. This would then act as a catalyst for treasury and organizational transformation to reach the target state of being data-driven.
The below roadmap offers a path to corporates that want to consistently make the best use of one of their most critical and under-appreciated resources – namely, data.
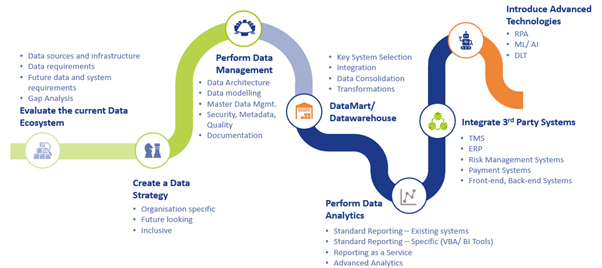
We have seen examples like Amazon and countless others where organizations have become data- driven and are reaping the benefits. The same can be said about some of the best treasury departments we at Zanders have interacted with. They are already creating substantial value by analyzing and making the optimum use of their digital footprint. The best part is that they are still on their journey to find better uses of data and have never stopped innovating.
The only thing that one should be asking now is: “Do we have opportunities to look at our digital footprint and create value (like Amazon did), and how soon can we act on it?”
References:
ESG-related derivatives: innovation or fad?

Next to sustainable funding instruments, including both green and social, we also see that these KPI’s can be used for other financial instruments, such as ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) derivatives. These derivatives are a useful tool to further drive the corporate sustainability strategy or support meeting environmental targets.
Since the first sustainability-linked derivative was executed in 2019, market participants have entered into a variety of ESG-related derivatives and products. In this article we provide you with an overview of the different ESG derivatives. We will touch upon the regulatory and valuation implications of this relatively new derivative class in a subsequent article, which will be published later this year.
Types of ESG-related derivatives products
Driven by regulatory pressure and public scrutiny, corporates have been increasingly looking for ways to manage their sustainability footprint. As a result of a blooming ESG funding market, the role of derivatives to help meet sustainability goals has grown. ESG-related derivatives cover a broad spectrum of derivative products such as forwards, futures and swaps. Five types (see figure 1) of derivatives related to ESG can be identified; of which three are currently deemed most relevant from an ESG perspective.
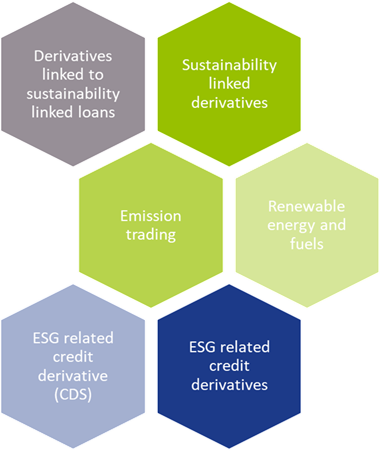
The first category consists of traditional derivatives such as interest rate swaps or cross currency swaps that are linked to a sustainable funding instrument. The derivative as such does not contain a sustainability element.
Sustainability-linked derivatives
Sustainability-linked derivatives are agreements between two counterparties (let’s assume a bank and a corporate) which contain a commitment of the corporate counterparty to achieve specific sustainability performance targets. When the sustainability performance targets are met by the corporate during the lifetime of the derivative, a discount is applied by the bank to the hedging instrument. When the targets are not met, a premium is added. Usually, banks invest the premium they receive in sustainable projects or investments. Sustainability-linked derivative transactions are highly customizable and use tailor-made KPIs to determine sustainability goals. Sustainability-linked derivatives provide market participants with a financial incentive to improve their ESG performance. An example is Enel’s sustainability-linked cross currency swap, which was executed in July 2021 to hedge their USD/EUR exchange rate and interest rate exposures.
Emission trading derivatives
Other ESG-related derivatives support meeting sustainable business models and consist of trading carbon offsets, emission trading derivatives, and renewable energy and renewable fuels derivatives, amongst others. Contrary to sustainability-linked derivatives, the use of proceeds of ESG-related derivatives are allocated to specific ESG-related purposes. For example, emissions trading is a market-based approach to reduce pollution by setting a (geographical) limit on the amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted. It consists of a limit or cap on pollution and tradable instruments that authorize holders to emit a specific quantity of the respective greenhouse gas. Market participants can trade derivatives based on emission allowances on exchanges or OTC markets as spots, forwards, futures and option contracts. The market consists of mandatory compliance schemes and voluntary emission reduction programs.
Renewable energy and fuel derivatives
Another type of ESG-related derivatives are renewable energy and renewable fuel hedging transactions, which are a valuable tool for market participants to hedge risks associated with fluctuations in renewable energy production. These ESG-related credit derivatives encourage more capital to be contributed to renewable energy projects. Examples are Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) futures, wind index futures and low carbon fuel standard futures.
ESG related credit derivatives
ESG-related CDS products can be used to manage the credit risk of a counterparty when financial results may be impacted by climate change or, more indirectly, if results are affected due to substitution of a specific product/service. An example of this could be in the airline industry where short-haul flights may be replaced by train travel. Popularity of ESG-related CDS products will probably increase with the rising perception that companies with high ESG ratings exhibit low credit risk.
Catastrophe and weather derivatives
Catastrophe and weather derivatives are insurance-like products as well. Both markets have existed for several decades and are used to hedge exposures to weather or natural disasters. Catastrophe derivatives are financial instruments that allow for transferral of natural disaster risk between market participants. These derivatives are traded on OTC markets and enable protection from enormous potential losses following from natural disasters such as earthquakes to be obtained. The World Bank has designed catastrophe swaps that support the transfer of risks related to natural disasters by emerging countries to capital markets. An example if this is the swap issued for the Philippines in 2017. Weather derivatives are financial instruments that derive their value from weather-related factors such as temperature and wind. There derivatives are used to mitigate risks associated with adverse or unexpected weather conditions and are most commonly used in the food and agriculture industry.
What’s old, what’s new and what’s next?
ESG-related credit derivatives would be best applied by organizations with credit exposures to certain industries and financial institutions. Despite the link to an environmental element, we do not consider catastrophe bonds and weather derivatives as a sustainability-linked derivative. Neither is it an innovative, new product that is applicable to corporates in various sectors.
Truly innovative products are sustainability-linked derivatives, voluntary emissions trading and renewable energy and fuel derivatives. These products strengthen a corporate’s commitment to meet sustainability targets or support investments in sustainable initiatives. A lack of sustainability regulation for derivatives raises the question to what extent these innovative products are sustainable on their own? An explicit incentive for financial institutions to execute ESG-related derivatives, such as a capital relief, is currently absent. This implies that any price advantage will be driven by supply and demand.
Corporate Treasury should ensure they consider the implications of using ESG-related derivatives that affect the cashflows of derivatives transactions. Examples of possible regulatory obligations consist of valuation requirements, dispute resolution and reporting requirements. Since ESG-related derivatives and products are here to stay, Zanders recommends that corporate treasurers closely monitor the added value of specific instruments, as well as the regulatory, tax and accounting implications. Part II of this series, later in the year, will focus on the regulatory and valuation implications of this relatively new derivative class.
For more information on ESG issues, please contact Sander van Tol.
EBA’s binding standards on Pillar 3 disclosures on ESG risks

This publication fits nicely into the ‘horizon priority’ of the EBA1 to provide tools to banks to measure and manage ESG-related risks. In this article we present a brief overview of the way the ITS have been developed, what qualitative and quantitative disclosures are required, what timelines and transitional measures apply – and where the largest challenges arise. By requiring banks to disclose information on their exposure to ESG-related risks and the actions they take to mitigate those risks – for example by supporting their clients and counterparties in the adaptation process – the EBA wants to contribute to a transition to a more sustainable economy. The Pillar 3 disclosure requirements apply to large institutions with securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state.
In an earlier report2, the EBA defined ESG-related risks as “the risks of any negative financial impact on the institution stemming from the current or prospective impacts of ESG factors on its counterparties or invested assets”. Hence, the focus is not on the direct impact of ESG factors on the institution, but on the indirect impact through the exposure of counterparties and invested assets to ESG-related risks. The EBA report also provides examples for typical ESG-related factors.
While the ITS have been streamlined and simplified compared to the consultation paper published in March 2021, there are plenty of challenges remaining for banks to implement these standards.
Development of the ITS
The EBA has been mandated to develop the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks in Article 434a of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The EBA has opted for a sequential approach, with an initial focus on climate change-related risks. This is further narrowed down by only considering the banking book. The short maturity and fast revolving positions in the trading book are out of scope for now. The scope of the ITS will be extended to included other environmental risks (like loss of biodiversity), and social and governance risks, in later stages.
In the development of the ITS, the EBA has strived for alignment with several other regulations and initiatives on climate-related disclosures that apply to banks. The most notable ones are listed below (and in Figure 1):
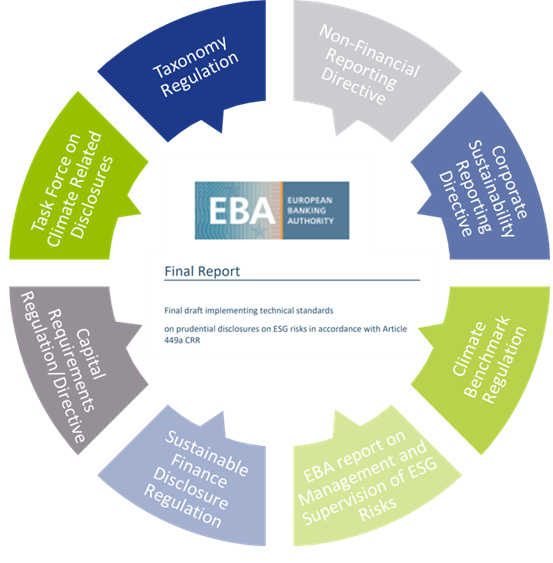
Figure 1 – Overview of related regulations and initiatives considered in the development of the ITS
- Capital Requirements Directive and Regulation (CRD and CRR): article 98(8) of the CRD3 mandated the EBA to publish the EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks, which includes the split of climate change-related risks in physical and transition risks. Article 434a of the CRR4 mandated the EBA to develop the draft ITS to specify the ESG disclosure requirements described in article 449a.
- EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks2: the report provides common definitions of ESG risks and contains proposals on how to include ESG risks in the risk frameworks of banks, covering its identification, assessment, and management. It also discusses the way to include ESG risks in the supervisory review process.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)5: the Financial Stability Board’s TFCD has published recommendations on climate-related disclosures. The metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) included in the ITS have been aligned with the TCFD recommendations.
- Taxonomy Regulation6: the European Union’s common classification system of environmentally sustainable economic activities is underpinning the main KPIs introduced in the ITS.
- Climate Benchmark Regulation (CBR)7: In the CBR, two types of climate benchmarks were introduced (‘EU Climate Transition’ and ‘EU Paris-aligned’ benchmarks) and ESG disclosures for all other benchmarks (excluding interest rate and currency benchmarks) were required.
- Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD)8: the NFRD introduces ESG disclosure obligations for large companies, which include climate-related information.
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)9: a proposal by the European Commission to extend the scope of the NFRD to also include all companies listed on regulated markets (except listed micro-enterprises). One of the ITS’s KPIs, the Green Asset Ratio (GAR) is directly linked to the scope of the NFRD/CSRD.
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)10: the SFDR lays down sustainability disclosure obligations for manufacturers of financial products and financial advisers towards end-investors. It applies to banks that provide portfolio management investment advice services.
Compared to the consultation paper for the ITS, several changes have been made to the required templates. Some templates have been combined (e.g., templates #1 and #2 from the consultation paper have been combined into template #1 of the final draft ITS) and several templates have been reorganized and trimmed down (e.g., the requirement to report exposures to top EU or top national polluters has been removed).
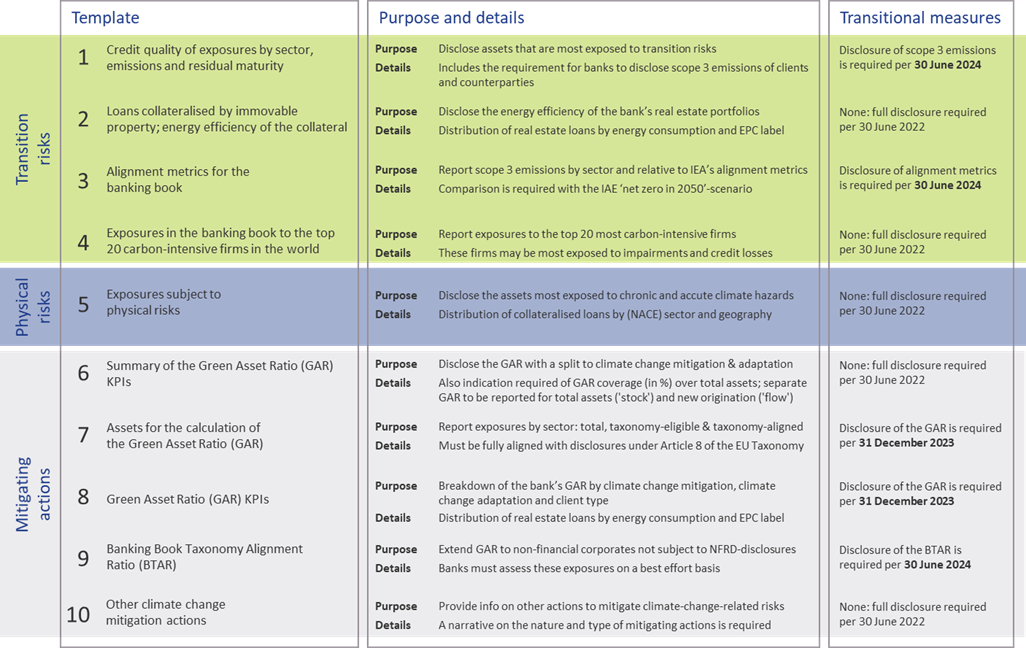
Quantitative disclosures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks introduce ten templates on quantitative disclosures. These can be grouped in four templates on transition risks, one on physical risks, and five on mitigating actions:
- Transition risks
Two of the required templates are relatively straightforward. Banks need to report the energy efficiency of real estate collateral in the loan portfolio (#2) and report their aggregate exposure to the top 20 of the most carbon-intensive firms in the world (#4).
The main challenge for banks though will be in completing the other two templates:- Template #1 requires banks to disclose the gross carrying amount of loans and advances provided to non-financial corporates, classified by NACE sector codes and residual maturities. It is also required to report on the counterparties’ scope 1, 2, and 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Reflecting the challenge in reporting on scope 3 emissions, a transitional measure is in place. Full reporting needs to be in place by June 2024. Until then, banks need to report their available estimates (if any) and explain the methodologies and data sources they intend to use.
- In the last template (#3), banks also need to report scope 3 emissions, but relate these to the alignment metrics defined by the International Energy Agency (IEA) for the ‘net zero by 2050’ scenario. For this scenario, a target for a CO2 intensity metric is defined for 2030. By calculating the distance to this target, it becomes clear how banks are progressing (over time) towards supporting a sustainable economy. A similar transitional measure applies as for template #1.
- Physical risks
In template #5, banks are required to disclose how their banking book positions are exposed to physical risks, i.e., “chronic and acute climate-related hazards”. The exposures need to be reported by residual maturity and by NACE sector codes and should reflect exposure to risks like heat waves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. Specialized databases need to be consulted to compile a detailed understanding of these exposures. To support their submissions, banks further need to compile a narrative that explains the methodologies they used. - Mitigating actions
The final set of templates covers quantitative information on the actions a bank takes to mitigate or adapt to climate change risks.- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
- In template #7, banks need to report the outstanding banking book exposures to different types of clients/issuers, as well as the amount of these exposures that are taxonomy-eligible (that is, to sectors included in the EU Taxonomy) and taxonomy-aligned (that is, taxonomy-eligible exposures financing activities that contribute to climate change mitigation or adaptation). Based on this information, the bank’s GAR can be determined.
- In template #8, a GAR needs to be reported for the exposures to each type of client/issuer distinguished in template #7, with a distinction between a GAR for the full outstanding stock of exposures per client/issuer type, and a GAR for newly originated (‘flow’) exposures.
- Template #6 contains a summary of the GARs from templates #7 and #8.
In these templates, the numerator of the GAR only includes exposures to non-financial corporations that are required to publish non-financial information under the NFRD. Any exposures to other corporate counterparties therefore are considered 0% Taxonomy-aligned.
- The main challenge in this group of templates is in template #9. To incentivize banks to support all of their counterparties to transition to a more sustainable business model, and to collect ESG data on these counterparties, the EBA introduces the Banking Book Taxonomy Alignment Ratio (BTAR). In this metric, the numerator does include the exposures to counterparties that are not subject to NFRD disclosure obligations. The BTAR ratios obtained from the information in template #9 therefore complement the GAR ratios obtained in templates #7 and #8.
- In the final template (#10), banks have the opportunity to include any other climate change mitigating actions that are not covered by the EU Taxonomy. They can for example report on their use of green or sustainable bonds and loans.
- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
An overview of the templates for quantitative disclosures in presented in Figure 2.
Qualitative disclosures
In the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks, three tables are included for qualitative disclosures. The EBA has aligned these tables with their Report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks11. The three tables are set up for qualitative information on environmental, social, and governance risks, respectively. For each of these topics, banks need to address three aspects: on business strategy and processes, governance, and risk management. An overview of the required disclosures is presented in Figure 3.
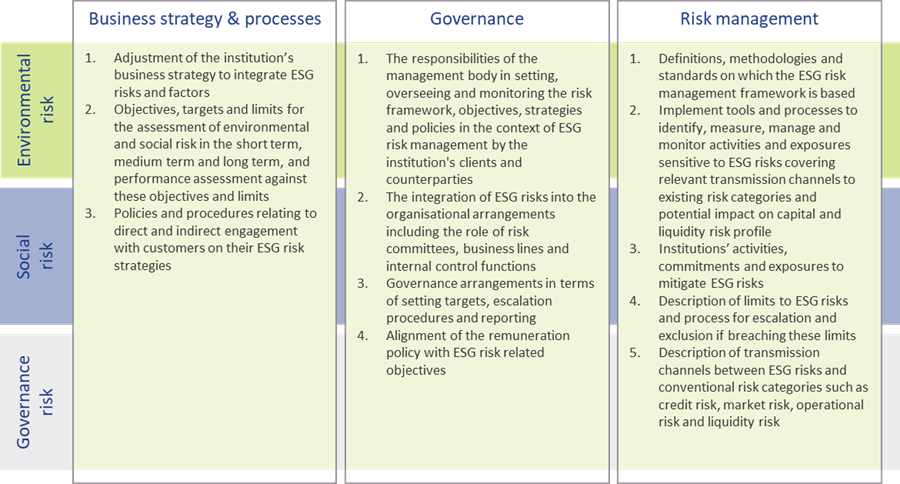
Figure 3 – Overview of qualitative ESG disclosures (based on templates & section 2.3.2 of the EBA ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks)
Timelines and transitional measures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks become effective per 30 June 2022 for large institutions that have securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state. A semi-annual disclosure is required, but the first disclosure is annual. Consequently, based on 31 December 2022 data, the first reporting will take place in the first quarter of 2023.
The EBA has introduced a number of transitional measures. These can be summarized as follows:
- The reporting of information on the GAR is only required as of 31 December 2023.
- The reporting of information on the BTAR, the bank’s financed scope 3 emissions, and the alignment metrics is only required as of June 2024.
The EBA has further indicated in the ITS that they will conduct a review of the ITS’s requirements during 2024. They may then also extend the ITS with other environmental risks (other than the climate change-related risks in the current version). The EU Taxonomy is expected to cover a broader range of environmental risks by the end of 2022. Sometime after 2024, it is expected that the EBA will further extend the ITS by including disclosure requirements on social and governance risks.
An overview of the main timelines and transitional measures is presented in Figure 4.
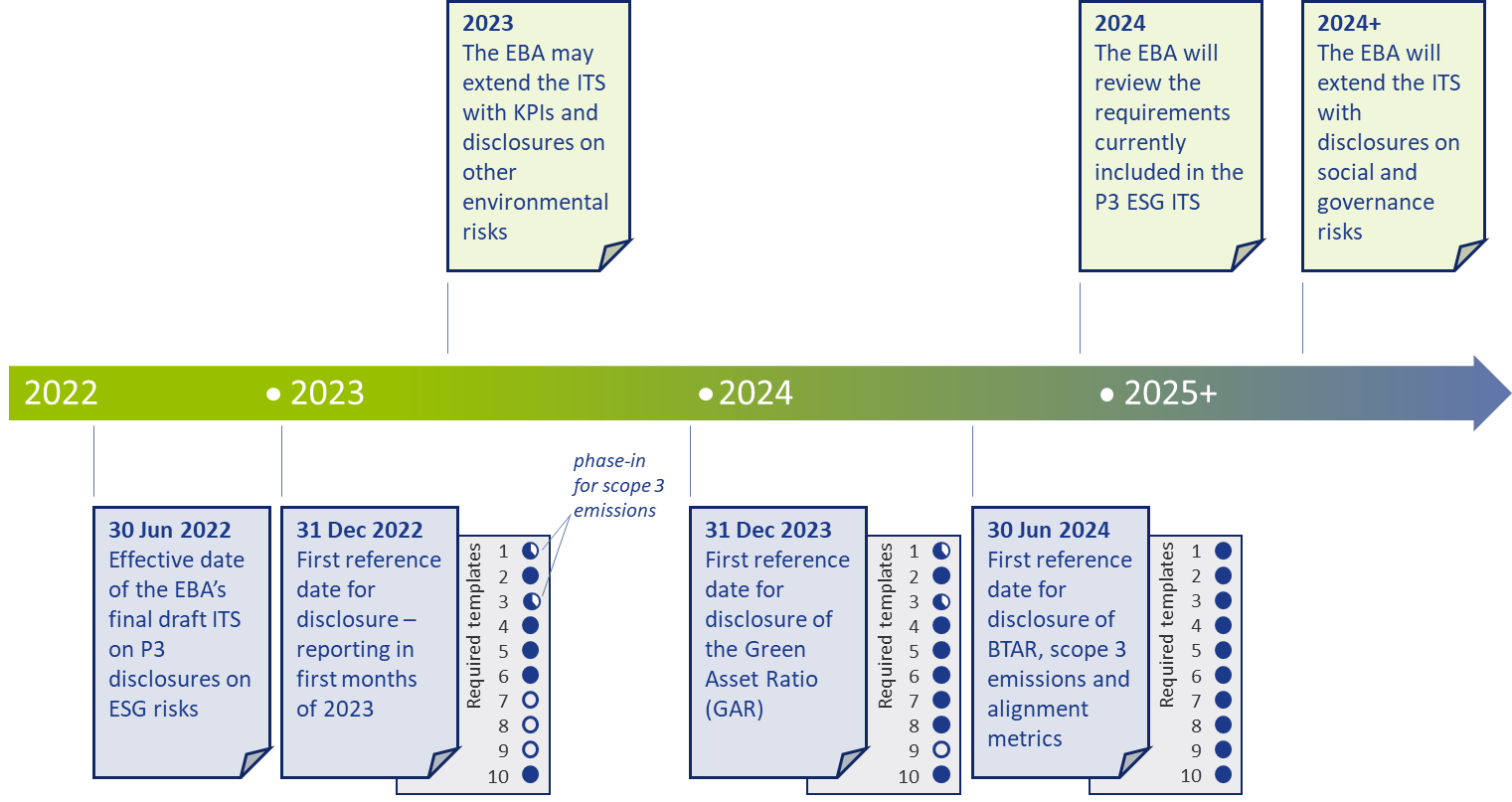
Figure 4 – Overview of the main timelines and transitional measures for the ESG disclosures
Conclusion
Society, and consequently banks too, are increasingly facing risks stemming from changes in our climate. In recent years, supervisory authorities have stepped up by introducing more and more guidance and regulation to create transparency about climate change risk, and more broadly ESG risks. The publication of the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks by the EBA marks an important milestone. It offers banks the opportunity to disseminate a constructive and positive role in the transition to a sustainable economy.
Nonetheless, implementing the disclosure requirements will be a challenge. Developing detailed assessments of the physical risks to which their asset portfolio is exposed and to estimate the scope 3 emissions of their clients and counterparties (‘financed emissions’) will not be straightforward. For their largest counterparties, banks will be able to profit from the NFRD disclosure obligations, but especially in Europe a bank’s portfolio typically has many exposures to small- and medium-sized enterprises. Meeting the disclosure requirements introduced by the EBA will require timely and intensive discussions with a substantial part of the bank’s counterparties.
Banks also need to provide detailed information on how ESG risks are reflected in the bank’s strategy and governance and incorporated in the risk management framework. With our extensive knowledge on market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and business risk, Zanders is well equipped to support banks with integrating the identification, measurement, and management of climate change-related risks into existing risk frameworks. For more information, please contact Pieter Klaassen or Sjoerd Blijlevens via +31 88 991 02 00.
References
- See the EBA 2022 Work Programme.
- The EBA’s Report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks for credit institutions and investment firms, published in June 2021.
- See the EBA’s interactive Single Rulebook.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/876.
- See the TCFD’s Final Report on Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures published in June 2017.
- See the EBA’s response to EC Call for Advice on Article 8 Taxonomy Regulation.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/2089.
- See Directive 2014/95/EU.
- See the European Commission’s Proposal for a Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive.
- See Regulation (EU) 2019/2088.
- The EBA report can be found here.
EBA’s binding standards on Pillar 3 disclosures on ESG risks

This publication fits nicely into the ‘horizon priority’ of the EBA to provide tools to banks to measure and manage ESG-related risks. In this article we present a brief overview of the way the ITS have been developed, what qualitative and quantitative disclosures are required, what timelines and transitional measures apply – and where the largest challenges arise.
By requiring banks to disclose information on their exposure to ESG-related risks and the actions they take to mitigate those risks – for example by supporting their clients and counterparties in the adaptation process – the EBA wants to contribute to a transition to a more sustainable economy. The Pillar 3 disclosure requirements apply to large institutions with securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state.
In an earlier report2, the EBA defined ESG-related risks as “the risks of any negative financial impact on the institution stemming from the current or prospective impacts of ESG factors on its counterparties or invested assets”. Hence, the focus is not on the direct impact of ESG factors on the institution, but on the indirect impact through the exposure of counterparties and invested assets to ESG-related risks. The EBA report also provides examples for typical ESG-related factors.
While the ITS have been streamlined and simplified compared to the consultation paper published in March 2021, there are plenty of challenges remaining for banks to implement these standards.
Development of the ITS
The EBA has been mandated to develop the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks in Article 434a of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR). The EBA has opted for a sequential approach, with an initial focus on climate change-related risks. This is further narrowed down by only considering the banking book. The short maturity and fast revolving positions in the trading book are out of scope for now. The scope of the ITS will be extended to included other environmental risks (like loss of biodiversity), and social and governance risks, in later stages.
In the development of the ITS, the EBA has strived for alignment with several other regulations and initiatives on climate-related disclosures that apply to banks. The most notable ones are listed below (and in Figure 1):
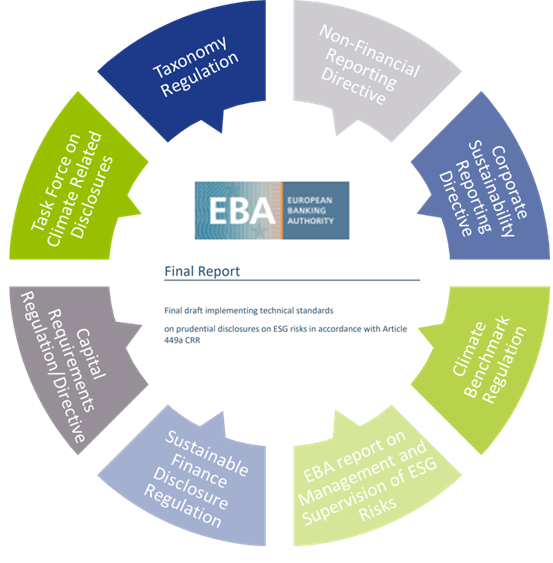
Figure 1 – Overview of related regulations and initiatives considered in the development of the ITS
- Capital Requirements Directive and Regulation (CRD and CRR): article 98(8) of the CRD3 mandated the EBA to publish the EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks, which includes the split of climate change-related risks in physical and transition risks. Article 434a of the CRR4 mandated the EBA to develop the draft ITS to specify the ESG disclosure requirements described in article 449a.
- EBA report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks2: the report provides common definitions of ESG risks and contains proposals on how to include ESG risks in the risk frameworks of banks, covering its identification, assessment, and management. It also discusses the way to include ESG risks in the supervisory review process.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)5: the Financial Stability Board’s TFCD has published recommendations on climate-related disclosures. The metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) included in the ITS have been aligned with the TCFD recommendations.
- Taxonomy Regulation6: the European Union’s common classification system of environmentally sustainable economic activities is underpinning the main KPIs introduced in the ITS.
- Climate Benchmark Regulation (CBR)7: In the CBR, two types of climate benchmarks were introduced (‘EU Climate Transition’ and ‘EU Paris-aligned’ benchmarks) and ESG disclosures for all other benchmarks (excluding interest rate and currency benchmarks) were required.
- Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD)8: the NFRD introduces ESG disclosure obligations for large companies, which include climate-related information.
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)9: a proposal by the European Commission to extend the scope of the NFRD to also include all companies listed on regulated markets (except listed micro-enterprises). One of the ITS’s KPIs, the Green Asset Ratio (GAR) is directly linked to the scope of the NFRD/CSRD.
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)10: the SFDR lays down sustainability disclosure obligations for manufacturers of financial products and financial advisers towards end-investors. It applies to banks that provide portfolio management investment advice services.
Compared to the consultation paper for the ITS, several changes have been made to the required templates. Some templates have been combined (e.g., templates #1 and #2 from the consultation paper have been combined into template #1 of the final draft ITS) and several templates have been reorganized and trimmed down (e.g., the requirement to report exposures to top EU or top national polluters has been removed).
Quantitative disclosures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks introduce ten templates on quantitative disclosures. These can be grouped in four templates on transition risks, one on physical risks, and five on mitigating actions:
- Transition risks
Two of the required templates are relatively straightforward. Banks need to report the energy efficiency of real estate collateral in the loan portfolio (#2) and report their aggregate exposure to the top 20 of the most carbon-intensive firms in the world (#4).
The main challenge for banks though will be in completing the other two templates:- Template #1 requires banks to disclose the gross carrying amount of loans and advances provided to non-financial corporates, classified by NACE sector codes and residual maturities. It is also required to report on the counterparties’ scope 1, 2, and 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Reflecting the challenge in reporting on scope 3 emissions, a transitional measure is in place. Full reporting needs to be in place by June 2024. Until then, banks need to report their available estimates (if any) and explain the methodologies and data sources they intend to use.
- In the last template (#3), banks also need to report scope 3 emissions, but relate these to the alignment metrics defined by the International Energy Agency (IEA) for the ‘net zero by 2050’ scenario. For this scenario, a target for a CO2 intensity metric is defined for 2030. By calculating the distance to this target, it becomes clear how banks are progressing (over time) towards supporting a sustainable economy. A similar transitional measure applies as for template #1.
- Physical risks
In template #5, banks are required to disclose how their banking book positions are exposed to physical risks, i.e., “chronic and acute climate-related hazards”. The exposures need to be reported by residual maturity and by NACE sector codes and should reflect exposure to risks like heat waves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. Specialized databases need to be consulted to compile a detailed understanding of these exposures. To support their submissions, banks further need to compile a narrative that explains the methodologies they used. - Mitigating actions
The final set of templates covers quantitative information on the actions a bank takes to mitigate or adapt to climate change risks.- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
- In template #7, banks need to report the outstanding banking book exposures to different types of clients/issuers, as well as the amount of these exposures that are taxonomy-eligible (that is, to sectors included in the EU Taxonomy) and taxonomy-aligned (that is, taxonomy-eligible exposures financing activities that contribute to climate change mitigation or adaptation). Based on this information, the bank’s GAR can be determined.
- In template #8, a GAR needs to be reported for the exposures to each type of client/issuer distinguished in template #7, with a distinction between a GAR for the full outstanding stock of exposures per client/issuer type, and a GAR for newly originated (‘flow’) exposures.
- Template #6 contains a summary of the GARs from templates #7 and #8.
In these templates, the numerator of the GAR only includes exposures to non-financial corporations that are required to publish non-financial information under the NFRD. Any exposures to other corporate counterparties therefore are considered 0% Taxonomy-aligned.
- The main challenge in this group of templates is in template #9. To incentivize banks to support all of their counterparties to transition to a more sustainable business model, and to collect ESG data on these counterparties, the EBA introduces the Banking Book Taxonomy Alignment Ratio (BTAR). In this metric, the numerator does include the exposures to counterparties that are not subject to NFRD disclosure obligations. The BTAR ratios obtained from the information in template #9 therefore complement the GAR ratios obtained in templates #7 and #8.
- In the final template (#10), banks have the opportunity to include any other climate change mitigating actions that are not covered by the EU Taxonomy. They can for example report on their use of green or sustainable bonds and loans.
- Templates #6-8 all relate to the GAR, which indicates what part of the bank’s banking book is aligned with the EU’s Taxonomy:
An overview of the templates for quantitative disclosures in presented in Figure 2.
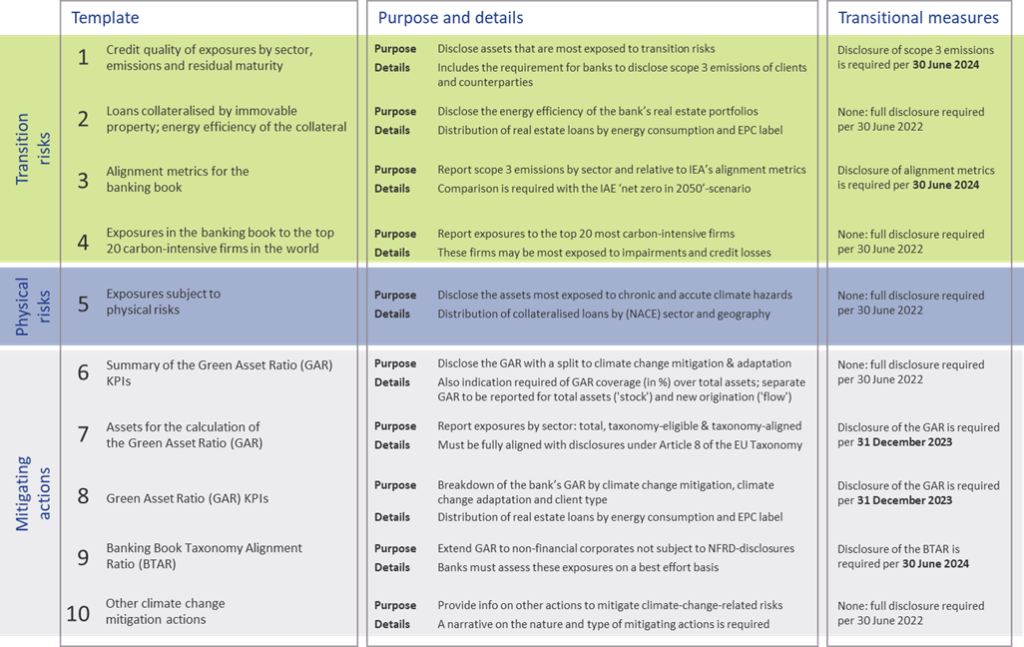
Figure 2 – Overview of the required quantitative ESG disclosures
Qualitative disclosures
In the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks, three tables are included for qualitative disclosures. The EBA has aligned these tables with their Report on Management and Supervision of ESG risks11. The three tables are set up for qualitative information on environmental, social, and governance risks, respectively. For each of these topics, banks need to address three aspects: on business strategy and processes, governance, and risk management. An overview of the required disclosures is presented in Figure 3.

Figure 3 – Overview of qualitative ESG disclosures (based on templates & section 2.3.2 of the EBA ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks)
Timelines and transitional measures
The ITS on P3 disclosure on ESG risks become effective per 30 June 2022 for large institutions that have securities traded on a regulated market of an EU member state. A semi-annual disclosure is required, but the first disclosure is annual. Consequently, based on 31 December 2022 data, the first reporting will take place in the first quarter of 2023.
The EBA has introduced a number of transitional measures. These can be summarized as follows:
- The reporting of information on the GAR is only required as of 31 December 2023.
- The reporting of information on the BTAR, the bank’s financed scope 3 emissions, and the alignment metrics is only required as of June 2024.
The EBA has further indicated in the ITS that they will conduct a review of the ITS’s requirements during 2024. They may then also extend the ITS with other environmental risks (other than the climate change-related risks in the current version). The EU Taxonomy is expected to cover a broader range of environmental risks by the end of 2022. Sometime after 2024, it is expected that the EBA will further extend the ITS by including disclosure requirements on social and governance risks.
An overview of the main timelines and transitional measures is presented in Figure 4.

Figure 4 – Overview of the main timelines and transitional measures for the ESG disclosures
Conclusion
Society, and consequently banks too, are increasingly facing risks stemming from changes in our climate. In recent years, supervisory authorities have stepped up by introducing more and more guidance and regulation to create transparency about climate change risk, and more broadly ESG risks. The publication of the ITS on P3 disclosures on ESG risks by the EBA marks an important milestone. It offers banks the opportunity to disseminate a constructive and positive role in the transition to a sustainable economy.
Nonetheless, implementing the disclosure requirements will be a challenge. Developing detailed assessments of the physical risks to which their asset portfolio is exposed and to estimate the scope 3 emissions of their clients and counterparties (‘financed emissions’) will not be straightforward. For their largest counterparties, banks will be able to profit from the NFRD disclosure obligations, but especially in Europe a bank’s portfolio typically has many exposures to small- and medium-sized enterprises. Meeting the disclosure requirements introduced by the EBA will require timely and intensive discussions with a substantial part of the bank’s counterparties.
Banks also need to provide detailed information on how ESG risks are reflected in the bank’s strategy and governance and incorporated in the risk management framework. With our extensive knowledge on market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and business risk, Zanders is well equipped to support banks with integrating the identification, measurement, and management of climate change-related risks into existing risk frameworks. For more information, please contact Pieter Klaassen or Sjoerd Blijlevens via +31 88 991 02 00.


