When will savings rates go up to match global interest rate rises?

The recent rises in global interest rates mark the first raise in a long time, as the loose monetary policies and quantitative easing (QE) introduced after the 2008 crash and Covid-19 pandemic abate.
There is now a clear trend break that is likely to significantly impact financial markets. Rate hikes have already caused rises in the mortgage rates offered by banks, but variable rate savings are still negligible in the eurozone. However, when you look further east, the first glimpses of positive compensations for client deposits are evident. What can we learn from Poland in this new and recently uncharted market territory?
Since the beginning of this year, interest rates are increasing at a fast pace after a long period of low rates. The Bank of England and the US Federal Reserve have already hiked their rates in an effort to tame high inflation, while the European Central Bank (ECB) has just announced it plans to up rates after 11 years of historically low or even negative interest rates. The consensus on financial markets is that positive rates will return in the eurozone towards the end of this year.
Looking towards Eastern Europe might offer a glimpse into the future for banks and their clients, as they are already ahead of the curve in terms of rising interest rates.
THE POLISH EXEMPLAR
Where interest rate hikes have only just been announced within the 19-nation eurozone, the markets in Hungary, Romania, Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe that remain outside the single currency are already in front of the trend. In Poland, for example, interest rates decreased to near-zero after the 2020 Covid-19 pandemic, driving down mortgage and savings rates to historically low levels. Due to high inflation, however, the Polish central bank has increased rates sharply since October of last year. As a result, short term rates in Poland have risen by almost 7% since the end of 2021, while the eurozone rates are only expected to increase in the coming months (see Figure 1).
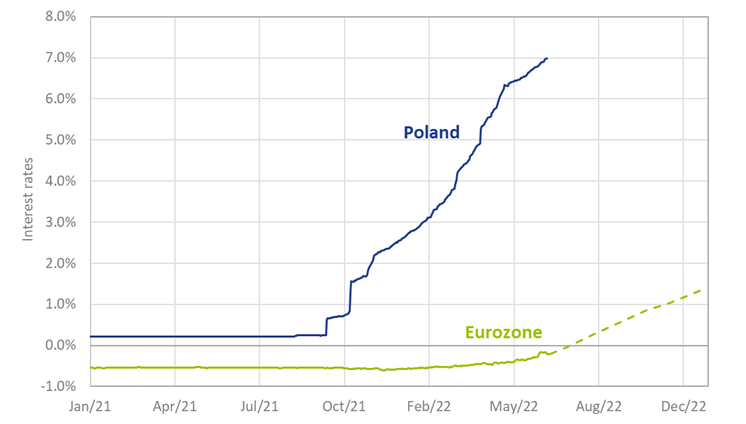
Figure 1: Three-month interest rate in Poland v the eurozone, including implied future rates for the eurozone (dashed line)
Polish consumers hoping for a similarly fast increase in their savings rate were left disillusioned. Since interest rates started to rise nine months ago in the country, savings rates have remained at a constant level of 0.5%, resulting in an extreme increase in margins for Polish banks. Since the majority of Polish mortgage owners pay a variable mortgage rate, rising interest rates have put a squeeze on many households.
As a reaction, the Polish government publicly urged banks to further increase the savings rate paid to consumers. Indeed, the National Bank of Poland recently began offering its own savings bonds directly to consumers. Retail clients are able to invest their savings for a fixed term against a coupon which tracks the central bank’s rate. As hoped, this has encouraged a response from the Polish banks. They are now providing similar fixed term deposits to clients.
Upward pricing pressure on savings rates is now evident. Recently, multiple banks announced a small raise of the general savings rate, towards 1%, slowly passing on some of the additional margin to clients. However, savings rates on offer in Poland still significantly lag the short-term interest rates in the market.
ARE POLISH TRENDS APPLICABLE TO EURO MARKETS?
Although Eastern European markets provide interesting insights into interest rate developments, it doesn’t necessarily provide a clear roadmap for Western European markets. Eastern markets on the continent have experienced a relatively low interest rate environment for a long time, but historically interest rates have been significantly higher when compared to the eurozone. Since the introduction of the Euro, interbank offered rates have hardly ever risen above 5% (see Figure 2). It remains to be seen, therefore, whether euro yields will rise to the same extremes currently observed in Eastern Europe.
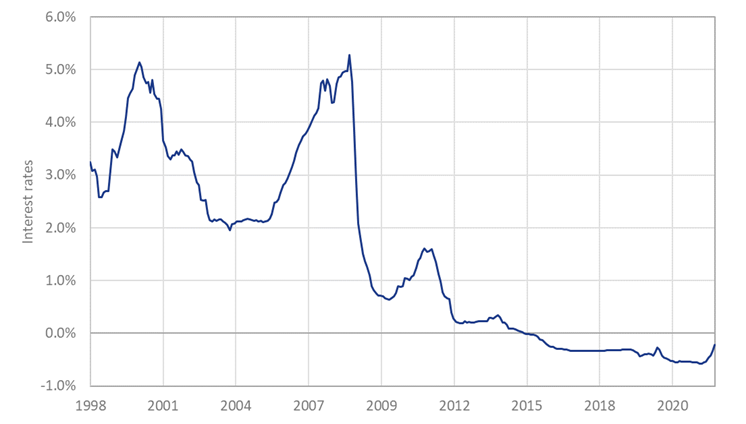
Figure 2: Historical interbank rates for the eurozone
Banks in the euro area face more competition making it challenging to maintain a savings margin that is similar to the Polish banks. Eurozone banks face more competition from peers within their own country and from foreign banks that can more easily operate in the single currency area. Those with their own domestic currencies face less displacement risk. Next to that, eurozone backs face more competition from newer Fintech-enabled banks that spy an opportunity to conquer market share by offering higher savings rates. Waiting too long to raise the compensation of depositors could lead to a large exodus of retail clients from traditional institutions.
It is unlikely that the ECB will take a similarly active role to the National Bank of Poland in pressuring banks to increase savings rates. ECB policies must be appropriate for all the 19 nation marketplaces within the eurozone, which generally exhibit less uniformity than the Polish market.
For example, the intervention of the National Bank of Poland resulted from the large portion of variable rate mortgages in Poland, but the eurozone market is much more diversified in this respect . It is therefore not expected that the ECB will start offering retail products to increase savings rates.
Although the ECB is planning to hike its interest rates in common with its Eastern European neighbors, a continuous series of significant rate hikes is less likely because financial markets tend to react stronger to expectations or announcements from the ECB, which necessitates a more graduated approach. The point is illustrated by the significant increase in the spread between Italian and German obligations seen following the recent announcement that the ECB will raise interest rates for the first time in 11 years. The foreshadowed change decreased the value of Italian obligations immediately. Some divergence with the trend observed in Poland is therefore inevitable, but the over-arching pattern of rising global rates is evident and over time this will course feed into savings rates with some local variations.
WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM SAVINGS MARKETS IN OTHER COUNTRIES?
Despite the differences between savings markets in Eastern Europe and the eurozone, there are plenty of lessons that we can still learn from the Polish situation. Interest rate hikes in the market will likely predate the increasing of deposit rates, although the lag between the two is likely to vary due to differences in the competitive environment.
In Poland, the savings rates offered by banks are slowly rising after more than six months of high short-term interest rates. This makes it unlikely that we will see large increases in deposit rates in the eurozone before the end of the year if we map that trend across the currency border.
While the approach of the ECB to interest rate hikes is less hawkish compared to the Eastern European central banks, there will still be multiple rate increases over the coming year. In the Polish market, the pressure to increase rates on savings deposits mostly came from a competitive price on fixed term deposits – in this case offered by the central bank itself. Although the ECB is unlikely to adopt such an active approach, the pricing pressure in the eurozone is likely to come from term deposits as well. Once the difference between short term rates, which are typically reflected in fixed term deposits, and rates on savings becomes large enough, banks are likely to increase their compensation on savings – or face a declining customer base.
From the banks point of view, it is critical to accurately capture the pricing dynamic between fixed term deposits and saving rates. This dynamic could be modeled explicitly when forecasting deposit rates to capture the risk in variable rate savings.
One approach is to consider the forward-looking behavior of savings while calibrating the models by formulating specific scenarios and the expected pricing strategy in these scenarios. Lessons from Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe offer an interesting case study to challenge the way the bank approaches increasing interest rates.
ECL calculation methodology

Credit Risk Suite – Expected Credit Losses Methodology article
INTRODUCTION
The IFRS 9 accounting standard has been effective since 2018 and affects both financial institutions and corporates. Although the IFRS 9 standards are principle-based and simple, the design and implementation can be challenging. Specifically, the difficulties that the incorporation of forward-looking information in the loss estimate introduces should not be underestimated. Using our hands-on experience and over two decades of credit risk expertise of our consultants, Zanders developed the Credit Risk Suite. The Credit Risk Suite is a calculation engine that determines transaction-level IFRS 9 compliant provisions for credit losses. The CRS was designed specifically to overcome the difficulties that our clients face in their IFRS 9 provisioning. In this article, we will elaborate on the methodology of the ECL calculations that take place in the CRS.
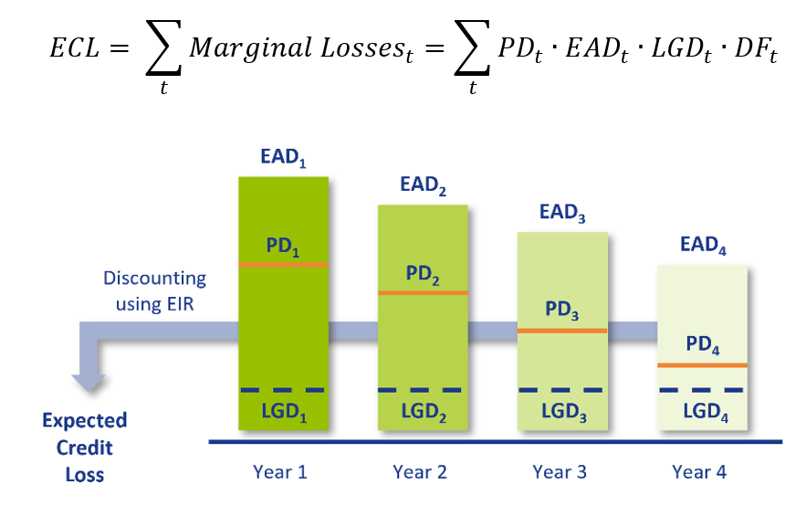
An industry best-practice approach for ECL calculations requires four main ingredients:
- Probability of Default (PD): The probability that a counterparty will default at a certain point in time. This can be a one-year PD, i.e. the probability of defaulting between now and one year, or a lifetime PD, i.e. the probability of defaulting before the maturity of the contract. A lifetime PD can be split into marginal PDs which represent the probability of default in a certain period.
- Exposure at Default (EAD): The exposure remaining until maturity of the contract based on current exposure, contractual, expected redemptions and future drawings on remaining commitments.
- Loss Given Default (LGD): The percentage of EAD that is expected to be lost in case of default. The LGD differs with the level of collateral, guarantees and subordination associated with the financial instrument.
- Discount Factor (DF): The expected loss per period is discounted to present value terms using discount factors. Discount factors according to IFRS 9 are based on the effective interest rate.
The overall ECL calculation is performed as follows and illustrated by the diagram below:
MODEL COMPONENTS
The CRS consists of multiple components and underlying models that are able to calculate each of these ingredients separately. The separate components are then combined into ECL provisions which can be utilized for IFRS 9 accounting purposes. Besides this, the CRS contains a customizable module for scenario-based Forward-Looking Information (FLI). Moreover, the solution allocates assets to one of the three IFRS 9 stages. In the component approach, projections of PDs, EADs and LGDs are constructed separately. This component-based setup of the CRS allows for customizable and easy to implement approach. The methodology that is applied for each of the components is described below.
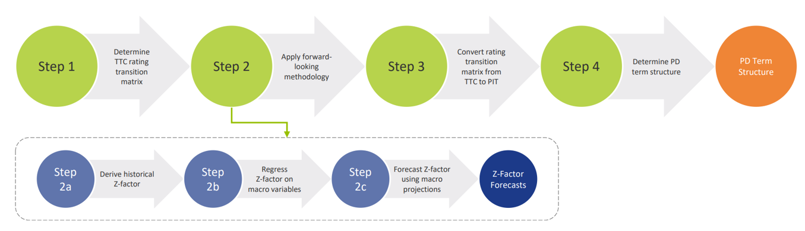
PROBABILITY OF DEFAULT
For each projected month, the PD is derived from the PD term structure that is relevant for the portfolio as well as the economic scenario. This is done using the PD module. The purpose of this module is to determine forward-looking Point-in-Time (PIT) PDs for all counterparties. This is done by transforming Through-the-Cycle (TTC) rating migration matrices into PIT rating migration matrices. The TTC rating migration matrices represent the long-term average annual transition PDs, while the PIT rating migration matrices are annual transition PDs adjusted to the current (expected) state of the economy. The PIT PDs are determined in the following steps:
- Determine TTC rating transition matrices: To be able to calculate PDs for all possible maturities, an approach based on rating transition matrices is applied. A transition matrix specifies the probability to go from a specified rating to another rating in one year time. The TTC rating transition matrices can be constructed using e.g., historical default data provided by the client or external rating agencies.
- Apply forward-looking methodology: IFRS 9 requires the state of the economy to be reflected in the ECL. In the CRS, the state of the economy is incorporated in the PD by applying a forward-looking methodology. The forward-looking methodology in the CRS is based on a ‘Z-factor approach’, where the Z-factor represents the state of the macroeconomic environment. Essentially, a relationship is determined between historical default rates and specific macroeconomic variables. The approach consists of the following sub-steps:
- Derive historical Z-factors from (global or local) historical default rates.
- Regress historical Z-factors on (global or local) macro-economic variables.
- Obtain Z-factor forecasts using macro-economic projections.
- Convert rating transition matrices from TTC to PIT: In this step, the forward-looking information is used to convert TTC rating transition matrices to point-in-time (PIT) rating transition matrices. The PIT transition matrices can be used to determine rating transitions in various states of the economy.
- Determine PD term structure: In the final step of the process, the rating transition matrices are iteratively applied to obtain a PD term structure in a specific scenario. The PD term structure defines the PD for various points in time.
The result of this is a forward-looking PIT PD term structure for all transactions which can be used in the ECL calculations.
EXPOSURE AT DEFAULT
For any given transaction, the EAD consists of the outstanding principal of the transaction plus accrued interest as of the calculation date. For each projected month, the EAD is determined using cash flow data if available. If not available, data from a portfolio snapshot from the reporting date is used to determine the EAD.
LOSS GIVEN DEFAULT
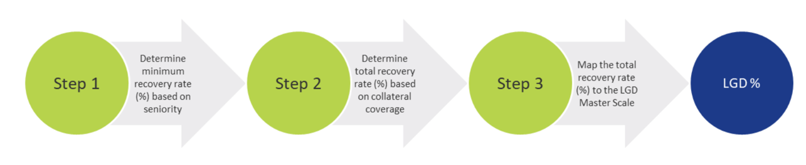
For each projected month, the LGD is determined using the LGD module. This module estimates the LGD for individual credit facilities based on the characteristics of the facility and availability and quality of pledged collateral. The process for determining the LGD consists of the following steps:
- Seniority of transaction: A minimum recovery rate is determined based on the seniority of the transaction.
- Collateral coverage: For the part of the loan that is not covered by the minimum recovery rate, the collateral coverage of the facility is determined in order to estimate the total recovery rate.
- Mapping to LGD class: The total recovery rate is mapped to an LGD class using an LGD scale.
SCENARIO-WEIGHTED AVERAGE EXPECTED CREDIT LOSS
Once all expected losses have been calculated for all scenarios, the weighted average one-year and lifetime loss are calculated for each transaction , for both 1-year and lifetime scenario losses:
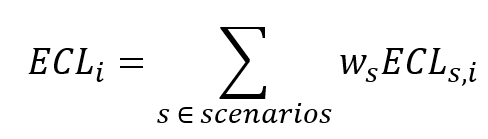
For each scenario , the weights are predetermined. For each transaction , the scenario losses are weighted according to the formula above, where is either the lifetime or the one-year expected scenario loss. An example of applied scenarios and corresponding weights is as follows:
- Optimistic scenario: 25%
- Neutral scenario: 50%
- Pessimistic scenario: 25%
This results in a one-year and a lifetime scenario-weighted average ECL estimate for each transaction.
STAGE ALLOCATION
Lastly, using a stage allocation rule, the applicable (i.e., one-year or lifetime) scenario-weighted ECL estimate for each transaction is chosen. The stage allocation logic consists of a customisable quantitative assessment to determine whether an exposure is assigned to Stage 1, 2 or 3. One example could be to use a relative and absolute PD threshold:
- Relative PD threshold: +300% increase in PD (with an absolute minimum of 25 bps)
- Absolute PD threshold: +3%-point increase in PD The PD thresholds will be applied to one-year best estimate PIT PDs.
If either of the criteria are met, Stage 2 is assigned. Otherwise, the transaction is assigned Stage 1.
The provision per transaction are determined using the stage of the transaction. If the transaction stage is Stage 1, the provision is equal to the one-year expected loss. For Stage 2, the provision is equal to the lifetime expected loss. Stage 3 provision calculation methods are often transaction-specific and based on expert judgement.
Rating model calibration methodology

At Zanders we have developed several Credit Rating models. These models are already being used at over 400 companies and have been tested both in practice and against empirical data. Do you want to know more about our Credit Rating models, keep reading.
During the development of these models an important step is the calibration of the parameters to ensure a good model performance. In order to maintain these models a regular re-calibration is performed. For our Credit Rating models we strive to rely on a quantitative calibration approach that is combined and strengthened with expert option. This article explains the calibration process for one of our Credit Risk models, the Corporate Rating Model.
In short, the Corporate Rating Model assigns a credit rating to a company based on its performance on quantitative and qualitative variables. The quantitative part consists of 5 financial pillars; Operations, Liquidity, Capital Structure, Debt Service and Size. The qualitative part consist of 2 pillars; Business Analysis pillar and Behavioural Analysis pillar. See A comprehensive guide to Credit Rating Modelling for more details on the methodology behind this model.
The model calibration process for the Corporate Rating Model can be summarized as follows:
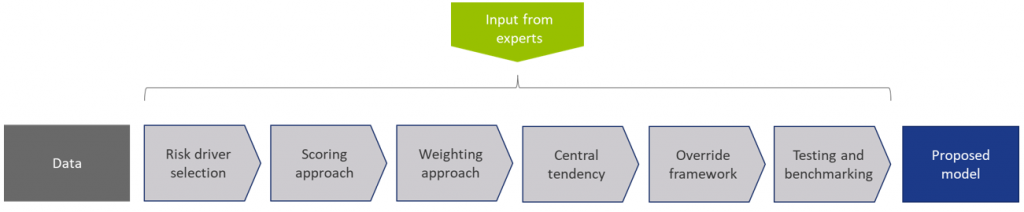
Figure 1: Overview of the model calibration process
In steps (2) through (7), input from the Zanders expert group is taken into consideration. This especially holds for input parameters that cannot be directly derived by a quantitative analysis. For these parameters, first an expert-based baseline value is determined and second a model performance optimization is performed to set the final model parameters.
In most steps the model performance is accessed by looking at the AUC (area under the ROC curve). The AUC metric is one of the most popular metrics to quantify the model fit (note this is not necessarily the same as the model quality, just as correlation does not equal causation). The AUC metric indicates, very simply put, the number of correct and incorrect predictions and plots them in a graph. The area under that graph then indicates the explanatory power of the model
DATA
The first step covers the selection of data from an extensive database containing the financial information and default history of millions of companies. Not all data points can be used in the calibration and/or during the performance testing of the model, therefore data filters are applied. Furthermore, the data set is categorized in 3 different size classes and 18 different industry sectors, each of which will be calibrated independently, using the same methodology.
This results in the master dataset, in addition data statistics are created that show the data availability, data relations and data quality. The master dataset also contains derived fields based on financials from the database, these fields are based on a long list of quantitative risk drivers (financial ratios). The long list of risk drivers is created based on expert option. As a last step, the master dataset is split into a calibration dataset (2/3 of the master dataset) and a test dataset (1/3 of the master dataset).
RISK DRIVER SELECTION
The risk driver selection for the qualitative variables is different from the risk driver selection for the quantitative variables. The final list of quantitative risk drivers is selected by means of different statistical analyses calculated for the long list of quantitative risk drivers. For the qualitative variables, a set of variables is selected based on expert opinion and industry practices.
SCORING APPROACH
Scoring functions are calibrated for the quantitative part of the model. These scoring function translate the value and trend value of each quantitative risk driver per size and industry to a (uniform) score between 0-100. For this exercise, different possible types of scoring functions are used. The best-performing scoring function for the value and trend of each risk driver is determined by performing a regression and comparing the performance. The coefficients in the scoring functions are estimated by fitting the function to the ratio values for companies in the calibration dataset. For the qualitative variables the translation from a value to a score is based on expert opinion.
WEIGHTING APPROACH
The overall score of the quantitative part of the model is combined by summing the value and trend scores by applying weights. As a starting point expert opinion-based weights are applied, after which the performance of the model is further optimized by iteratively adjusting the weights and arriving at an optimal set of weights. The weights of the qualitative variables are based on expert opinion.
MAPPING TO CENTRAL TENDENCY
To estimate the mapping from final scores to a rating class, a standardized methodology is created. The buckets are constructed from a scoring distribution perspective. This is done to ensure the eventual smooth distribution over the rating classes. As an input, the final scores (based on the quantitative risk drivers only) of each company in the calibration dataset is used together with expert opinion input parameters. The estimation is performed per size class. An optimization is performed towards a central tendency by adjusting the expert opinion input parameters. This is done by deriving a target average PD range per size class and on total level based on default data from the European Banking Authority (EBA).
The qualitative variables are included by performing an external benchmark on a selected set of companies, where proxies are used to derive the score on the qualitative variables.
The final input parameters for the mapping are set such that the average PD per size class from the Corporate Rating Model is in line with the target average PD ranges. And, a good performance on the external benchmark is achieved.
OVERRIDE FRAMEWORK
The override framework consists of two sections, Level A and Level B. Level A takes country, industry and company-specific risks into account. Level B considers the possibility of guarantor support and other (final) overriding factors. By applying Level A overrides, the Interim Credit Risk Rating (CRR) is obtained. By applying Level B overrides, the Final CRR is obtained. For the calibration only the country risk is taken into account, as this is the only override that is based on data and not a user input. The country risk is set based on OECD country risk classifications.
TESTING AND BENCHMARKING
For the testing and benchmarking the performance of the model is analysed based on the calibration and test dataset (excluding the qualitative assessment but including the country risk adjustment). For each dataset the discriminatory power is determined by looking at the AUC. The calibration quality is reviewed by performing a Binomial Test on Individual Rating Classes to check if the observed default rate lies within the boundaries of the PD rating class and a Traffic Lights Approach to compare the observed default rates with the PD of the rating class.
Concluding, the methodology applied for the (re-)calibration of the Corporate Rating Model is based on an extensive dataset with financial and default information and complemented with expert opinion. The methodology ensures that the final model performs in-line with the central tendency and an performs well on an external benchmark.
The impact of liquidity spread risk on banks’ earnings

Typical retail banks often use short-term funding such as customer deposits to fund long-term loans. The profitability of this business activity is highly dependent on the pricing of the deposits and loans.
External client rates can be split up in an interest-rate component, a liquidity spread and a margin covering, for example, operational and credit risk. To limit the risk of a decline in profitability, banks often hedge the interest-rate risk as part of their risk management framework. Since the global financial crisis of 2007-2008, it has become clearer that the liquidity spread also has a significant impact on profitability. However, the measurement and hedging of liquidity spread risk is still at an early stage in the banking sector. In this article we use a stylized example to illustrate the impact of liquidity spread risk on banks’ earnings. Furthermore, we discuss which challenges banks face regarding the management of liquidity spread risk.
WHAT ARE LIQUIDITY SPREADS?
The global financial crisis of 2007-2008 was a major turning point in terms of liquidity in the financial system. In preceding years, funding was available on a large scale and at low rates, especially for creditworthy and large banks. These banks often only paid a small spread above the swap rates for attracting funding. This enabled banks to earn significant profits. Meanwhile, there was a wide belief in the sustainability of the attractive funding conditions. During the global financial crisis, liquidity declined as banks were less willing to lend to each other because of their uncertainty about the exposure on structured products. To account for declined liquidity, banks charged each other a higher spread on top of the swap rates when lending funds. The liquidity spread can therefore be described as the spread banks pay and receive on top of the swap rate to account for liquidity.
Liquidity spreads exhibit procyclical behavior as liquidity spreads typically decrease during economic expansion when there is plenty of liquidity, while liquidity spreads increase during economic contraction when liquidity is declining or limited. This procyclical behavior also has an impact on the pricing of shortterm deposits and long-term loans. As a result, the profitability of a bank is affected by changes in liquidity spreads. The embedded risk of the procyclical behavior of liquidity spreads in banks’ profitability is called liquidity spread risk.
CHALLENGES IN THE MEASUREMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF LIQUIDITY SPREAD RISK
Banks face a number of challenges in the measurement and management of liquidity spread risk. The first one is the non-trivial estimation of the liquidity spread repricing speed for variable rate products like on-demand savings. The second one is the measurement of liquidity spread risk in a Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) context. The final challenge is the hedging of liquidity spread risk.
Estimation of liquidity spread pass through rate As shown in the example in this article, measurement of the liquidity spread pass through rate is crucial for determining the impact of liquidity spread risk on earnings. Measuring the liquidity spread pass through rate is quite straightforward for maturing products like mortgages and other loans, as the liquidity spread is often fixed until a pre-specified horizon. For non-maturing products like on-demand savings this estimation is often harder to make. Analysis on the historical relationship between liquidity spreads and external client rates is a possible approach.
MEASUREMENT OF LIQUIDITY SPREAD RISK IN A FUNDS TRANSFER PRICING CONTEXT
The hypothetical bank taken as a starting point in this article is a stylized example, where short-term customer deposits are directly used to fund long-term mortgages. In practice, many banks have a Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP) framework in place which attributes liquidity costs and benefits to each line of business activity. Interest rate risk and liquidity risk is managed by the central treasury department of the bank. Such a framework is also in line with Internal Liquidity Assessment Adequacy Process regulations from for example the Dutch National Bank (DNB).
An FTP framework also serves as a monitoring and management tool for the bank as certain products might be priced more or less attractive, thereby impacting the balance sheet structure. This makes it hard to measure, or even identify, liquidity spread risk for business lines. Often liquidity spreads are not externally set, but the bank management can adjust the externally observed liquidity spreads to steer the balance sheet. In this way bank management can influence the liquidity spreads (FTP) business lines will pay/receive on their products.
HEDGING OF LIQUIDITY SPREAD RISK
Banks typically use swaps to hedge interest rate risk, aiming to steer towards a target duration of equity as set in the Risk Appetite Statement. Without the use of interest rate swaps, banks bear interest rate risk as shocks in the interest rate will affect the bank’s value or earnings. From a liquidity spread risk perspective, the situation is identical as shocks in the liquidity spread will also affect the bank’s value or earnings. In practice it is, in contrary to interest rate risk where there are plenty of derivatives available to use for hedging purposes, quite a challenge to find suitable derivative contracts.
STYLIZED EXAMPLE
Consider a bank that uses retail customer deposits (on-demand savings) to fund retail mortgages, with a balance sheet as shown on the left in Figure 1. For the analysis in this article, a static balance sheet is assumed. The retail mortgages all have a contractual maturity of 20 years, with a fixed liquidity spread and coupon until maturity. The retail on-demand savings do not have a contractual maturity. The client rates the bank receives on the mortgages and pays on the on-demand savings are shown on the right in Figure 1. The figure shows the contribution of the interest rate component, a liquidity spread and a margin, to the client rates. Cash and cash equivalents are assumed to be non-interest bearing.
From Figure 1 it is clear that future movements in each of the components of the client rate have an impact on the bank’s earnings. The impact of these movements depends on the degree of sensitivity of the client rates on mortgages and on-demand savings towards its components. The degree of sensitivity can be measured by the pass-through rate of each of the components. The pass-through rate measures what percentage of a certain change in the market interest rate or liquidity spread is reflected in the client rates on mortgages and on-demand savings.
The pass-through rate for fixed-rate contracts is purely driven by the repricing date of the contract, because a contract generally fully reprices at repricing date for both interest rates and liquidity spreads. For savings, this is more difficult as there is no clear repricing date. First, changes in market rate and liquidity spreads are gradually passed through in the client rate over time. Second, when banks would choose to not pass through these changes in the client rate, clients would switch to competing banks that would increase their client rates.
IMPACT OF LIQUIDITY SPREAD RISK ON EARNINGS
To show the impact on earnings for the first year, we consider three market scenarios. Next to the base scenario with no changes in the interest rate and liquidity spread, instantaneous parallel 100 bps increases in the market interest rate and liquidity spread are considered. It is assumed that the pass-through rate for the interest rate and liquidity spread for savings equals 50% in the first year (see Figure 2). This means that 50% of the changes in market interest rate and liquidity spread are passed through to the client rates in the first year. For mortgages, the pass-through rate is set at 0% in the first year as these fully reprice after 20 years and no repricing takes place in the first year.
"Liquidity spreads exhibit procyclical behavior as liquidity spreads typically decrease during economic expansion when there is plenty of liquidity, while liquidity spreads increase during economic contraction when liquidity is declining or limited."
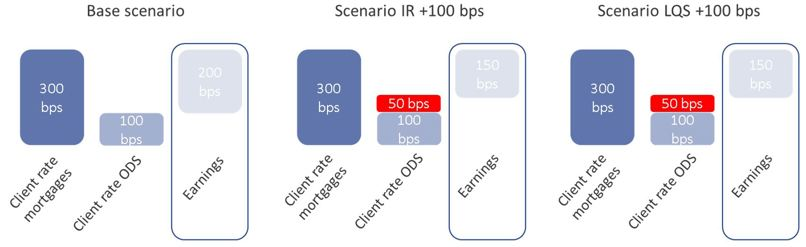
Figure 3 shows earnings for the three scenarios. In the scenario with an upward shock of 100 bps to the interest rate, the on-demand savings client rate increases by 50 bps. Given that the mortgage client rate remains the same, earnings drop from 200 bps to 150 bps. For liquidity spreads the impact of an upward shock of 100 bps to the liquidity spread on earnings is identical. Earnings drop from 200 bps to 150 bps because the on-demand savings client rate increases by 50 bps and the mortgage client rate remains the same. This example shows that both market interest rate and liquidity spread movements have impact on the banks’ earnings.
HEDGING OF INTEREST RATE AND LIQUIDITY SPREAD RISK
Under normal market conditions, the interest-rate risk on earnings can be hedged using interest-rate swaps. This is illustrated in Figure 4 for the hypothetical bank in our example. The bank buys a (for example) 10-year interest-rate swap with notional equal to half of the total savings volume. If the market interest rate increases by 100 bps, the client rate increases by 50 bps. However, this increase is offset by the interest-rate swap payoff, which also equals 50 bps. As a result, earnings remain stable on 200 bps.
CONCLUSION
Liquidity spreads have an impact on banks’ earnings. The degree of impact depends on the sensitivity of the client rates on deposits and loans towards the liquidity spread movements. For a typical retail bank using short-term funding for long-term loans, earnings can drop when liquidity spreads increase.
Banks can improve their risk measurement and management systems by incorporating liquidity spread risk. A first step might be Earnings-at-Risk scenarios for liquidity spread risk, independent of scenarios for interest rates. This enables banks to gain insight into the impact that liquidity spreads have on a bank’s earnings, and to set up relevant liquidity spread risk management systems. Doing so is non-trivial as banks face several additional challenges compared to interest rate risk management. The main challenges are the measurement of the sensitivity of non-maturing product client rates towards liquidity spreads, liquidity spread risk measurement for business lines in an FTP context, and the hedging of liquidity spread risk.
Replicating investment portfolios: a quantitative analysis

Many banks use a framework of replicating investment portfolios to measure and manage the interest rate risk of variable savings deposits. There are two commonly used methodologies, known as the marginal investment strategy and the portfolio investment strategy. While these have the same objective, the effects for margin and interest maturity may vary. We review these strategies on the basis of a quantitative and a qualitative analysis.
A replicating investment portfolio is a collection of fixed income investments based on an investment strategy that aims to reflect the typical interest rate maturity of the savings deposits (also referred to as ‘non-maturing deposits’). The investment strategy is formulated so that the margin between the portfolio return and the savings interest rate is as stable as possible, given various scenarios. A replicating framework enables a bank to base its interest rate risk measurement and management on investments with a fixed maturity and price – while the deposits have no contractual maturity or price. In addition, a bank can use the framework to transfer the interest rate risk from the business lines to the central treasury, by turning the investments into contractual obligations. There are two commonly used methodologies for constructing the replicating portfolios: the marginal investment strategy and the portfolio investment strategy. These strategies have the same objective, but have different effects on margin and interest-rate term, given certain scenarios.
STRATEGIES DEFINED
An investment strategy determines the monthly allocation of the investable volume across various maturities. The investable volume in month t (It) consists of two parts:
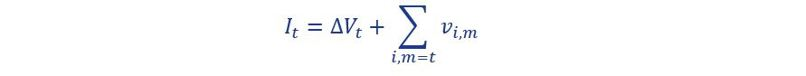
The first part is equal to the decrease or increase in the volume of savings deposits compared to the previous month. The second part is equal to the total principal of all investments in the investment portfolio maturing in the current month (end date m = t ), ∑i,m=t vi,m. By investing or re-investing the volume of these two parts, the total principal of the investment portfolio will equal the savings volume outstanding at that moment. When an investment is generated, it receives the market interest rate relating to the maturity at that time. The portfolio investment return is determined as the principal weighted average interest rate. The difference between a marginal investment strategy and a portfolio investment strategy is that in a marginal investment strategy, the volume is invested with a fixed allocation across fixed maturities. In a portfolio strategy, these parameters are flexible, however investments are generated in such a way that the resulting portfolio each month has the same (target) proportional maturity profile. The maturity profile provides the total monthly principal of the currently outstanding investments that will mature in the future. In the savings modelling framework, the interest rate risk profile of the savings portfolio is estimated and defined as a (proportional) maturity profile. For the portfolio investment strategy, the target maturity profile is set equal to this estimated profile. For the marginal investment strategy, the ‘investment rule’ is derived from the estimated profile using a formula. Under long lasting constant or stable volume of savings deposits, the investment portfolio given the investment rule converges to the estimated profile.
STRATEGIES ILLUSTRATED
In Figure 1, the difference between the two strategies is graphically illustrated in an example. The example provides the development of replicating portfolios of the two strategies in two consecutive months upon increasing savings volume. The replicating portfolios initially consist of the same investments with original maturities of one month, 12 months and 36 months. To this end, the same investments and corresponding principals mature. The total maturing principal will be reinvested and the increase in savings volume will be invested.
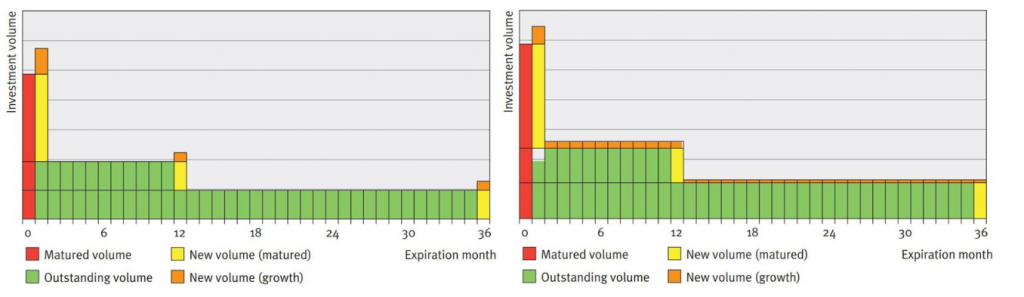
Figure 1: Two replication portfolio strategies
Note that if the savings volume would have remained constant, both strategies would have generated the same investments. However, with changing savings volume, the strategies will generate different investments and a different number of investments (3 under the marginal strategy, and 36 under the portfolio strategy). The interest rate typical maturities and investment returns will therefore differ, even if market interest rates do not change. For the quantitative properties of the strategies, the decision will therefore focus mainly on margin stability and the interest rate typical maturity given changes in volume (and potential simultaneous movements in market interest rates).
SCENARIO ANALYSIS
The quantitative properties of the investment strategies are explained by means of a scenario analysis. The analysis compares the development of the duration, margin and margin stability of both strategies under various savings volume and market interest rate scenarios.
CLIENT INTEREST RATE
As part of the simulation of a margin, a client interest rate is modeled. The model consists of a set of sensitivities to market interest rates (M1,t) and moving averages of market interest rates (MA12,t). The sensitivities to the variables show the degree to which the bank has to reflect market movements in its client interest rate, given the profile of its savings clients. The model chosen for the interest rate for the point in time t (CRt ) is as follows:
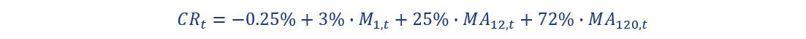
Up to a certain degree, the model is representative of the savings interest rates offered by (retail) banks.
INVESTMENT STRATEGIES
The investment rules are formulated so that the target maturity profiles of the two strategies are identical. This maturity profile is then determined so that the same sensitivities to the variables apply as for the client rate model. An overview of the investment strategies is given in Table 1.
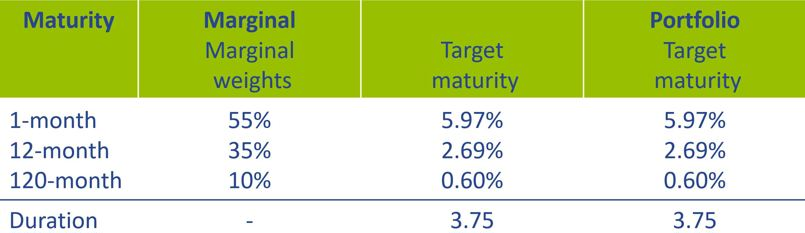
The replication process is simulated for 200 successive months in each scenario. The starting point for the investment portfolio under both strategies is the target maturity profile, whereby all investments are priced using a constant historical (normal) yield curve. In each scenario, upward and downward shocks lasting 12 months are applied to the savings volume and the yield curve after 24 months.
EXAMPLE SCENARIO
The results of an example scenario are presented in order to show the dynamics of both investment strategies. This example scenario is shown in Figure 2. The results in terms of duration and margin are shown in Figure 3.
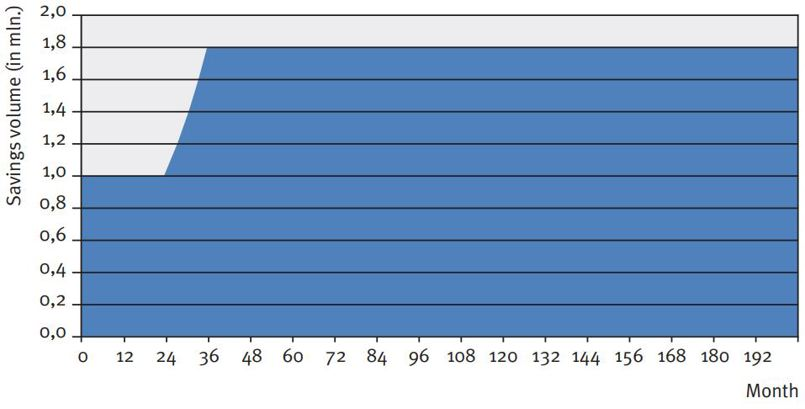
Figure 2: Example scenario in volume and market interest rate development
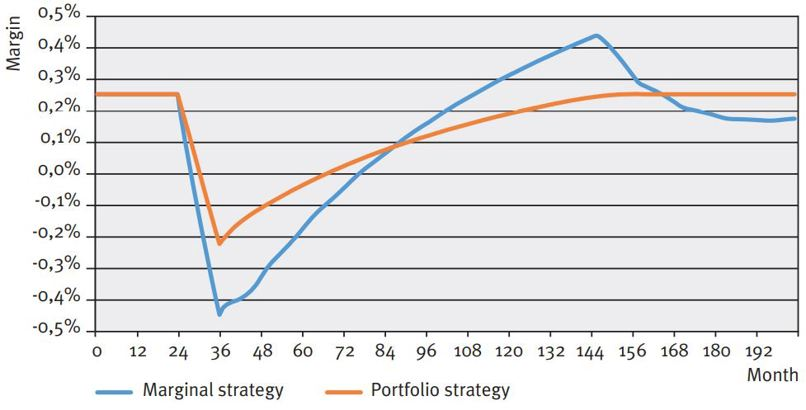
Figure 3: Impact on duration and margin from interest up and down scenarios
As one would expect, the duration for the portfolio investment strategy remains the same over the entire simulation. For the marginal investment strategy, we see a sharp decline in the duration during the ‘shock period’ for volume, after which a double wave motion develops on the duration. In short, this is caused by the initial (marginal) allocation during the ‘stress’ and subsequent cycles of reinvesting it. With an upward volume shock, the margin for the portfolio strategy declines because the increase in savings volume is invested at downward shocked market interest rates. After the shock period, the declining investment return and client rate converge. For the marginal strategy this effect also applies and in addition the duration effects feed into the margin development.
SCENARIO SPECTRUM
In the scenario analysis the standard deviation of the margin series, also known as the margin volatility, serves as a proxy for margin stability. The results in terms of margin stability for the full range of market interest rate and volume scenarios are summarized in Figure 4. From the figures, it can be seen that the margin of the marginal investment strategy has greater sensitivity to volume and interest rate shocks. Under these scenarios the margin volatility is on average 2.3 times higher, with the factor ranging between 1.5 and 4.5. In general, for both strategies, the margin volatility is greatest under negative interest-rate shocks combined with upward or downward volume shocks.
REPLICATION IN PRACTICE
The scenario analysis shows that the portfolio strategy has a number of advantages over the marginal strategy. First of all, the maturity profile remains constant at all times and equal to the modeled maturity of the savings deposits. Under the marginal strategy, the interest rate typical maturity can vary from it over long periods, even when there are no changes in market interest environment or behavior in the savings portfolio. Secondly, the development of the margin is more stable under volume and interest rate shocks. The margin volatility under the marginal investment strategy is actually at least one and a half times higher under the chosen scenarios.
AN INTUITIVE PROCESS
These benefits might, however, come at the expense of a number of qualitative aspects that may form an important consideration when it comes to implementation. Firstly, the advantage of a constant interest-rate profile for the portfolio strategy, comes at the expense of intuitive combinations of investments. This may be important if these investments form contractual obligations.
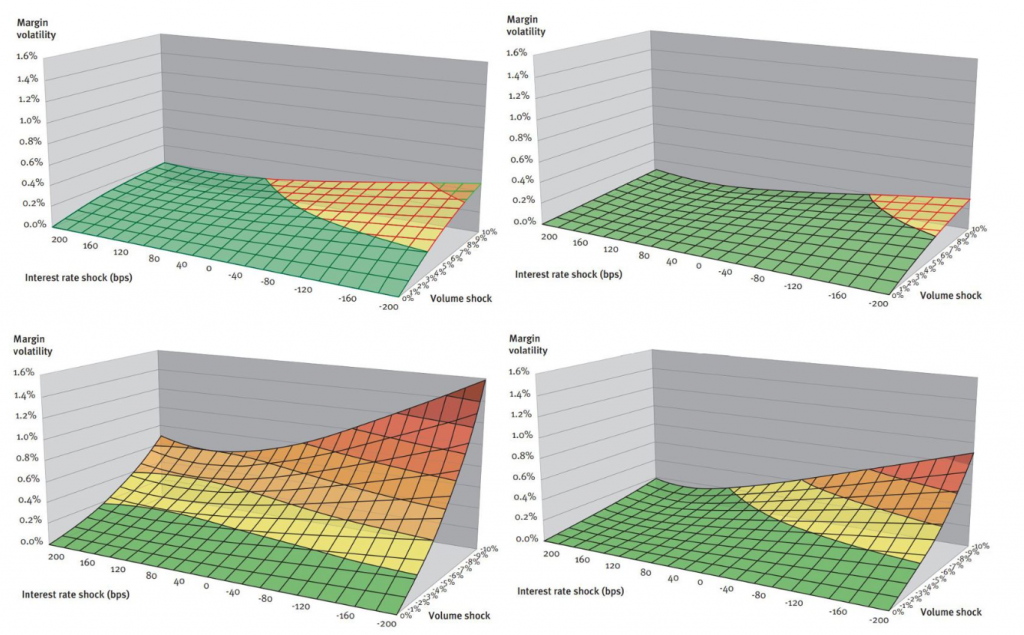
Figure 4: Margin volatility of marginal (left-hand) and portfolio strategy (right-hand) for upward (above) and downward shocks (below)
for the transfer of the interest rate risk. The strategy, namely, requires generating a large number of investments that can even have negative principals in case of a (small) decline of savings volume. Secondly, the shocks in the duration in a marginal strategy might actually be desirable and in line with savings portfolio developments. For example, if due to market or idiosyncratic circumstances there is high inflow of deposit volume, this additional volume may be relatively more interest rate sensitive justifying a shorter duration. Nevertheless, the example scenario shows that after such a temporary decline a temporary increase will follow for which this justification no longer applies.
THE CHOICE
A combination of the two strategies may also be chosen as a compromise solution. This involves the use of a marginal strategy whereby interventions trigger a portfolio strategy at certain times. An intervention policy could be established by means of limits or triggers in the risk governance. Limits can be set for (unjustifiable) deviations from the target duration, whereas interventions can be triggered by material developments in the market or the savings portfolio.
In its choice for the strategy, the bank is well-advised to identify the quantitative and qualitative effects of the strategies. Ultimately, the choice has to be in line with the character of the bank, its savings portfolio and the resulting objective of the process.
Why is modelling non-maturing deposits essential?

For banks, using variable savings as a source of financing differs fundamentally from ‘professional’ sources of financing.
For banks, using variable savings as a source of financing differs fundamentally from ‘professional’ sources of financing. What risks are involved and how do you determine the return? With capital market financing, such as bond financing, the redemption is known in advance and the interest coupon is fixed for a longer period of time. Financing using variable savings differs from this on two points: the client can withdraw the money at any given time and the bank has the right to adjust the interest rate when it wants to. An essential question here is: why would a bank opt to use savings for financing rather than other sources of financing? The answer to this question is not a simple one, but has to do with the relationship between risk and return.
DETERMINING RETURNS ON THE SAVINGS PORTFOLIO
How do you determine the yield on savings? In order to get as accurate an estimate as possible of the return on a balance sheet instrument, the client rate for a product is often compared to what is called the internal benchmark price, also referred to as the ‘funds transfer price’ (FTP). For savings, the FTP represents the theoretical yield achieved from investing these funds. The difference between the theoretical yield and the actual costs (which includes not only the costs of paying interest on savings, but also the operating/IT costs, for instance) can be regarded as the return on the savings. Calculating this theoretical yield is not a simple task, however. It is often based on a notional investment portfolio, with the same interest rate and liquidity periods as the savings. These periods reflect the interest rate and liquidity characteristics of the savings.
"By ensuring that the expected outflow of savings coincides with the expected influx from investments, the liquidity requirements can be satisfied in the future as well."
MANAGING MARGIN RISK
The question that now arises is: what risks do the savings pose for the bank? Fluctuating market interest rates have an impact on both the yields on the investments and the interest costs on the savings. Although the bank has the right to set its own interest rate, there is a great deal of dependency since banks often follow the interest rate of the market (i.e., their competitors) in order to retain their volume of savings. The bank is therefore exposed to margin risk if the income from the investments does not keep pace with the savings rate offered to clients.
The risk-free interest rate is often the biggest driver behind these kinds of movements on the market for savings interest. The dependency between the savings interest and risk-free interest is indicated using the (estimated) interest rate period. This information makes it possible to mitigate the margin risk in two ways. The interest rate period of the investment portfolio can be aligned with the savings, which causes this income to respond to the interest-free interest rate to the same degree as the costs of paying the savings interest rate. It is also possible to enter into interest rate swaps to influence the interest rate period of the investments.
ASSESSING LIQUIDITY RISK
The liquidity risk of savings manifests if clients withdraw their money and the bank does not have enough cash/liquid investments to comply with these withdrawals. By ensuring that the expected outflow of savings coincides with the expected influx from investments, the liquidity requirements can be satisfied in the future as well. Consequently a bank will be less likely to find itself forced to raise financing or sell illiquid investments in crisis situations. A bank also maintains liquidity buffers for its liquidity requirements in the short term; the regulator requires it to do this by means of the LCR (Liquidity Coverage Ratio) requirement. Since it is expensive to maintain liquidity buffers, a bank aims for a prudent liquidity buffer, but one that is as low as possible. It is also essential for the bank to determine the liquidity period (how long savings remain in the client’s account). It must do this in order to manage the liquidity risk, but also to determine the right level of cash buffers, which improves the return. Savings modeling is a must In order to get the right insight into savings - and to manage them - it is essential to determine both the interest rate period and liquidity period of those savings. It is only with this information that management can gain insight into how the return on savings relates to the margin and liquidity risk.
Regulators are also putting increasing pressure on banks to have better insight into savings. In interest rate risk management, for instance, DNB requires that the interest rate risk of savings be properly substantiated. There is also increasing attention to this from the standpoint of liquidity risk management, for instance as part of the ILAAP (Internal Liquidity Adequacy Assessment Process). Modeling of savings is therefore an absolute must for banks.
GROWING INTEREST IN SAVINGS
At the end of 2012, approximately EUR 950 million of the total of EUR 2.7 billion on Dutch banks’ balance sheets was financed with private savings. EUR 545 million of this comes from Dutch households and businesses. Given the fact that the credit extended to this sector totals EUR 997 million, the Dutch funding gap is the highest of all the euro-zone countries except for Ireland. Since the start of the financial crisis in 2008, there have been two developments that have contributed to the growing interest in savings on the part of banks. First of all, after the collapse of the (inter-bank) money and capital markets, banks had to seek out alternative stable sources of financing. Secondly, compared to other forms of financing, savings have secured a relatively favourable position in the liquidity regulations under Basel III. This culminated in a price war on the savings market in 2010.
A comprehensive guide to Credit Rating Modelling

Credit rating agencies and the credit ratings they publish have been the subject of a lot of debate over the years. While they provide valuable insight in the creditworthiness of companies, they have been criticized for assigning high ratings to package sub-prime mortgages, for not being representative when a sudden crisis hits and the effect they have on creating ‘self fulfilling prophecies’ in times of economic downturn.
For all the criticism that rating models and credit rating agencies have had through the years, they are still the most pragmatic and realistic approach for assessing default risk for your counterparties. Of course, the quality of the assessment depends to a large extent on the quality of the model used to determine the credit rating, capturing both the quantitative and qualitative factors determining counterparty credit risk. A sound credit rating model strikes a balance between these two aspects. Relying too much on quantitative outcomes ignores valuable ‘unstructured’ information, whereas an expert judgement based approach ignores the value of empirical data, and their explanatory power.
In this white paper we will outline some best practice approaches to assessing default risk of a company through a credit rating. We will explore the ratios that are crucial factors in the model and provide guidance for the expert judgement aspects of the model.
Zanders has applied these best practices while designing several Credit Rating models for many years. These models are already being used at over 400 companies and have been tested both in practice and against empirical data. Do you want to know more about our Credit Rating models, click here.
Credit ratings and their applications
Credit ratings are widely used throughout the financial industry, for a variety of applications. This includes the corporate finance, risk and treasury domains and beyond. While it is hardly ever a sole factor driving management decisions, the availability of a point estimation to describe something as complex as counterparty credit risk has proven a very useful piece of information for making informed decisions, without the need for a full due diligence into the books of the counterparty.
Some of the specific use cases are:
- Internal assessment of the creditworthiness of counterparties
- Transparency of the creditworthiness of counterparties
- Monitoring trends in the quality of credit portfolios
- Monitoring concentration risk
- Performance measurement
- Determination of risk-adjusted credit approval levels and frequency of credit reviews
- Formulation of credit policies, risk appetite, collateral policies, etc.
- Loan pricing based on Risk Adjusted Return on Capital (RAROC) and Economic Profit (EP)
- Arm’s length pricing of intercompany transactions, in line with OECD guidelines
- Regulatory Capital (RC) and Economic Capital (EC) calculations
- Expected Credit Loss (ECL) IFRS 9 calculations
- Active Credit Portfolio Management on both portfolio and (individual) counterparty level
Credit rating philosophy
A fundamental starting point when applying credit ratings, is the credit rating philosophy that is followed. In general, two distinct approaches are recognized:
- Through-the-Cycle (TtC) rating systems measure default risk of a counterparty by taking permanent factors, like a full economic cycle, into account based on a worst-case scenario. TtC ratings change only if there is a fundamental change in the counterparty’s situation and outlook. The models employed for the public ratings published by e.g. S&P, Fitch and Moody’s are generally more TtC focused. They tend to assign more weight to qualitative features and incorporate longer trends in the financial ratios, both of which increase stability over time.
- Point-in-Time (PiT) rating systems measure default risk of a counterparty taking current, temporary factors into account. PiT ratings tend to adjust quickly to changes in the (financial) conditions of a counterparty and/or its economic environment. PiT models are more suited for shorter term risk assessments, like Expected Credit Losses. They are more focused on financial ratios, thereby capturing the more dynamic variables. Furthermore, they incorporate a shorter trend which adjusts faster over time. Most models incorporate a blend between the two approaches, acknowledging that both short term and long term effects may impact creditworthiness.
Rating methodology
Modelling credit ratings is very complex, due to the wide variety of events and exposures that companies are exposed to. Operational risk, liquidity risk, poor management, a perishing business model, an external negative event, failing governments and technological innovation can all have very significant influence on the creditworthiness of companies in the short and long run. Most credit rating models therefore distinguish a range of different factors that are modelled separately and then combined into a single credit rating. The exact factors will differ per rating model. The overview below presents the factors included the Corporate Rating Model, which is used in some of the cloud-based solutions of the Zanders applications.
The remainder of this article will detail the different factors, explaining the rationale behind including them.
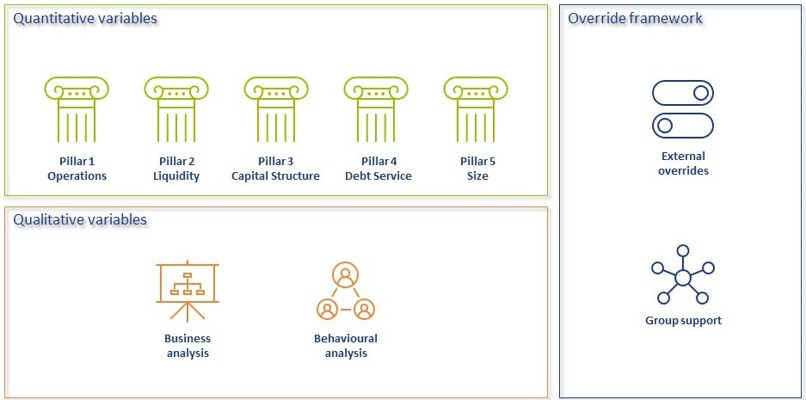
Quantitative factors
Quantitative risk factors are crucial to credit rating models, as they are ‘objective’ and therefore generate a large degree of comparability between different companies. Their objective nature also makes them easier to incorporate in a model on a large scale. While financials alone do not tell the whole story about a company, accounting standards have developed over time to provide a more and more comparable view of the financial state of a company, making them a more and more thrustworthy source for determining creditworthiness. To better enable comparisons of companies with different sizes, financials are often represented as ratios.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are being used for credit risk analyses throughout the financial industry and present the basic characteristics of companies. A number of these ratios represent (directly or indirectly) creditworthiness. Zanders’ Corporate Credit Rating model uses the most common of these financial ratios, which can be categorised in five pillars:
Pillar 1 - Operations
The Operations pillar consists of variables that consider the profitability and ability of a company to influence its profitability. Earnings power is a main determinant of the success or failure of a company. It measures the ability of a company to create economic value and the ability to give risk protection to its creditors. Recurrent profitability is a main line of defense against debtor-, market-, operational- and business risk losses.
Turnover Growth
Turnover growth is defined as the annual percentage change in Turnover, expressed as a percentage. It indicates the growth rate of a company. Both very low and very high values tend to indicate low credit quality. For low turnover growth this is clear. High turnover growth can be an indication for a risky business strategy or a start-up company with a business model that has not been tested over time.
Gross Margin
Gross margin is defined as Gross profit divided by Turnover, expressed as a percentage. The gross margin indicates the profitability of a company. It measures how much a company earns, taking into consideration the costs that it incurs for producing its products and/or services. A higher Gross margin implies a lower default probability.
Operating Margin
Operating margin is defined as Earnings before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) divided by Turnover, expressed as a percentage. This ratio indicates the profitability of the company. Operating margin is a measurement of what proportion of a company's revenue is left over after paying for variable costs of production such as wages, raw materials, etc. A healthy Operating margin is required for a company to be able to pay for its fixed costs, such as interest on debt. A higher Operating margin implies a lower default probability.
Return on Sales
Return on sales is defined as P/L for period (Net income) divided by Turnover, expressed as a percentage. Return on sales = P/L for period (Net income) / Turnover x 100%. Return on sales indicates how much profit, net of all expenses, is being produced per pound of sales. Return on sales is also known as net profit margin. A higher Return on sales implies a lower default probability.
Return on Capital Employed
Return on capital employed (ROCE) is defined as Earnings before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) divided by Total assets minus Current liabilities, expressed as a percentage. This ratio indicates how successful management has been in generating profits (before Financing costs) with all of the cash resources provided to them which carry a cost, i.e. equity plus debt. It is a basic measure of the overall performance, combining margins and efficiency in asset utilization. A higher ROCE implies a lower default probability.
Pillar 2 - Liquidity
The Liquidity pillar assesses the ability of a company to become liquid in the short-term. Illiquidity is almost always a direct cause of a failure, while a strong liquidity helps a company to remain sufficiently funded in times of distress. The liquidity pillar consists of variables that consider the ability of a company to convert an asset into cash quickly and without any price discount to meet its obligations.
Current Ratio
Current ratio is defined as Current assets, including Cash and Cash equivalents, divided by Current liabilities, expressed as a number. This ratio is a rough indication of a firm's ability to service its current obligations. Generally, the higher the Current ratio, the greater the cushion between current obligations and a firm's ability to pay them. A stronger ratio reflects a numerical superiority of Current assets over Current liabilities. However, the composition and quality of Current assets are a critical factor in the analysis of an individual firm's liquidity, which is why the current ratio assessment should be considered in conjunction with the overall liquidity assessment. A higher Current ratio implies a lower default probability.
Quick Ratio
The Quick ratio (also known as the Acid test ratio) is defined as Current assets, including Cash and Cash equivalents, minus Stock divided by Current liabilities, expressed as a number. The ratio indicates the degree to which a company's Current liabilities are covered by the most liquid Current assets. It is a refinement of the Current ratio and is a more conservative measure of liquidity. Generally, any value of less than 1 to 1 implies a reciprocal dependency on inventory or other current assets to liquidate short-term debt. A higher Quick ratio implies a lower default probability.
Stock Days
Stock days is defined as the average Stock during the year times the number of days in a year divided by the Cost of goods sold, expressed as a number. This ratio indicates the average length of time that units are in stock. A low ratio is a sign of good liquidity or superior merchandising. A high ratio can be a sign of poor liquidity, possible overstocking, obsolescence, or, in contrast to these negative interpretations, a planned stock build-up in the case of material shortages. A higher Stock days ratio implies a higher default probability.
Debtor Days
Debtor days is defined as the average Debtors during the year times the number of days in a year divided by Turnover. Debtor days indicates the average number of days that trade debtors are outstanding. Generally, the greater number of days outstanding, the greater the probability of delinquencies in trade debtors and the more cash resources are absorbed. If a company's debtors appear to be turning slower than the industry, further research is needed and the quality of the debtors should be examined closely. A higher Debtors days ratio implies a higher default probability.
Creditor Days
Creditor days is defined as the average Creditors during the year as a fraction of the Cost of goods sold times the number of days in a year. It indicates the average length of time the company's trade debt is outstanding. If a company's Creditors days appear to be turning more slowly than the industry, then the company may be experiencing cash shortages, disputing invoices with suppliers, enjoying extended terms, or deliberately expanding its trade credit. The ratio comparison of company to industry suggests the existence of these or other causes. A higher Creditors days ratio implies a higher default probability.
Pillar 3 - Capital Structure
The Capital pillar considers how a company is financed. Capital should be sufficient to cover expected and unexpected losses. Strong capital levels provide management with financial flexibility to take advantage of certain acquisition opportunities or allow discontinuation of business lines with associated write offs.
Gearing
Gearing is defined as Total debt divided by Tangible net worth, expressed as a percentage. It indicates the company’s reliance on (often expensive) interest bearing debt. In smaller companies, it also highlights the owners' stake in the business relative to the banks. A higher Gearing ratio implies a higher default probability.
Solvency
Solvency is defined as Tangible net worth (Shareholder funds – Intangibles) divided by Total assets – Intangibles, expressed as a percentage. It indicates the financial leverage of a company, i.e. it measures how much a company is relying on creditors to fund assets. The lower the ratio, the greater the financial risk. The amount of risk considered acceptable for a company depends on the nature of the business and the skills of its management, the liquidity of the assets and speed of the asset conversion cycle, and the stability of revenues and cash flows. A higher Solvency ratio implies a lower default probability.
Pillar 4 - Debt Service
The debt service pillar considers the capability of a company to meet its financial obligations in the form of debt. It ties the debt obligation a company has to its earnings potential.
Total Debt / EBITDA
The debt service pillar considers the capability of a company to meet its financial obligations. This ratio is defined as Total debt divided by Earnings before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA). Total debt comprises Loans + Noncurrent liabilities. It indicates the total debt run-off period by showing the number of years it would take to repay all of the company's interest-bearing debt from operating profit adjusted for Depreciation and Amortization. However, EBITDA should not, of course, be considered as cash available to pay off debt. A higher Debt service ratio implies a higher default probability.
Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest coverage ratio is defined as Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) divided by interest expenses (Gross and Capitalized). It indicates the firm's ability to meet interest payments from earnings. A high ratio indicates that the borrower should have little difficulty in meeting the interest obligations of loans. This ratio also serves as an indicator of a firm's ability to service current debt and its capacity for taking on additional debt. A higher Interest coverage ratio implies a lower default probability.
Pillar 5 - Size
In general, the larger a company is, the less vulnerable the company is, as there is, usually, more diversification in turnover. Turnover is considered the best indicator of size. In general, turnover is related to vulnerability. The higher the turnover, the less vulnerable a company (generally) is.
Ratio Scoring and Mapping
While these financial ratios provide some very useful information regarding the current state of a company, it is difficult to assess them on a stand-alone basis. They are only useful in a credit rating determination if we can compare them to the same ratios for a group of peers. Ratio scoring deals with the process of translating the financials to a score that gives an indication of the relative creditworthiness of a company against its peers.
The ratios are assessed against a peer group of companies. This provides more discriminatory power during the calibration process and hence a better estimation of the risk that a company will default. Research has shown that there are two factors that are most fundamental when determining a comparable peer group. These two factors are industry type and size. The financial ratios tend to behave ‘most alike’ within these segmentations. The industry type is a good way to separate, for example, companies with a lot of tangible assets on their balance sheet (e.g. retail) versus companies with very few tangible assets (e.g. service based industries). The size reflects that larger companies are generally more robust and less likely to default in the short to medium term, as compared to smaller, less mature companies.
Since ratios tend to behave differently over different industries and sizes, the ratio value score has to be calibrated for each peer group segment.
When scoring a ratio, both the latest value and the long-term trend should be taken into account. The trend reflects whether a company’s financials are improving or deteriorating over time, which may be an indication of their long-term perspective. Hence, trends are also taken into account as a separate factor in the scoring function.
To arrive to a total score, a set of weights needs to be determined, which indicates the relative importance of the different components. This total score is then mapped to a ordinal rating scale, which usually runs from AAA (excellent creditworthiness) to D (defaulted) to indicate the creditworthiness. Note that at this stage, the rating only incorporates the quantitative factors. It will serve as a starting point to include the qualitative factors and the overrides.
"A sound credit rating model strikes a balance between quantitative and qualitative aspects. Relying too much on quantitative outcomes ignores valuable ‘unstructured’ information, whereas an expert judgement based approach ignores the value of empirical data, and their explanatory power."
Qualitative Factors
Qualitative factors are crucial to include in the model. They capture the ‘softer’ criteria underlying creditworthiness. They relate, among others, to the track record, management capabilities, accounting standards and access to capital of a company. These can be hard to capture in concrete criteria, and they will differ between different credit rating models.
Note that due to their qualitative nature, these factors will rely more on expert opinion and industry insights. Furthermore, some of these factors will affect larger companies more than smaller companies and vice versa. In larger companies, management structures are far more complex, track records will tend to be more extensive and access to capital is a more prominent consideration.
All factors are generally assigned an ordinal scoring scale and relative weights, to arrive at a total score for the qualitative part of the assessment.
A categorisation can be made between business analysis and behavioural analysis.
Business Analysis
Business analysis deals with all aspects of a company that relate to the way they operate in the markets. Some of the factors that can be included in a credit rating model are the following:
Years in Same Business
Companies that have operated in the same line of business for a prolonged period of time have increased credibility of staying around for the foreseeable future. Their business model is sound enough to generate stable financials.
Customer Risk
Customer risk is an assessment to what extent a company is dependent on one or a small group of customers for their turnover. A large customer taking its business to a competitor can have a significant impact on such a company.
Accounting Risk
The companies internal accounting standards are generally a good indicator of the quality of management and internal controls. Recent or frequent incidents, delayed annual reports and a lack of detail are clear red flags.
Track record with Corporate
This is mostly relevant for counterparties with whom a standing relationship exists. The track record of previous years is useful first hand experience to take into account when assessing the creditworthiness.
Continuity of Management
A company that has been under the same management for an extended period of time tends to reflect a stable company, with few internal struggles. Furthermore, this reflects a positive assessment of management by the shareholders.
Operating Activities Area
Companies operating on a global scale are generally more diversified and therefore less affected by most political and regulatory risks. This reflects well in their credit rating. Additionally, companies that serve a large market have a solid base that provides some security against adverse events.
Access to Capital
Access to capital is a crucial element of the qualitative assessment. Companies with a good access to the capital markets can raise debt and equity as needed. An actively traded stock, a public rating and frequent and recent debt issuances are all signals that a company has access to capital.
Behavioral Analysis
Behavioural analysis aims to incorporate prior behaviour of a company in the credit rating. A separation can be made between external and internal indicators
External indicators
External indicators are all information that can be acquired from external parties, relating to the behaviour of a company where it comes to honouring obligations. This could be a credit rapport from a credit rating agency, payment details from a bank, public news items, etcetera.
Internal Indicators
Internal indicators concern all prior interactions you have had with a company. This includes payment delay, litigation, breaches of financial covenants etcetera.
Override Framework
Many models allow for an override of the credit rating resulting from the prior analysis. This is a more discretionary step, which should be properly substantiated and documented. Overrides generally only allow for adjusting the credit rating with one notch upward, while downward adjustment can be more sizable.
Overrides can be made due to a variety of reasons, which is generally carefully separated in the model. Reasons for overrides generally include adjusting for country risk, industry adjustments, company specific risk and group support.
It should be noted that some overrides are mandated by governing bodies. As an example, the OECD prescribes the overrides to be applied based on a country risk mapping table, for the purpose of arm’s length pricing of intercompany contracts.
Combining all the factors and considerations mentioned in this article, applying weights and scoring functions and applying overrides, a final credit rating results.
Model Quality and Fit
The model quality determines whether the model is appropriate to be used in a practical setting. From a statistical modelling perspective, a lot of considerations can be made with regard to model quality, which are outside of the scope of this article, so we will stick to a high level consideration here.
The AUC (area under the ROC curve) metric is one of the most popular metrics to quantify the model fit (note this is not necessarily the same as the model quality, just as correlation does not equal causation). The AUC metric indicates, very simply put, the number of correct and incorrect predictions and plots them in a graph. The area under that graph then indicates the explanatory power of the model. A more extensive guide to the AUC metric can be found here.
Alternative Modelling Approaches
The model structure described above is one specific way to model credit ratings. While models may widely vary, most of these components would typically be included. During recent years, there has been an increase in the use of payment data, which is disclosed through the PSD2 regulation. This can provide a more up-to-date overview of the state of the company and can definitely be considered as an additional factor in the analysis. However, the main disadvantage of this approach is that it requires explicit approval from the counterparty to use the data, which makes it more challenging to apply on a portfolio basis.
Another approach is a purely machine learning based modelling approach. If applied well, this will give the best model in terms of the AUC (area under the curve) metric, which measures the explanatory power of the model. One major disadvantage of this approach, however, is that the interpretability of the resulting model is very limited. This is something that is generally not preferred by auditors and regulatory bodies as the primary model for creditworthiness. In practice, we see these models most often as challenger models, to benchmark the explanatory power of models based on economic rationale. They can serve to spot deficiencies in the explanatory power of existing models and trigger a re-assessment of the factors included in these models. In some cases, they may also be used to create additional comfort regarding the inclusion of some factors.
Furthermore, the degree to which the model depends on expert opinion is to a large extent dependent on the data available to the model developer. Most notably, the financials and historical default data of a representative group of companies is needed to properly fit the model to the empirical data. Since this data can be hard to come by, many credit rating models are based more on expert opinion than actual quantitative data. Our Corporate Credit Rating model was calibrated on a database containing the financials and default data of an extensive set of companies. This provides a solid quantitative basis for the model outcomes.
Closing Remarks
Model credit risk and credit ratings is a complex affair. Zanders provides advice, standardized and customizable models and software solutions to tackle these challenges. Do you want to learn more about credit rating modelling? Reach out for a free consultation. Looking for a tailor made and flexible solution to become IFRS 9 compliant, find out about our Condor Credit Risk Suite, the IFRS9 compliance solution.
The ECB’s thematic review on climate risks and the focus areas for 2023

The European Central Bank (ECB) recently completed another important step in the supervisory process to assess the management of climate-related and environmental (C&E) risks by European banks. On 2 November, they published the results of their thematic review on C&E risks performed earlier this year.
This review1 followed the initial publication of expectations on C&E risks in their November 2020 Guide on C&E risks (the Guide)2 and the self-assessment performed by European banks in 2021 on the ECB’s request. The scope of the thematic review included 186 banks with a total balance sheet size of EUR 25 trillion: 107 significant institutions (SIs) supervised by the ECB and 79 less significant institutions (LSIs) supervised by national competent authorities.
In this article, we provide an overview of the main conclusions of the thematic review and of the main focus areas related to the management of C&E risk for banks that we expect for 2023.
Main results
The thematic review shows that European banks have progressed with the integration of C&E risks into their business strategy, governance, and risk management frameworks. This matters, because the review shows that C&E risks are real. Depending on the time horizon, 70% to 80% of all banks consider C&E risks to be material for their portfolios. About 75% of all banks expect material impacts on their credit risk. To a lesser extent, material impacts are expected on strategic and reputational risks (about 50%), and on market and liquidity risks (about 25%). In the short term, banks are most concerned with transition risks, while the relevance of physical risks is clearly increasing with the time horizon.
The ECB concludes, however, that the management of C&E risks still is on a relatively basic and general level. For example, banks have updated their governance, assigning responsibility for the management of C&E risks to the Management Board. Many have also set up dedicated committees for these risk types and/or assigned responsibility within the organisation in other ways. Further, over 90% of all banks have at least performed a basic risk identification and materiality assessment to understand how their portfolios are exposed to C&E risks. In many cases, this has led to the introduction of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Key Risk Indicators (KRIs), and the (often qualitative) integration of C&E risks into their business strategy and Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP).
According to the ECB, the work performed so far is not sufficient though. The ECB observes gaps in the risk identification and materiality assessment at almost all banks. In 60% of the cases, these are deemed major. Of all banks, 10% is yet to start with this process. Improvements are also required with respect to data collection. Only a small selection of banks (about 15%) is systematically collecting data that is sufficiently granular and forward-looking to support processes like risk identification, stress testing and reporting. In most cases, banks rely to a large extent on the use of proxies.
Even if banks have progressed well with the identification of C&E risks, the ECB concludes that this awareness has not been translated effectively into policies and targets by more than half of the banks. The high-level KPIs and KRIs for example, are not cascaded down to business lines or individual portfolios, non-restrictive targets are set, or relevant counterparties are excluded from a policy’s scope. Furthermore, the ECB finds that banks are significantly underestimating the level of skilled resources required for a proper management of C&E risks.
The ECB has set deadlines tailored to each bank that they supervise. As part of the publication of the results of the thematic review, however, they shared the minimum milestones European banks need to adhere to:
- By the end of March 2023, banks need to have a sound and comprehensive materiality assessment in place, including a robust scanning of the business environment.
- By the end of 2023, banks need to manage C&E risks with an institution-wide approach covering business strategy, governance and risk appetite, as well as risk management, including credit, operational, market and liquidity risk management.
- By the end of 2024, banks need to be fully aligned with all supervisory expectations, including having in place a sound integration of C&E risks in their stress testing framework and ICAAP.
Focus areas 2023
Based on the results of the ECB’s thematic review and our conversations with clients, we see five focus areas related to the management of C&E risks for banks in 2023.
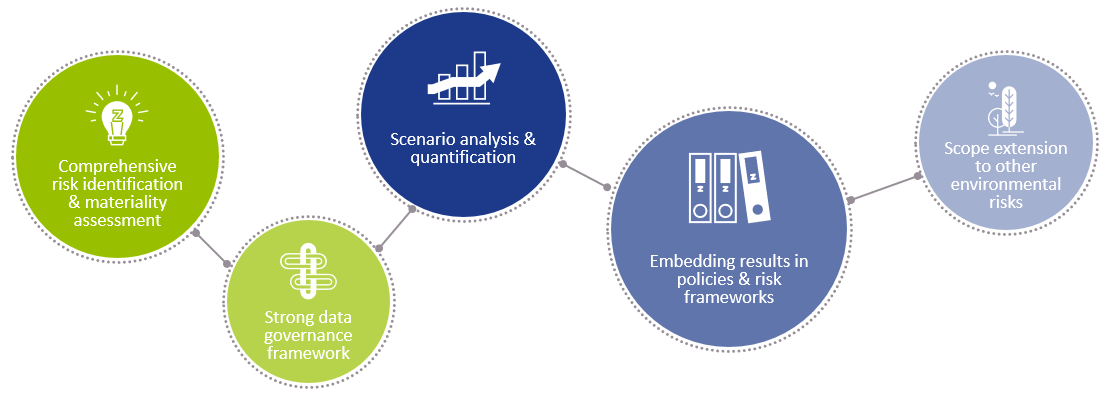
- Comprehensive risk identification and materiality assessment: The ECB is clear about its expectations that banks should complete their risk identification and materiality assessment in the first quarter of 2023. More importantly, they expect this process to be comprehensive. For a start, a bank should assess all its material business lines (or portfolios) and cover all relevant regions and geographies the bank is active in. A step-wise approach can be used, as long as the full scope is covered in the end. Further, the analysis should cover a wide range of physical and transition risks. It is not sufficient to investigate the impact of a limited set of risk factors. Finally, the analysis needs to be performed for different time horizons: the short, medium, and long term.
- Strong data governance framework: To take the next step in the management of C&E risks, a robust and structured process to collect data is required. For the analyses performed by banks so far, it may have sufficed to extensively use proxies. More is needed, however, to fully meet the expectations described in the ECB’s Guide. Data needs to be collected on a granular level: to be able to properly measure and report on C&E risks, banks need to understand the risks on counterparty, facility, and/or asset level. A first step would be to compile a complete overview of the bank’s data requirements. A bank would need to synthesize all data requirements stemming from processes like risk identification, credit granting, risk modelling, and disclosure to ensure a sufficiently granular (and future-proof) data collection process is designed. Such a process will have to source data from internal systems, but also from a bank’s counterparties and most likely external data vendors. A structured approach exploits potential overlapping data requirements and prevents inconsistencies in definitions.
- Scenario analysis and quantification: With improved data comes the possibility to perform more sophisticated scenario analysis and to quantify C&E risks. About a quarter of all banks are already employing advanced and/or forward-looking quantification methods; for example to inform the ICAAP, to perform scenario analysis, or to reflect C&E risks into internal ratings-based (PD and LGD) models. Most banks expect that it will take one to three years to truly advance in this area. In 2023, however, banks should already focus on improving their scenario analysis (and stress testing) capabilities, and take the first steps towards integrating C&E risks into their credit risk modelling.
- Embedding results into policies and risk management frameworks: In 2023, banks will need to “walk the talk”, to paraphrase the ECB. The improved understanding of how physical and transitions risks may impact the risk profile of the bank needs to be translated into actionable policies and become part of the risk management framework. Overall targets need to align with scientific pathways, high-level Risk Appetite Statements on C&E risks need to be cascaded down to the lower business line levels, controls need to be implemented accordingly, product offerings need to be reviewed, and a dialogue with clients needs to be initiated – including clear steps if and how a bank will continue the relationship if the client’s transition is not meeting expectations.
- Scope extension to other environmental risks: Attention from banks and supervisors alike has mostly focussed on climate risks so far. Other environmental risks, like loss of biodiversity, pollution and water scarcity have received less attention. Now that some progress has been achieved in the area of climate risk, banks should increase efforts for these other risk types. Initiatives like the Partnership for Biodiversity Accounting Financials (PBAF, a sister-initiative of PCAF, which is focussed on financed emissions) and the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) can be useful to progress with this.
Since the management of C&E risks is a new field of expertise, many banks are (re)inventing the wheel. Much can be learned from other banks though. To facilitate this, the ECB published, together with the results of the thematic review, an overview of good practices they observed among SIs3. This document can be a useful source of inspiration for banks. De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB, the Dutch central bank) published a similar document, based on their observations among Dutch LSIs4.
Conclusion
Banks have worked hard in 2022 to advance their management of C&E risks. Much work remains, however. With the clear milestones communicated by the ECB, banks have their work cut out for them. And this is not a voluntary effort, as the 30 institutions where the ECB imposed binding qualitative requirements as part of the Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP) know. For some, supervisory exercises were even reflected in SREP scores, impacting their Pillar 2 capital requirements.
To achieve sufficient progress, we believe that banks should focus on the five areas described in the previous section: risk identification, data collection, scenario analysis and quantification, integration of C&E risks into policies and risk frameworks, and a scope extension to broader environmental risks. By combining our extensive experience with the ‘classical’ risk types with our track record on C&E risks, Zanders is well-positioned to support your organization.
References
1) ECB – Walking the talk – Banks gearing up to manage risks from climate change and environmental degradation – link
2) ECB – Guide on climate-related and environmental risks – Supervisory expectations relating to risk management and disclosure – link
3) ECB – Good practices for climate-related and environmental risk management – Observations from the 2022 thematic review – link
4) DNB – Guide to managing climate and environmental risks – link
TMS Selection Service – Boost the traditional selection process using bespoke technology!

Are you overwhelmed by the sheer volume of different Treasury Technology Systems on the market?
Do you have difficulties setting out your treasury technology requirements (both from a functional as well as IT perspective), or matching those to the latest capabilities of a modern Treasury Systems? Are you wishing for a technology selection process that is less cumbersome and time consuming? If you said ‘yes’ to any of these, then we might have the solution for you!
Introducing Zanders’ Treasury Technology Selection Service powered by Tech-Select, our proprietary cloud-based Treasury Technology Selection tool designed to give you an easier, quicker way to select a new treasury system that best supportis your specific needs, or to evaluate your current system against other alternatives. For over 30 years, Zanders has been helping organizations globally to select treasury management systems and other related treasury technology. As an independent and unbiased expert, we have built extensive experience into how best to assist our clients to select, implement and deploy the most appropriate solution for their technology needs – it is this insight that drove us to develop a system to modernize the commonly used RfP process.
Zanders Tech-Select is the driving force behind our Treasury Technology Selection Service and accelerates your treasury system selection project by addressing the traditional challenges faced by organizations when choosing treasury technology solutions and introduces several other benefits as follows:
- Provides a broad overview of the systems market, giving you access to a wider range of potential vendors that can provide systems supporting your needs, and the most up-to-date insights on their current capabilities and new product developments
- Allows you to easily identify and define your functional needs, short-list suitable vendors, and automatically create and issue your RfP, by providing access to our comprehensive library of functional and technical requirements alongside our curated database of vendors, system functionality and capabilities
- Facilitates and accelerates multi-user assessment and evaluation of vendor responses, by utilizing workflows for scoring, the ability to assess user scoring differences, and the opportunity to determine final scores for each vendor
- Helps you to understand key differentiators between services and functionality on offer from each vendor, using our pre-defined results analytics and drilldowns
- Helps to streamline and accelerate the RfP process from end-to-end within a single cloud-based platform, removing the need for multiple emails, spreadsheets or complex scoring models, and
- Reduces the resource and time investment required to engage with multiple vendors, freeing you to focus on key analysis and value-add activities
Let’s take a deeper look at how Zanders Tech-Select achieves this:
- Once you’ve chosen from Zanders Tech-Select’s comprehensive library of functional and technical requirements, these are matched to our curated database of system functionality and capabilities in order to present you with a shortlist of systems and vendors that are suited to your specific needs. You can then select which of those vendors you would like to invite for your RfP process, utilise our templates to create cover letters and other attachments, and specify deadlines for acknowledgement, Q&As and final responses.
- When you are ready to launch your RfP, you simply click the ‘Issue’ button to automatically generate RfP invite emails quickly and easily to all chosen vendors. Once they receive the invite, vendors can use Zanders Tech-Select to access all document attachments, view your requirements, ask any questions, and respond to the RfP.

- Once vendors have completed submitting their RfP responses, multiple users from your treasury, finance, IT and procurement teams can use Zanders Tech-Select to independently compare each vendor’s responses to each requirement in a consolidated view, and can assign scores to each. When all users have completed their scoring, the system automatically consolidates their scores and provides you with the opportunity to review and moderate the final scores before moving forwards to analyze the results.
- At the final stage, Zanders Tech-Select’s interactive results analytics provide you with several ways to view and drill down into your results. Simply hover over data points to see more detailed information, check or uncheck to include or exclude vendors, sections and subsections, or most importantly click on specific scores to drilldown and quickly understand the reasons behind any scoring differences between vendors.
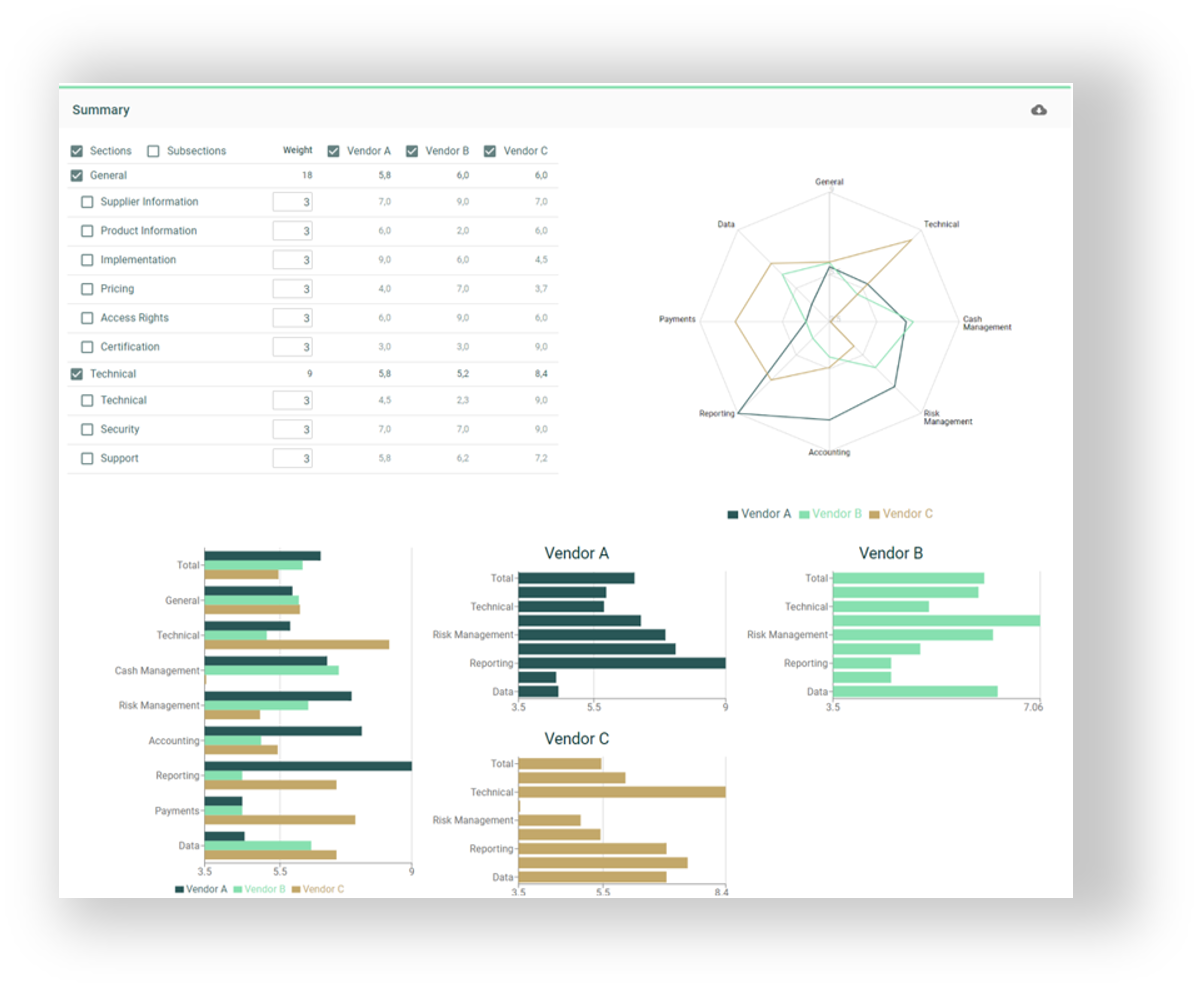
Based on experience from our clients, Zanders’ Treasury Technology Selection Service powered by Tech-Select drastically improves the current RfP processes many corporates are using today.
Zanders is unique in offering a system selection solution that includes an extensive library of the most common technology requirements alongside pre-populated and curated responses from over 90% of the leading treasury systems currently on the market. The structured, end-to-end process helps to streamline and automate your selection project and is applicable to a wide variety of use cases, enabling a consistent approach to vendor selection based on objective and rigorous evaluation.
Zanders Tech-Select uniquely provides the most efficient, thorough and cost-effective digital selection service within the treasury space, with Zanders experts to guide you throughout. If you would like to find out more about how Zanders can help to streamline your next technology or service selection process, get in touch now.
Article updated in May 2024
Treasury trends 2023

With year-end approaching quickly it is a natural moment to look back, zoom-out a bit and look forward to the coming year(s). Last year was, for most treasurers, a bumpy road. We witnessed another year with uncertainty and volatility in the financial markets due to the residual effects of the pandemic; the impact of the War in Ukraine; and rising inflation, interest rates and commodity prices. In this context, Corporate Treasuries are continuously facing internal and external challenges, and therefore need to operate in an increasingly complex and uncertain environment. Based on these challenges, we have identified four main Treasury themes for the year 2023 which are interlinked with each other and will be addressed in more detail in this article:
- Digital Treasury
- Fit for Future Treasury Teams
- Financial Resilience
- Increasing Treasury remit
Digital Treasury
Implementing and deploying fit-for-purpose technology in the Treasury function continues to be one of the main themes for Treasurers. The importance of embracing technology, with the aim to become a Digital Treasury function, stems from both internal and external drivers. Due to the strategic position of Treasury within the broader Finance function, different factors (like new regulations, volatility in financial markets, political decision making and economic instability, et cetera) lead to a broader and more complex remit. At the same time, treasurers are expected to implement cost reduction programs while simultaneously facing increasing performance requirements, and the expectation to present accurate and real-time transparency on liquidity, cash flows and exposures. Technology is the key enabler for a future proof value adding Treasury organization including to effectively manage the change in Treasury’s traditional tasks (e.g. requirement for real-time liquidity and exposure data) as well as new tasks (e.g. include ESG Financing, broader working capital responsibility or new B2C payment methods).
A Digital Treasury or Treasury 4.0 as it is often called is defined by certain characteristics:
- Treasury Target Operating Model which is ‘fit for purpose’, this means a formalized governance structure and mandate for the Treasury function in combination with the organizational structure in which ‘virtual’ centralization is achieved by means of technology.
- Fully integrated and automated Treasury operations to reach the highest degree of Straight Through Processing (STP) were possible, which effectively leads to a Manage by Exception (MBE) structure.
- Utilize exponential technology in a standardized way with a clear focus on the additional benefits of this new technology. Deploying exponential technology, like blockchain, AI, robotics, et cetera, should be a means to an end and not a goal in itself for Treasury.
- Enable a ‘Real-time’ Treasury by having real-time data available, process payments on a real-time basis and have access to real-time liquidity.
- Build a resilient Treasury framework of both governance, methodology and technology components to allow Treasury reacting to different scenarios and to anticipate them.
- Shift focus on the full financial supply chain and working capital management by expanding process design and data flow beyond the core Treasury activities.
By embedding Treasury into the financial supply chain regarding processes and data it enables Treasury to work in multiple unforeseen scenarios and make informed decisions based on analytics. When we talk about Treasury data and analytics the “ABCD of Digital Treasury” is paramount, which are:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Application Programming interfaces (APIs)
- Blockchain & distributed ledger technology
- Cloud computing
- Data & advanced data analytics.
As part of the Treasury transformation towards a Digital Treasury, there should be a clear focus on deliverables and output to ensure these are fully aligned with CFO and other business partners expectations. Given the trend of increased focus on performance, it is key to utilize the power of technology which enable Treasury to elevate the quality of deliverables and output. For example, AI can be used to adjust forecasted cash flows based upon the historical patterns behind actuals and forecast variances as well as assisting in decision making in the area of foreign exchange risk or commodity price risk management.
The concept of real-time Treasury has become one of the hottest topics in Treasury over the last few years. The availability of real-time data, payments and liquidity can take away many inefficiencies in Treasury’s day-to-day operations. Thanks to growing adoption of exponential technologies such as APIs and Blockchain, Treasury teams can access external real-time data in a speedy and precise manner. Being able to obtain data from all relevant sources in real-time reduces the manual work, decreases the possibility of errors, and improves the decision-making capabilities of Treasury teams. Rather than having to wait and be constraint by bank cut-off times and end of day processing, Treasury teams can operate more efficiently by achieving actual real-time visibility from faster payments to settlements.
In the pursuit of a better payment system, real-time payments have been evolving and creating a safer, more efficient, and accessible environment. Numerous countries have been creating new payment rails and upgrading their infrastructure to support secure real-time payments. We are seeing blockchain technology challenging the existing payment solutions such as SWIFT to enable real-time payments with extended data and enhanced tracking and tracing at a lower cost.
Real-time payments give rise to the need of real-time liquidity. Banks might offer a solution that enables to leverage liquidity across multiple accounts (without the need to have intraday limits). So, if a bank account requires liquidity to make payments, the bank will look across other bank accounts to check whether other liquidity can be used to cover the payment need.
Enabling the ‘Real-time’ requires Treasury to have a resilient and automated technology landscape. Identifying the requirements and then selecting the technology provider(s is the key component to automated ‘real-time’ functionalities.
Fit for Future Treasury Teams
The most crucial asset of any Treasury organisation is its people. Building a Treasury team that can (a) quickly adapt to new circumstances, (b) understand the added value of the Treasury function for the business, and (c) leverage the use of technology, is a key differentiator when it comes to Treasury. The ability of an organisation to successfully deploy technology stems from aligning three interlinked forces:
- Translating business requirements into functional technology requirements;
- Understanding full capabilities of the new technology;
- Availability and development of functional, technical and change management skills within the team to drive successful implementation of new processes and activities.
Training, retaining the talent and maximizing the business partnering skills is the key to create a fit for future Treasury team. In the recent years, we observe many organisations struggle with building a high-quality talent pipeline and lack of succession planning when it comes to their Treasury functions. This combined with the widening ‘skill gaps’ created by the digitisation of Treasury, puts organisations in a very challenging position. For 2023, we expect companies to focus on developing and managing talent of individuals with digital acumen, ability to interpret data, and ability make forward-looking decisions. This can be done via training and upskilling of current staff, the revision of strategic positions to diminish key-person risk, implementing a broader finance rotation program in which technology plays a central role and lastly entering into strategic partnerships with external expertise and resource partners.
Financial Resilience
Financial Resilience is the ability of an organization to financially withstand and recover from diverse types of unexpected events, for example, external shocks. Coping with financial shocks means, for a Treasury, to have the analytical skills to devise both short-term and long-term strategies to measure and manage the impact of external shocks on the financial side of the organization. Financial resilience requires strategically planning ahead and putting preventive strategies in place, including amongst others detailed analysis of corporate finance strategies, pro-actively creating access to funding sources, and defining alternative risk transfer strategies.
After many years of low interest rates and inflation, treasurers had not to worry too much about interest rate risks (except for the negative yields on their investments). Given the recent interest rate increases by the central banks and the expectation that central banks will further increase interest rates to combat the high inflationary market, interest rate risk is back on the agenda for Treasurers! Treasurers should not only analyse the direct impact of increasing interest rates on the financial expense line, but should also consider how the increasing interest rates, in combination with the increasing commodity prices and volatile FX market impact the full supply chain. There are many (Zombie) companies out there which are on the brink of collapse given the current volatile financial markets in combination with ending government COVID-19 support programs. It is vital for a company to have a clear view on its risk bearing capacity; to which extent is the company able to absorb financial headwinds like increased interest rates, adverse movements in commodity and FX rates and potential defaults of key suppliers and/or customers. Traditional risk management measurement techniques, which consider the linear impact of a change in a single risk factor to a single line item in the financial statements (e.g. financial results), are not suitable in an environment of complexity and uncertainty. Treasurers should upskill their financial risk management practice by challenging the assumptions used in current measurement techniques, like scenario analysis. For example, it was not expected and not in line with economic theory that real interest rates would move below zero, which contradicts the current market conditions of high inflation rates accompanied with disproportionate increases in the nominal interest rate. As guardians of the company’s financial risks, Treasurers should expect the unexpected!
Increasing Treasury remit
Given the critical role of Treasury within an organization, we have already seen (for many years) an increase in the Treasury remit. As strategic partner to the CFO and the business, Treasury’s skills are leveraged for more and more activities. To continue the financial resilience trend, working capital management is a key example of Treasury’s increasing remit in many organizations, which stems from the risk capabilities within Treasury. Treasury is not only involved in securing that the company is resilient for financial market movements but is also acting as a business partner for both procurement and the commercial team to analyse how the full supply chain can be made more resilient. Potential hiccups in the physical supply chain as well as the impact of defaulting suppliers or customers can have a detrimental effect on working capital. Many treasuries have an increased focus on working capital management and evaluate how strategic and critical customers and suppliers can be supported via supply chain finance programs to strengthen the supply chain and thereby the position of the company.
Another key trend which is increasing the remit of Treasury, is the movement towards Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) proof organizations. Treasurers are the trailblazers in sustainable funding and now need to work with accounting and ESG teams for the necessary reporting. Impact can also be expected in the banking relationship. The European Central Bank (ECB) and European Banking Authority (EBA) are rapidly increasing the pressure on banks to integrate ESG risks into their risk frameworks. For example, the ECB published their expectations with respect to the management of climate-related and environmental risks in 2020 and they are now requiring banks to achieve full compliance by the end of 2024. Among others, banks need to assess to what extent their counterparties are exposed to physical (e.g. floods and droughts) or transition risks (e.g. changes in regulation or consumer sentiment). These factors then need to be integrated in the loan origination process. Apart from the potential impact on the pricing of loans and facilities, corporates can also expect a more data-intensive process. Detailed data on emissions and the geographical location of production facilities may be requested.
Conclusion
To conclude, 2023 is expected to be another exciting year for Treasury professionals! The combination of the expanding Treasury remit, challenging labour market and continuing uncertainties in financial and geopolitical markets give rise to create clear and actionable analysis and advice towards the CFO and other business partners. The transformation towards a Digital Treasury is the path which enables Treasury to deliver in an environment which is increasingly focusing on performance while at the same time becoming more complex. We are optimistic for the future and look forward to collaborating with many of you on this exciting journey! For now, Zanders would like to wish you wonderful holidays with friends and family and a great start of the new year!


